Understanding Ionic Bonding in Chemistry
230 likes | 341 Vues
Learn about ions, cations, anions, and how atoms gain or lose electrons in ionic bonding. Discover the principles behind stable electron structures and naming ionic compounds.

Understanding Ionic Bonding in Chemistry
E N D
Presentation Transcript
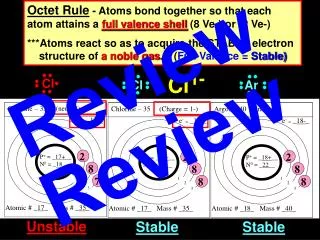
Chlorine – 35 (neutral) Argon – 40 (neutral) Chlorine – 35 (Charge = 1-) e-= _18-_ e-= _17-_ e-= _18-_ Cl Cl Ar 2 8 8 8 2 8 7 8 2 P+ = _18+__ N0 = _22__ P+ = _17+__ N0 = _18__ P+ = _17+__ N0 = _18__ 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 Atomic # _18_ Mass # _40_ Atomic # _17_ Mass # _35_ Atomic # _17_ Mass # _35_ Octet Rule - Atoms bond together so that each atom attains a full valence shell (8 Ve-) or (2 Ve-) ***Atoms react so as to acquire the STABLE electron structure of a noble gas.– (Full Valence =Stable) Review Cl1- Review Unstable Stable Stable
Formation of Cations Na1+ + Na e- Lose 1 e- Mg2+ + Mg e- e- Lose 2 e- Metals willlosevalence electrons to form positive cations.
Metals will lose electrons to form cations (+) 1+ 2+ Be – 2, 2 Mg – 2, 8, 2 Ca – 2, 8, 8, 2 Sr – 2, 8, 18, 8, 2 Ba- 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 2 Ra-2,8,18,32,18,8,2 Cations of Group 1A elements always have a charge of 1+ Group2A = 2+ Group 3A = 3+ (Metals)
3+ 3- 2- 1- 1+ 2+ Naming Metals - 1A, 2A, 3A Name of the Atom = Name of Cation Lithium ( Li ) = ( Li1+ ) Lithium Ion Magnesium ( Mg ) = ( Mg2+ ) Magnesium Ion Aluminum ( Al ) = ( Al3+ ) Aluminum Ion Transition Metals
Non-Metals gain electrons to form anions (-) 3- 2- 1- Formation of Anions F – 2, 7 Cl – 2, 8, 7 Br – 2, 8, 18, 7 I – 2, 8, 18, 18, 7 Anions of Group 5A = charge of 3- Group 6A = 2- Group 7A = 1- (Non-Metals) (Metalloids)
3+ 3- 2- 1- 1+ 2+ • All anions end in -ide Nonmetals - 5A, 6A, 7A) Name of the Atom = Name of Anion w/ - ide ending • Metals in Group 4A and 5A will always LOSE electrons to form cations (+) • Sn2+,Sn4+,Pb2+, Pb4+, Bi3+ Nitrogen ( N ) = ( N3- ) Nitride Oxygen ( O ) = ( O2- ) Oxide Chlorine ( Cl ) = ( Cl1- ) Chloride Transition Metals
3+ 3- 2- 1- 1+ 2+ Naming Ionic Compounds • All anions (non-metals) end in -ide Transition Metals
3+ 3- 2- 1- 1+ 2+ Transition Metals – Ions can have more than one charge Charge of Cation = Roman Numeral in Name Fe2+ = Iron (II) Fe3+ = Iron (III) Cu1+ = Copper (I) Cu2+ = Copper (II) Pb2+ = Lead (II) Pb4+ = Lead (IV) Transition Metals
3+ 3- 2- 1- 1+ 2+ Naming Ionic Compounds Transition Metals
NO3- Sulfide 1- • nitrate 2- • NOTE: I have made changes to your copy
Cl Al S P K Ar Ca QUESTION – If metals lose electrons & non-metalsgain electrons, Where do these electrons come from or go to? P 3- Ar Al3+ K 1+ Cl1- S 2- Ca2+ QUESTION – What makes an atom stable? ANSWER – Having a completely filled outer energy level of electrons –Full Octet (2 e- H, He, Li, Be)
