Fundamental Counting Principle
140 likes | 513 Vues
Fundamental Counting Principle. a x b x c …. PR-L4 Objectives: To count outcomes using the fundamental counting principle. Learning Outcome B-4.

Fundamental Counting Principle
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Fundamental Counting Principle axb xc … PR-L4 Objectives:To count outcomes using the fundamental counting principle. Learning Outcome B-4
When solving probability problems, we often have to count things (number of events in a sample space, number of success outcomes, etc.). Tree diagrams and charts can help. So can the Fundamental Counting Principle. The Fundamental Counting Principle states the following: If one event can occur in a ways, a second event in b ways, a third event in c ways, and so on, then the number of ways that all events can occur one after the other is the product a*b*c. . . Theory – Intro
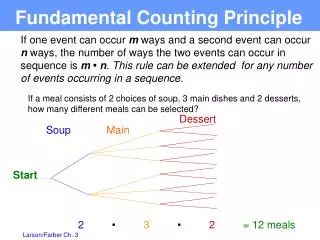
A certain brand of bicycle is available in three colours (yellow, blue, and red), two tire types (smooth, grip), and two different seats (economy, custom). How many different bicycles could be bought?We could determine the answer by drawing a tree diagram or creating a chart of our sample space. We see that 12 different bicycles are possible. Theory – Counting Outcomes
We could also calculate the total number of models available in using the Fundamental Counting Principle (FCP = a x b x c …) We must make three choices: colour, tire, seat. The number of options available for each choice are: 3, 2, 2 The total number of ways you could select the bicycle are:# of colours x # of tires x # of seats = # of options 3 x 2 x 2 = 12 waysWe have multiplied the number of ways each choice can be made, and the product is the number of choices. We see that this is the same result derived by using a tree diagram or chart. Theory – Calculating Outcomes
Sue has four pairs of shoes, five pairs of jeans, and seven sweaters. How many different clothing combinations can she select?A useful technique to use when solving this question is to draw spaces to represent the number of events, and then writing the number of ways each event can occur. The three events are shoes, jeans, and sweater:and the number of ways each choice can be made is written in the space:The total number of clothing combinations possible is: 4 x 5 x 7 = 140 Example
The map shows roads between the four towns. How many different routes are possible from Killarney to Brandon? Willie’s lunch will consist of a sandwich (ham, egg, or peanut butter), a fruit (apple, orange, banana, or pomegranate) and a drink (coffee or tea). How many different lunches might Willie have? The score at the end of a hockey game was 3-2. How many different scores were possible at the end of the 2nd period? Example
The map shows roads between the four towns. How many different routes are possible from Killarney to Brandon and back to Killarney, if no road is used twice? Sometimes, restrictions will limit your options for a given choice (eg. reuse). You can go on one date per evening. Once you date a girl, you never see her again (of course). If Kate, Jennifer, Angelina and Jessica are available on Wednesday, Thursday, or Friday, how many dates can you go on? How many arrangements of the letters of the word MONKEY are there? Theory – Restrictions (Reuse)
9 x 9 x 9 x 9 = 6561 • 9 x 8 x 7 x 6 = 3024 • 8 x 7 x 6 x 4 = 1344 Example – Restrictions
A license plate takes the form AAA 999, where A is any letter, and 9 is any digit (0-9). How many license plates can be created? How many license plates can be created if no letter or digit is repeated? How many license plates can be created if the letters I and O can’t be used and you can’t start the digit string with a 0? (repetition ok) How many license plates can be created if you must start the letters with a V, can’t use I and O at all, can’t start with a 0, and must end with an odd number? (no repetition) Example – Restrictions