The language of probability
500 likes | 1.36k Vues
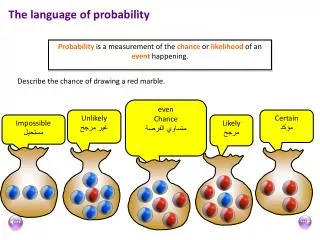
Probability is a measurement of the chance or likelihood of an event happening. The language of probability. Describe the chance of drawing a red marble. even Chance متساوي الفرصة. Unlikely غير مرجح. Certain مؤكد. Impossible مستحيل. Likely مرجح. The probability scale. 1. 1.

The language of probability
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Probability is a measurement of the chance or likelihood of an event happening. The language of probability Describe the chance of drawing a red marble. even Chance متساوي الفرصة Unlikely غير مرجح Certain مؤكد Impossible مستحيل Likely مرجح
1 1 1 1 1 1 6 6 6 6 6 6 1 Since each number on the dice is equally likely the probability of getting any one of the numbers is 1 divided by 6 or . 6 When you roll a fair dice you are equally likely to get one of six possible outcomes: Listing possible outcomes
1) A coin landing tails up? 3) Drawing a seven of hearts from a pack of 52 cards? 1 P(7 of ) = 52 1 1 1 7 2 4 2) This spinner stopping on the red section? 4) A baby being born on a Friday? What is the probability of the following events? Calculating probability P(tails) = P(Friday) = P(red) =
4 1 2 1 1 = 8 8 2 4 8 = This spinner has 8 equal divisions: What is the probability of the spinner landing on • a red sector? • a blue sector? • a green sector? Calculating probability a) P(red) = b) P(blue) = c) P(green) =
1 2 3 1 3 1 1 = 6 6 2 2 6 3 6 • A fair dice is thrown. What is the probability of getting • a 2? • an odd number? • a prime number? • a number greater than 4? Calculating probability P( 2 ) = P( odd number ) = = = P( prime number) = P( number > 4 ) =
The probability of a factory component being faulty is 0.03. What is the probability of a randomly chosen component not being faulty? The probability of an event not occurring P(not faulty) = 1 – 0.03 = 0.97 P( NOT A ) = 1 – P ( A )
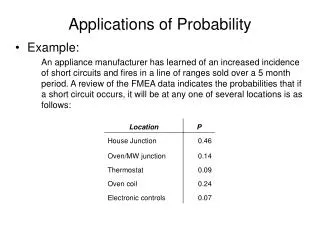
Event A B C D 3 2 5 5 11 9 20 20 The following table shows the probabilities of 4 events. For each one work out the probability of the event not occurring. The probability of an event not occurring Probability of the event occurring Probability of the event not occurring 0.77 0.23 8% 92%
For example, a game is played with the following cards: 1 1 1 1 3 2 2 3 1 9 3 3 3 9 3 3 3 3 + = If two outcomes are mutually exclusive then their probabilities can be added together to find their combined probability. Adding mutually exclusive outcomes A card is randomly chosen .What is the probability that : If A & B are two mutually exclusive events then: P ( A & B ) = 0 P ( A OR B ) = P ( A ) + P ( B ) متباعدة لا يمكن حدوثهما معا P(moon) = P(not moon ) = = = 1 - = P(sun) = P(moon andsun) = 0 P(moon or sun) = P(moon) + P(sun) =
Second coin H T First coin H T 1 4 2) We can use a two-way table. Finding all possible outcomes of two events HH HT TH TT From the table we see that there are four possible outcomes one of which is two heads so, P(HH) =
H H T H T 1 T 4 3) We can use a probability tree diagram. Outcomes Second coin Finding all possible outcomes of two events HH First coin HT TH TT Again we see that there are four possible outcomes so, P(HH) =
H H T H H T H H H T T 1 T T T 8 3) We can use a probability tree diagram. Outcomes third coin HHH Second coin Finding all possible outcomes of two events HHT First coin HTH HTT THH THT TTH TTT Again we see that there are 8 possible outcomes so, P(HHH) =
8 5 15 8 8 8 9 8 9 9 9 10 10 10 12 11 11 36 12 + From the sample space we can see that there are 36 possible outcomes when two dice are thrown. 2 3 4 5 6 7 Finding the sample space 3 4 5 6 7 8 = 4 5 6 7 8 9 5 6 7 8 9 10 Find P ( SUM ≥ 8 ) 6 7 8 9 10 11 P(sum ≥8) = 7 8 9 10 11 12
Worksheet ( 1 ) SUM المجموع ……………. ……………. ……………. ……………. ……………. ……………. ……………. ……………. ……………. ……………. ……………. Zayed althani school Math department Mohamad badawi : hamadaa_math@yahoo.com A box contains four cards with numbers 1 to 4 Two cards were randomly selected. A ) Complete the tree diagram to find all possible outcomes of their sum يحتوي كيس على بطاقات مرقمة بالأعداد 1 وحتى 4 تم سحب بطاقتين معا بشكل عشوائي اكمل الشجرة البيانية لتجد النواتج الممكنة لمجموع البطاقتين Find P ( المجموع= 6 ) = ……………….. B) Find P ( SUM= 6 ) = ……………….. Find P ( المجموع≤4 ) = ……………….. ……………. C) Find P ( SUM≤ 4 ) = ………………..
Worksheet ( 2) Zayed althani school Math department Mohamad badawi : hamadaa_math@yahoo.com A ) A bag contains the letters of the word “ MATHEMATICS “ Ali draw a card at random. Find the probability that the letter “ M “ is written on that card. …………………………… M كتبت على بطاقات ووضعت داخل حقيبة ، سحب علي بطاقة عشواءياً ما احتمال انها تحمل الحرف حروف كلمة “ MATHEMATICS “ صندوق يحوي 5 كرات حمراء ، 6 كرات خضراء وكرة زرقاء . تم سحب كرة عشوائيا ما احتمال انها خضراء .................... ما احتمال انها ليست زرقاء ................ B ) A box contains 5 red balls , 6 green balls and one blue ball . A ball was drawn randomly . 1 ) Find P ( green ) = …………….. 2 ) Find P ( the ball is not blue ) = ……………… C ) A and B are mutually exclusive events such that : P ( A ) = 0.76 , P ( B ) = 0.19 Find : 1 ) P ( not A ) = …………….. 2 ) P ( A & B ) = ................ 3 ) P ( A OR B ) = ……………… اوجد : P ( A ) = 0.76 , P ( B ) = 0.19 حدثان متباعدان بحيث : A , B