Research on RDF-based XML Access Control Models
10 likes | 136 Vues
Explore the development of secure access control models for patient health records using RDF-based XML language, ensuring data integrity and protection against illegal inferences. Understand the layered access control architecture and conflict resolution mechanisms.

Research on RDF-based XML Access Control Models
E N D
Presentation Transcript
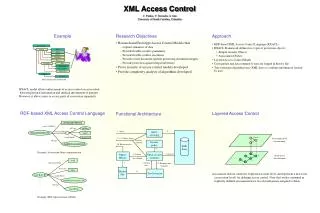
2. 1. Query Query screening 2, 5, 8. Reject Query /MedicalDb/Patient/ -read MedicalDb Security violated Object - Patient Patient SSN rxacl:accesstype Association level classification Security policy XML Store rxacl:AsscRoot * Name Name Patient rdf:type 10. Return answer rdf:Bag Phone Phone rxacl:user rxacl:includes rxacl:Association-A0 Alice 4. Birthdate Birthdate name Race Race rxacl:Rule-R0 * rxacl:relpath Update History Check security violations 3. Answer diagnosis rxacl:object Diagnosis Date Diagnosis Date 8. Security rdf:type Physician meddb:Association-A0 Node level classification meddb:Association-A0 not violated Prescription + Comments Comments - 9. 7. Return trees rdf:type 5. Security not violated + Allergies * rxacl:Rule Allergen + + History File + Tree Extension 6. XML Access Control C. Farkas, V. Gowadia, A. Jain University of South Carolina, Columbia • Example • Research Objectives • Research and Prototype Access Control Models that • Capture semantics of data • Provide flexible security granularity • Provide flexible conflict resolution • Provide secure document updates preserving document integrity • Provide protection against illegal inferences • Prove security of access control models developed • Provide complexity analysis of algorithms developed • Approach • RDF-based XML Access Control Language (RXACL) • RXACL Framework defines two types of protection objects: • Simple security Objects • Association Objects • Layered Access Control Model • User queries and data returned to user are logged in history file • Tree extension algorithms uses XML-keys to combine information viewed by user DTD of Patient Health Record RXACL model allows enforcement of access control on association between personal information and medical information of patients. However, it allows users to access parts of association separately. • RDF-based XML Access Control Language • Layered Access Control • Functional Architecture Example: Association Object representation Association objects cannot be expressed at node-level, and represent a new layer (association-level) for defining access control. Note that, nodes contained in explicitly defined associations have two classifications assigned to them. Example: RDF representation of Rules