Big Data and the Database Community
40 likes | 154 Vues
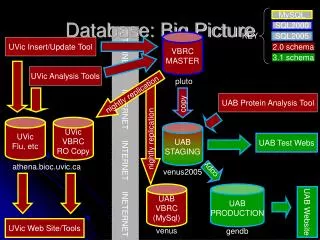
The Big Data phenomenon presents an unprecedented opportunity for the database community, emphasizing the need for scalable database systems capable of handling substantial data volumes. While the traditional database technologies have faced challenges from MapReduce and NoSQL systems, the community continues to adapt. This adaptation includes the integration of cost-based optimizers, traditional query execution, and effective data analysis techniques. Despite these advancements, the struggle to develop distributed databases capable of managing transactions at scale remains a critical question.

Big Data and the Database Community
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Big Data and the Database Community Daniel Abadi Yale University
The Big Data phenomenon is the best thing that could have happened to the database community • Despite other definitions related to ‘3 Vs’ --- Big Data means BIG Data • Which means we need scalable database systems • Still two main components of Big Data • Performing data analysis at scale • Performing requests on data at scale Big Data
Database community has won the battle • Some thought that MapReduce might replace traditional database technology as the primary means to perform analysis at scale • Just about every MapReduce vendor has abandoned this goal • Hadapt, Impala, Tez, and several others are in a race to see who can add the most traditional database execution technology to Hadoop fastest • Everyone is going in the direction of cost-based optimizers, traditional database operators, and push-based query execution Performing Data Analysis at Scale
The database community is losing the battle • NoSQL systems still have very little traditional database technology inside (despite adding SQL interfaces) • No race to add DB technology --- why? • Don’t blame CAP --- CAP is only relevant when there’s a network partition • We never figured out how to do ACID and active replication at scale • Many new proposals make simplifying assumptions in order to handle scale • It’s been 30 years ---- why can’t we build a distributed database that can handle distributed transactions over actively replicated data at scale? Performing Requests on Data at Scale