Arrays
510 likes | 657 Vues
Arrays. Chapter 6. Outline. Array Basics Arrays in Classes and Methods Sorting Arrays Multidimensional Arrays. Introduction to Arrays. An array is an object used to store a (possibly large) collection of data. All the data stored in the array must be of the same type.

Arrays
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Arrays Chapter 6
Outline • Array Basics • Arrays in Classes and Methods • Sorting Arrays • Multidimensional Arrays
Introduction to Arrays • An array is an object used to store a (possibly large) collection of data. • All the data stored in the array must be of the same type. • An array object has a small number of predefined methods.
Introduction to Arrays, cont. • Sometimes you want to know several things about a collection of data: • the average • the number of items below the average • the number of items above the average • etc. • This requires all the items to be stored as variables of one kind or another.
Introduction to Arrays, cont. • Arrays satisfy this need. • Even though an array is an object in Java, it can be convenient to think of it as a collection of variables of the same type.
Array Basics: Outline • Creating and Accessing Arrays • Array Details • The length Instance Variable • Initializing Arrays
Creating and Accessing Arrays • example double[] temperature = new double[7]; is like declaring seven variables of type double, named temperature[0], temperature[1], temperature[2], temperature[3], temperature[4], temperature[5], temperature[6].
Creating and Accessing Arrays, cont. • These variables can be used just like any other variables of type double. • examples temperature[3] = 32.0; temperature[6] = temperature[3] + 5; System.out.println(temperature[6]); temperature[index+1] = 66.5; • These variables are called indexed variables, elements, or subscripted variables. • The integer expression within the square brackets is called the index (or subscript).
Array Details • syntax for creating an array Base_Type[] Array_Name = new Base_Type[Length]; • example int[] pressure = new int[100]; or int[] pressure; pressure = new int[100];
Array Details, cont. • The type of the elements is called the base type. • The base type of an array can be any type including a class type. • for example, Species[] entry = new Species[3]; • The number of elements is the length or size of the array.
Brackets[] • Brackets [] serve three purposes: • creating the type name example: int[] pressure; • creating the new array pressure = new int[100]; • naming an indexed variable of the array pressure[3] = keyboard.nextInt();
The length Instance Variable • An array has only one public instance variable, namely length. • The length variable stores the number of elements the array can hold. • Using Array_Name.length typically produces clearer code than using an integer literal.
Indices and length • The indices of an array start with 0 and end with Array_Name.length-1. • When a for loop is used to step through an array, the loop control variable should start at 0 and end at length-1. • example for (lcv = 0; lcv < temperature.length; index++)
Array Index Out of Bounds • Every index must evaluate to an integer which is not less than 0 and not greater than Array_Name.length-1. • Otherwise, the index is said to be out of bounds or invalid. • An out-of-bounds index will produce a run-time error.
Incomplete Array Processing • Loops fail to process an entire array correctly when they • begin with an index other than 0 • end with an index other than length-1. • Examples for (i = 1; i < oops.length-1; index++) for (i = 1; i <= oops.length; index++) for (i = 0; i <= oops.length; index++) for (i = 0; i < oops.length-1; index++)
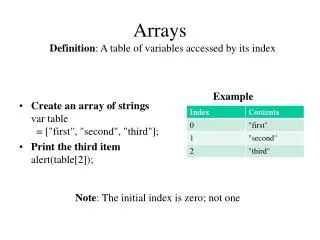
Initializing Arrays • An array can be initialized at the time it is declared. • example double[] reading = {3,3, 15.8, 9.7]; • The size of the array is determined by the number of values in the initializer list.
Initializing Arrays, cont. • Uninitialized array elements are set to the default value of the base type. • However, it’s better to use either an initializer list or a for loop. int[] count = new int[100]; for (int i = 0, i < count.length, i++) a[i] = 0;
Arrays in Classes and Methods • Arrays can be used as instance variables in classes. • Both an indexed variable of an array and an entire array can be a argument of a method. • Methods can return an indexed variable of an array or an entire array. • example double[] a = new double[10]; SampleClass.change(a); ... public static void change(double[] d)
Array Subtleties • If the base type of an array is a primitive type, then a method to which an array element is passed creates a copy of the array element, and cannot change the original array element. • If the base type of an array is a class type, then a method to which an array element is passed creates an alias, and the referenced object can be changed.
