Intelligent Ground Vehicle Navigation and Image Processing Software Development
20 likes | 170 Vues
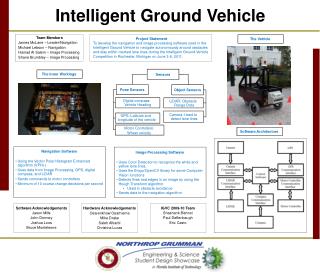
This project focuses on developing sophisticated navigation and image processing software for the Intelligent Ground Vehicle (IGV) to autonomously navigate around obstacles and maintain lane discipline. Utilizing various sensors, including pose sensors, LiDAR, cameras, and GPS, the vehicle can make real-time decisions about its course. The software employs advanced algorithms like the Vector Polar Histogram Enhanced (VPH+) and the Hough Transform for image recognition and processing. The project culminated in the IGVC competition held in Rochester, Michigan, on June 3-6, 2011.

Intelligent Ground Vehicle Navigation and Image Processing Software Development
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Team Members James McLane – Leader/Navigation Michael Lebson – Navigation Hamad Al Salem – Image Processing Shane Brumbley – Image Processing Project Statement To develop the navigation and image processing software used in the Intelligent Ground Vehicle to navigate autonomously around obstacles and stay within marked lane lines during the Intelligent Ground Vehicle Competition in Rochester, Michigan on June 3-6, 2011. Sensors Pose Sensors Object Sensors Digital compass: Vehicle Heading LiDAR: Obstacle Range Data Camera: Used to detect lane lines GPS: Latitude and longitude of the vehicle Motor Controllers: Wheel velocity Software Architecture The Inner Workings The Vehicle • Navigation Software • Using the Vector Polar Histogram Enhanced algorithm (VPH+) • Uses data from Image Processing, GPS, digital compass, and LiDAR • Sends commands to motor controllers • Minimum of 10 course change decisions per second • Image Processing Software • Uses Color Detection to recognize the white and yellow lane lines. • Uses the Emgu/OpenCV library for some Computer Vision functions • Detects lines and edges in an image by using the Hough Transform algorithm • Used in obstacle avoidance • Sends data to the navigation algorithm Software Acknowledgements Jason Mills John Dormey Joshua Loos Bruce Monteleone IGVC 2009-10 Team Shashank Bishnoi Paul Deffenbaugh Eric Casto Hardware Acknowledgements Osarenkhow Osarhieme Mike Drake Saleh Alharbi Christina Lucas Intelligent Ground Vehicle