Chemical Reactions and Redox Processes Overview
90 likes | 185 Vues
Detailed overview of Metathesis (Double Displacement), Oxidation-Reduction, Combination, Decomposition, and Displacement Reactions along with examples and naming conventions for inorganic compounds and acids. Understand key concepts in chemistry with this comprehensive guide.

Chemical Reactions and Redox Processes Overview
E N D
Presentation Transcript
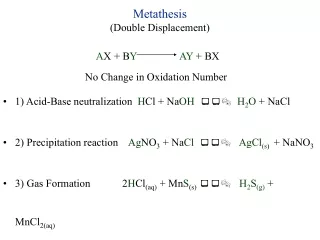
Metathesis (Double Displacement) AX + BYAY + BX No Change in Oxidation Number • 1) Acid-Base neutralization HCl + NaOH H2O + NaCl • 2) Precipitation reaction AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl(s) + NaNO3 • 3) Gas Formation 2HCl(aq) + MnS(s) H2S(g)+ MnCl2(aq) • oxidation numbers (+1)(-1) (+2)(-2) (+1)(-2) (+2)(-1)
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox Rxn) -2 +3 0 -2 Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) Al2O3(s) + Fe(s) • Al is oxidized and is therefore the reducing agent • Fe is reduced and therefore Fe2O3 is the oxidizing agent • Oxidation- in the ox # (state) • Reduction- in the ox # (state) +3 0 = heat supplied by the exothermic reaction 2Mg(s) + O2(g) MgO(s)
Combination Rxn: 2 or more substances combine to form a compound • Element + Element Compound • Metal + Nonmetal Binary Ionic Compound • 2Na(s) + Cl2(g)NaCl(s) (also Redox) • Nonmetal + Nonmetal Binary Covalent Compound • P4(s) + 10Cl2(g) PCl5(s) (also Redox) • Compound + Element Compound • PCl3(l) + Cl2(g)PCl5(s) (also Redox) • Compound + Compound Compound • CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(aq) (NOT a Redox)
Decomposition Rxn: a compound decomposes to form products • Compound Element + Element • 2HgO(s) Hg(l) + O2(g) • Compound Compound + Element • 2H2O2(l) 2H2O(l) + O2(g) • (Disproportionation rxn-H2O2 is the reducing agent and the oxidizing agent) • Compound Compound + Compound • CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Displacement Rxn: one element displaces another from a compound Table 4-12 (pg. 148) Activity series of SOME Elements The more active element displaces the less active element • more active metal + salt of less active metal less active metal +salt of more active metal • Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) • active metal + nonoxidizing acid salt of acid + H2(g) • Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) ZnSO4 + H2(g) • more active nonmetal + salt of less active nonmetal less active nonmetal +salt of more active nonmetal • Br2(l) + 2NaI(aq) I2(s) + 2NaBr(aq) • F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
Naming Inorganic Compounds • Binary Compounds-compounds that only contain two elements • Know the stem names of the nonmetals listed on page 162 • Always name the more metalic element first • BinaryIonic Compounds-Metal with a nonmetal • KCl - potassium chloride • FeO - iron (II) oxide (IUPAC) ; ferrous oxide (common) • Fe2O3 - iron (III) oxide (IUPAC) ; ferric oxide (common) • Pseudobinary Ionic Compounds-Know the ions in Tbl 4-15 pg 164 • NH4Cl - ammonium chloride • FeSO4 - iron (II) sulfate ; ferrous sulfate • Binary Molecular Compounds-nonmetal with a nonmetal • Know the common prefixes given on page 163 • SO2- sulfur dioxide • N2O4 - dinitrogen tetroxide (note: tetra tetr when stem begins with o)
Acids • Binary Acids-H combined with Group VIA (except O) or VIIA • HCl - hydrogen chloride ; HCl(aq) hydrochloric acid • H2S - hydrogen sulfide ; H2S(aq) hydrosulfuric acid • Ternary Acids (oxoacids) - Acids with H, O and a nonmetal • suffix -ic is assigned arbitrarily to one ox. state of each nonmetal • need to know the common ic acids on page 165 • hypostemous lowest ox state HClO hypochlorous acid +1 • stemous next lowest ox state HClO2chlorous acid +3 • stemic next highest ox state HClO3chloric acid +5 • perstemic highest ox state HClO4 perchloric acid +7 • Ternary Salts-Ternary acid with the H replaced by another ion • ous ite NaClO sodium hypochlorite • ic ate NH4ClO4 ammonium perchlorate