Acid-Base Reactions
100 likes | 146 Vues
Acid-Base Reactions. Adding a base to an acid neutralizes the acid ’ s acidic properties. This reactions is called a neutralization reaction. The products of a neutralization reaction are water and salt. Acid + base water + salt

Acid-Base Reactions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
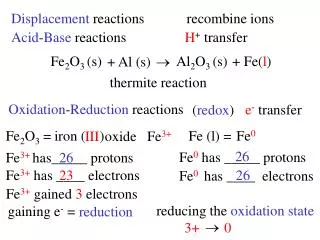
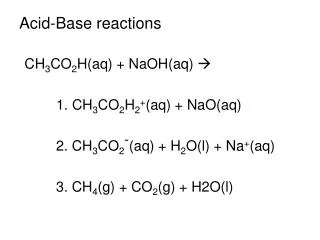
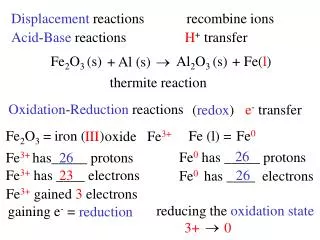
Acid-Base Reactions • Adding a base to an acid neutralizes the acid’s acidic properties. This reactions is called a neutralization reaction. • The products of a neutralization reaction are water and salt. • Acid + base water + salt • A salt is an ionic compound that is composed of the anion from the acid and the cation from the base.
HNO3 (aq) + NaOH(aq) NaNO3 (aq) + H2O(l) Anion from acid Cation from base
The balanced chemical equation for this reaction shows that 1 mol of nitric acid reacts with 1 mol of sodium hydroxide. • If equal molar quantities of reactants are used, then the result is a neutral (pH 7) aqueous solution. • For most neutralization reactions, there are no visible signs that a reaction is occurring. One way is to use an acid-base indicator, which is a substance that changes color in acidic or basic solutions.
H+(indicator) H+ + indicator one color another color
Finding Concentration Example • 13.84 mL of hydrochloric acid just neutralizes 25.00 mL of a 0.1000 mol/L solution of sodium hydroxide. What is the concentration of the hydrochloric acid? • Write the balanced equation • Calculate the amount of sodium hydroxide added, based on volume and concentration of solution • Determine the amount of hydrochloric acid needed to neutralize the sodium hydroxide • Find the concentration based on the amount and volume of hydrochloric acid solution needed.
Balanced equation • HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + HOH(l) • Calculate NaOH • Amount NaOH added (in mol) = Concentration x volume = 0.1000 mol/L x 0.025 00 L = 2.500 x 10-3 mol
Determine HCl • HCl reacts with NaOH in a 1:1 ratio, so there must be 2.500 x 10-3 mol HCl • Concentration (mol/L) HCl = Amount (mol) volume (L) = 2.500 x 10-3 mol 0.01384 L = 0.1806 mol/L
Finding Volume Example • What volume of 0.250 mol/L sulfuric acid is needed to react completely with 37.2 mL of 0.650 mol/L potassium hydroxide? • Write a balanced equation • Calculate the amount (in mol) of potassium hydroxide • Determine the amount of sulfuric acid needed • Find the volume of sulfuric acid
Balanced equation • H2SO4(aq) + 2 KOH(aq) K2SO4(aq) + 2 H2O(l) • Calculate KOH • Amount KOH added (in mol) = Concentration x volume = 0.650 mol/L x 0.0372 L = 2.41 x 10-2 mol
Determine H2SO4 • 1 H2SO4 = x H2SO4 2 KOH 2.41 X 10-2 • 1.21 x 10-2mol H2SO4 • Concentration (mol/L) HCl = Amount (mol) volume (L) Volume = Amount / Concentration = 1.21 x 10-2mol / 0.250 mol/L = 4.84 x 10-2 L