Understanding Incomplete Dominance in Flower Color Genetics
40 likes | 170 Vues
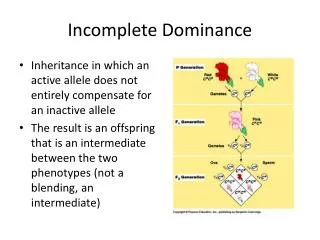
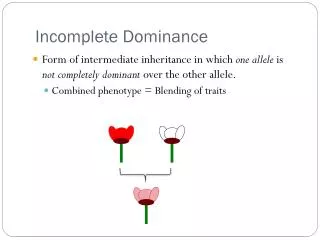
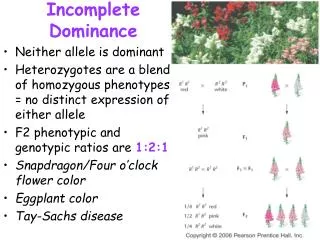
Incomplete dominance occurs when the phenotypes of alleles blend rather than one dominating the other. This phenomenon was notably observed by Mendel in four o’clocks, leading him to halt his genetic studies due to the complexities it introduced. For instance, crossing a red petal flower (RR) with a white petal flower (R'R') can produce pink flowers (R'R). When a pink flower (R'R) is crossed with a red flower (RR), the resulting offspring exhibit a mix of red, white, and pink flowers based on their genotypes.

Understanding Incomplete Dominance in Flower Color Genetics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Incomplete Dominance Sometimes, depending on the way the different proteins from each allele interact genes don’t completely dominate the alternate allele Mendel, studying four o’clocks, gave up genetic research because of this fact.
Example Some species of flowers when you cross a red petal with a white petal produce a pink petal. Red = R White=R’ Possible genotypes: Red = RR White = R’R’ Pink = RR’
Cross an incompletely dominant pink flower with a red flower. 1. Dom = Red & White Blend= Pink Hybrid 2. R = red R’= white RR’= pink 3. Mom = RR’ Dad = RR 4. • 5/6. • Red = 2/4 • White = 0/4 • Pink = 2/4 R R’ R R