Arguments for the Method main • Recall the heading for method main: public static void main(String[] args) • Method main takes an array of String values as its argument. • A default array of String values is when you run a program.
Arguments for the Method main, cont. • Alternatively, an array of String values can be provided in the command line. • example java TestProgram Mary Lou • args[0]is set to“Mary” • args[1]is set to“Lou” System.out.println(“Hello “ + args[0] + “ “ + args[1]); printsHello Mary Lou.
Use of = and == with Arrays • The assignment operator = and the equality operator ==, when used with arrays, behave the same as when used with other objects. • The assignment operator creates an alias, not a copy of the array. • The equality operator determines if two references contain the same memory address, not if two arrays contain the same values.
Making a Copy of an Array • example int[] a = new int[50]; int[] b = new int[50]; ... for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) b[j] = a[j];
Sorting Arrays: Outline • Selection Sort • Other Sorting Algorithms
Sorting Arrays • Sometime we want numbers in an array sorted from smallest to largest, or from largest to smallest. • Sometimes we want the strings referenced by an array to be in alphabetical order. • Sorting techniques typically are easy to adapt to sort any type that can be ordered.
Selection Sort • The selection sort arranges the values in an an array so that a[0] <= a[1] <= a[2] … <= a[a.length-1] • The selection sort places the smallest item in a[0], the next smallest item in a[1], and so on for all but the last item. for(i = 0; i <a.length-1; i++) place the ith smallest item in a[i]
Selection Sort, cont. • Selection sort begins by finding a smallest item in the array and swapping it with the item in a[0]. • Selection sort continue by finding a smallest item in the remainder of the array and swapping it with the next item in array a. • Selection sort terminates when only one item remains.
Swapping Elements • To swap two elements a[i] and a[j], one of them must be saved temporarily.
Other Sorting Algorithms • The selection sort is not particularly efficient, but it is easy to code. • More efficient algorithms, such as quicksort, are more difficult to code.
Multidimensional Arrays • Introduction to Multidimensional Arrays • Multidimensional-Array Basics • Multidimensional-Array Parameters and Returned Values • Implementation of Multidimensional Arrays • (optional) Ragged Arrays • Programming Example
Introduction to Multidimensional Arrays • An array with more than one index sometimes is useful. • example: savings account balances at various interest rates for various numbers of years • columns for interest rates • rows for years • This two-dimensional table calls for a two-dimensional array.
Introduction to Multidimensional Arrays, cont. • An array with n indices is called an n-dimensional array. • The arrays we considered previously, which had one index, were one-dimensional arrays.
Multidimensional-Array Basics • example declaration int[][] table = new int [10][6]; or int[][] table; table = new int[10][6]; • The number of bracket pairs in the declaration is the same as the number of indices.
Multidimensional-Array Basics, cont. • syntax Base_Type[]…[] Array_Name = new Base_Type[Length_1]…[Length_n]; • examples char[][] page = new char [100][80]; double[][][] threeDPicture = new double[10][20][30]; SomeClass[][] entry = new SomeClass[100][80];
Multidimensional-Array Parameters • Methods may have multidimensional-array parameters and return a multidimensional array.
Implementation of Multidimensional Arrays • Multidimensional arrays are implemented in Java using one-dimensional arrays. • Consider int[][] table = new int[10][6]; • The array table is a one-dimensional array of length 10. • Its base type is int[]. • Therefore, it is an array of arrays.
Implementation of Multidimensional Arrays, cont. • This permits us to use the length instance variable, instead of an integer literal, to control a for loop used to initialize or print the values of the elements of an array. • example for (r = 0; r < table.length; r++) for (c = 0; c < table[r].length; c++)
(optional) Ragged Arrays • Since a two-dimensional array in Java is an array of arrays, each row can have a different number of elements (columns). • Arrays in which rows have different numbers of elements are called ragged arrays. • Example int[][] b = new int[3][]; b[0] = new int[5]; b[1] = new int[7]; b[2] = new int[4];
Summary • You have learned about arrays and how to use them in Java programs. • You have learned how to use array parameters and how to define methods that return an array. • You have learned the proper use of an array as an instance variable. • You have learned about multidimensional arrays.