Quantum Mechanical Model in Chemistry
190 likes | 361 Vues
Explore the quantum mechanical model of the atom in chemistry, including the 1s orbital, probability distribution of electrons, quantum numbers, orbital shapes, Pauli Exclusion Principle, Aufbau Principle, and periodic trends like ionization energies and atomic radius. Understand the principles governing electron configurations and atomic properties.

Quantum Mechanical Model in Chemistry
E N D
Presentation Transcript
AWESOME Quantum Mechanical Model February 28, 2007 Chem 102B
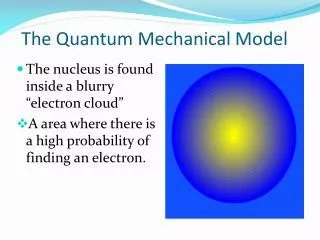
1s Orbital () • Probability of electron in 3-D space around the nucleus
More “s” orbitals • The higher the energy level, the larger the size, and the more nodes that are present • Note the Nodes
Nodes • Region of zero probablity
“P” Orbitals • Dumbell shapes • Sets of 3
Quantum Numbers • n - principalSize and Energy • integer values • l - angularShape • integral values from 0 to n-1 • ml - magneticOrientation • integral values from -l to l including 0 • ms - spinSpin • +1/2 or -1/2
Pauli Exclusion Principle • Two electrons in the same orbital have opposing spins • In a given atom: No two electrons can have same QN’s!
Aufbau Principle • “Building up” • Add electrons one at a time • Energy tells us what order to fill the electrons in the orbitals - Hund’s Rule • Lowest energy equals max number of “unpaired electrons”
Ionization Energies • Energy required to completely remove an electron from an atom.
Electron Affinity • The energy change associated with the addition of an electron to a gaseous atom • X(g) + e- X-(g) • Atoms that tend to form negative ions release more energy when an electron is added
Atomic radius • Half the distance between the nuclei in a molecule consisting of identical atoms • Not exact measure!
Radii trends • Down the group the atoms get larger, more electrons, bigger size. • Across the period the atoms get smaller, why?
R Summary of Trends Too erratic to predict IE EA