Mastering Graphing with Slope-Intercept Form: A Comprehensive Review
80 likes | 208 Vues
This review covers the essentials of graphing linear equations using the slope-intercept form (y = mx + b). Learn two methods to find the slope of a line, the significance of the slope (m) and y-intercept (b), as well as techniques for identifying these values in various equations. Detailed examples guide you through rewriting equations to slope-intercept form, plotting points, and understanding rise and run. Test your knowledge with a fun quiz at the end to solidify your learning!

Mastering Graphing with Slope-Intercept Form: A Comprehensive Review
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Review • What are two ways you find the slope of a line? • Slope formula • Plotting points and finding the rise and run between points
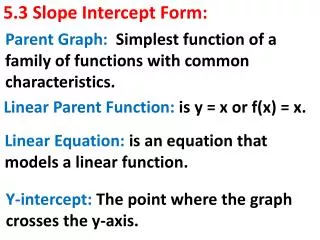
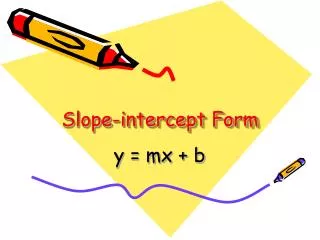
Slope-Intercept Form • y = mx + b When the equation is in this form, you can identify the slope (m) and the y-intercept (b). y-intercept slope
Examples • Identify the slope and y-intercept m = 3 b = 4 m = -3 b = 2 If the equation is not setup like y = mx + b, then you must manipulate the equation to that format. The general steps include: -Add/Subtract your x value -Multiply/Divide both sides of the equation by the coefficient of y
Do these examples on your own paper slope y-intercept slope y-intercept m = 1 b = -4 m = -¼ b =
Graph the equation 2x + y = 3 Step 1: Rewrite the equation in slope-intercept form y = -2x + 3 Step 2: Identify the slope and the y-intercept m = -2 b = 3 Step 3: Plot the point that corresponds to the y-intercept y-intercept - (0,3) Step 4: Use the slope to locate a second point on the line. Draw a line through the two points.
Quiz time!!!! Take everything off your desk and get ready for the quiz!