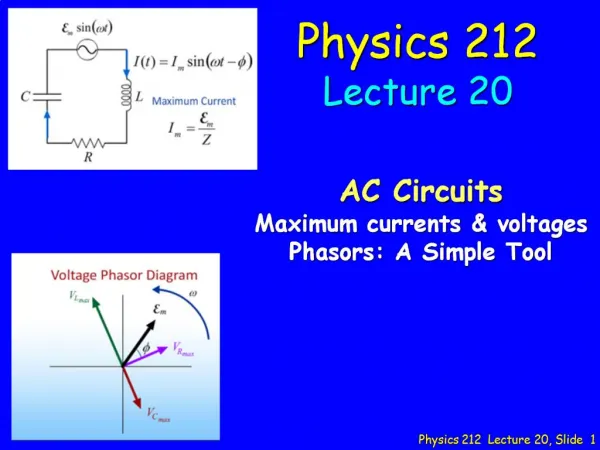
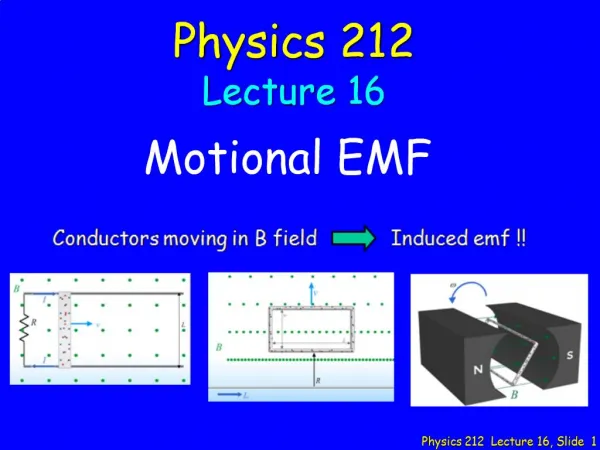
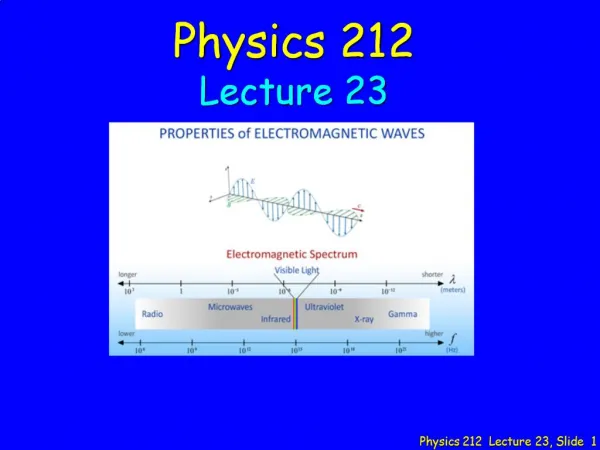
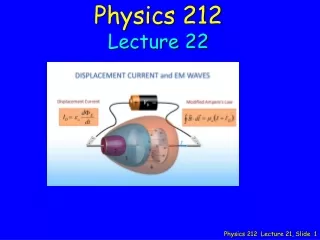
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 1
E N D
Presentation Transcript
1. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 1
2. Main Point 1 First, we defined what we had previously called �plane harmonic waves� as linearly polarized waves. In particular, we defined the direction of polarization to be the axis of the electric field oscillations of the plane wave.
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 2
3. Main Point 2 Second, we introduced polarizers, materials that totally absorb the E-field component perpendicular to its transmission axis, while completely passing the E-field component parallel to that axis. Consequently, light passing through these polarizers is linearly polarized along the transmission axis. If the incident light is unpolarized, the transmitted light has half the initial intensity, while if the incident light is linearly polarized, the intensity of the transmitted light is equal to the incident intensity times the cos2q, where q is the angle between the initial polarization direction and the transmission axis.
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 3
4. Main Point 3 Third, we introduced circular polarization in which the E-field oscillations in two orthogonal transverse directions were 90 degrees out of phase with each other. We distinguished between right-handed and left-handed circular polarization by observing the sense of rotation of the E-field oscillations in space at a fixed time. Circular polarization can be produced by passing linearly polarized light through birefrigent materials that have an asymmetric structure in transverse directions which results in the speed of light being different in each of those directions. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 4
5. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 5
6. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 6
7. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 7
8. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 8
9. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 9
10. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 10
11. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 11
12. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 12
13. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 13
14. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 14
15. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 15
16. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 16
17. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 17
18. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 18
19. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 19 Circular Light on Linear Polarizer
20. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 20
21. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 21
22. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 22 Calculation The purpose of this Check is to jog the students minds back to when they studied work and potential energy in their intro mechanics class.The purpose of this Check is to jog the students minds back to when they studied work and potential energy in their intro mechanics class.
23. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 23
24. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 24
25. Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 25