Atoms and Elements
140 likes | 349 Vues
Atoms and Elements. 8.P.1.1 I can explain the relationships between atoms and elements. What is Matter ?. Anything made of atoms and molecules Anything that has mass and takes up space What is an example of matter ?. What is an Atom ?.

Atoms and Elements
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Atoms and Elements 8.P.1.1 I can explain the relationships between atoms and elements.
What is Matter? • Anything made of atoms and molecules • Anything that has mass and takes up space What is an example of matter?
What is an Atom? • How small can a piece of aluminum foil be broken into? • What is all matter made of? • How does the video define an atom? • What are different types of matter made of?
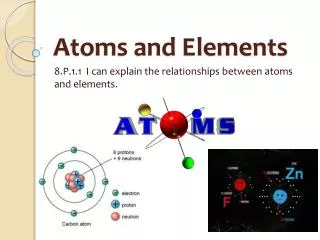
An atom… • Is the smallest unit of matter that retains the identity of the substance • Atoms are known as the building blocks of all matter What can be found in an atom? • It consists of protons, neutrons, and electrons • Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom • Electrons are located in the electron cloud which surrounds the nucleus of an atom accounting for most of the space an atom occupies
What are protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons • Positively charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom Neutrons • Subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom which are neutral Electrons • Negatively charged subatomic particles found orbiting the nucleus of an atom
What is an Element? • What do the types of matter in the video have in common? • How does the video define an element? • How many known elements exist? • What is used to organize the known elements?
An element… • Is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means • Consists of one type of atom • If you change the number of protons the type of element changes • Examples • Hydrogen consists of one proton and one electron. • Carbon consists of six protons and six electrons.
What does an element’s atomic number tell us? • The atomic number of an element tells us the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus 1) How many protons are in an atom of Nitrogen? 2) How many protons are in an atom of Helium? 3) How many protons are in an atom of Neon? 4) How many protons are in an atom of Sodium? 5) How many electrons are in each of the atoms 1- 4? 1) 7 2) 2 3) 10 4) 11 - Hint: The protons = the electrons 7 2 10 11
What is the atomic mass number? • The atomic mass number of an element tells us the number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • How do you think we can determine the number of neutrons in each of the atoms 1-4? Atomic mass number = protons + neutrons - protons- protons Atomic mass number – protons = neutrons
How many neutrons? Atomic mass number – protons = neutrons 1) How many protons are in an atom of Nitrogen? 2) How many protons are in an atom of Helium? 3) How many protons are in an atom of Neon? 4) How many protons are in an atom of Sodium? 5) How many protons are in an atom of Potassium? 7 2 10 12 20
How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in one atom of each element? • Iron (Fe) p+ = n0 = e- = • Oxygen (O) p+ = n0 = e- = • Boron (B) p+ = n0 = e- = • Chlorine (Cl) p+ = n0 = e- = • Zinc (Zn) p+ = n0 = e- = • Lead (Pb) p+ = n0 = e- = • Copper (Cu) p+ = n0 = e- =
How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in one atom of each element? • Iron (Fe) p+ = 26 n0 = 29 e- = 26 • Oxygen (O) p+ = 8 n0 = 8 e- = 8 • Boron (B) p+ = 5 n0 = 5 e- = 5 • Chlorine (Cl) p+ = 17 n0 = 18 e- = 17 • Zinc (Zn) p+ = 30 n0 = 35 e- = 30 • Lead (Pb) p+ = 82 n0 = 125 e- = 82 • Copper (Cu) p+ =29 n0 = 34 e- = 29
Wrap-up 1) What is matter? 2) What are atoms made of? 3) What is the difference between atoms and elements? 4) What is the atomic mass? 5) How do you determine the number of protons? Neutrons? Electrons?