Exploring Graphs of Quadratic and Cubic Functions: Equations and Key Features
50 likes | 179 Vues
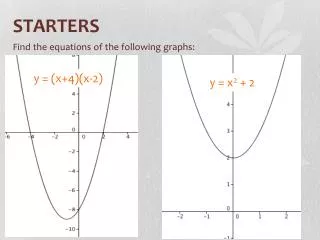
This guide covers finding equations for various quadratic and cubic graphs. Start with the quadratic equation y = (x + 4)(x - 2) and its equivalent y = x² + 2. Next, explore cubic functions, including y = x³ and its transformations. Learn about the point of inflection in cubic functions and how shifts affect their graphs. Example equations include y = x³ + 4, y = (x - 5)³ + 2, and y = (x + 1)³ - 2. Graphing these expressions reveals their unique characteristics and relationships.

Exploring Graphs of Quadratic and Cubic Functions: Equations and Key Features
E N D
Presentation Transcript
STARTERS Find the equations of the following graphs: y = (x+4)(x-2) y = x2 + 2
Note 7: Cubics - Basic y = x3 This “central point” is called a “point of inflexion”
Any functions of the basic cubic are treated the same as the shifts in the parabola. Examples: Graph y = x3 + 4 y = x3 + 4 y-intercept is 4
Examples: Graph y = (x – 5)3 + 2 Vertex (5, 2) y = (x - 5)3 + 2
Graph the following cubics y = x3 + 1 y = (x – 2)3 y = -x3y = (x + 1)3 – 2 y = x3– 3 y = (x – 3)3