O Mg Cl O Ionic Bonding = Transfer of electrons (Gaining or Losing e-) (Forming IONS) Lose 1 e- Gain 1 e- Lose 2 e- Gain 2 e- Ionic Bonding typically occurs between a metal cation (+) and a nonmetal anion (-) due to a transfer of electrons --- has a net charge of ZERO Cl Na Na Mg Mg 2+ O2- Cl- Na+ ( MagnesiumOxide - MgO) ( SodiumChloride - NaCl) ( Metal + Nonmetal ) ( Metal + Nonmetal ) Ionic Bonding typically occurs between a metal cation (+) and anonmetal anion (-) due to a transfer of electrons --- has a net charge of ZERO
S S K K Ca Lose 2 e- Lose 1 e- Gain 2 e- Gain 2 e- S2- Ca 2+ S2- 2K1+ ( PotassiumSulfide – K2S ) ( CalciumSulfide – CaS ) ( Metal + Nonmetal ) ( Metal + Nonmetal ) 2(1+) + (2-) = zero (2+) + (2-) = zero (2+) + (2-) = zero Ionic Compounds have a net charge of zero
Ionic Compounds have a net charge of zero NaBr Li2O 2Li1+ Na+ O2- Br - 2(1+) + (2-) = zero (1+) + (1-) = zero MgBr2 Al2S3 2Al3+ Mg2+ 3S2- 2Br - 2(3+) + 3(2-) = zero (2+) + 2(1-) = zero (6+) + (6-) = zero
Subscripts2 = more than one MONOATOMIC ion No subscript= only ONE atom/ion
The “4” is part of the ion NH41+ The “3” is part of the ion CO32- NH4 = One polyatomic ion - no subscript (NH4 )2 = Two polyatomic ions - subscript (parenthesis)2 are used when there is more than one POLYATOMIC ION
- - - + + + Ionic Bonding - the electrostatic attraction (Force) that binds oppositely chargedions (cations (+) &anions (-))together Electrostatic FORCE between the charges causes the attraction & repulsion
Ionic Bonding - the electrostatic FORCE that holds cations and anions together Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Cl- Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Crystal Lattice – Orderly, repeating, three dimensional pattern of ions (cations/anions) *NOTE: All ionic solids form a crystal lattice -- Atoms, ions, and molecules can form a crystal (crystal lattice)
Sodium - 23 (neutral) Chlorine – 35 (neutral) e-= _11-_ e-= _17-_ 8 8 7 1 2 2 P+ = _17+__ N0 = _18__ P+ = _11+__ N0 = _12__ 1 1 2 2 3 3 Atomic # _11_ Mass # _23_ Atomic # _17_ Mass # _35_ Chlorine, Cl2 Sodium Chloride, NaCl Table Salt + = = + Chlorine Gas is poisonous - The German Army first used chlorine gas cylinders in April 1915 against the French Army. French soldiers reported seeing yellow-green clouds drifting slowly towards the Allied trenches. They also noticed its distinctive smell which was like a mixture of pineapple and pepper. When the gas arrived at the Allied front-trenches soldiers began to complain about pains in the chests and a burning sensation in their throats. Chlorine gas destroyed the respiratory organs of its victims and this led to a slow DEATH by asphyxiation
1. How many valence electrons are there in an atom of oxygen? a) 2 b) 4 c) 6 d) 8
7.1 Section Quiz. 2. Atoms that tend to gain a noble gas configuration by losing valence electrons are a) metals. b) nonmetals. c) noble gases. d) representative elements.
3. When a magnesium atom forms a cation, it does so by a) losing two electrons. b) gaining two electrons. c) losing one electron. d) gaining one electron.
4. When a bromine atom forms an anion, it does so by a) losing two electrons. b) gaining two electrons. c) losing one electron. d) gaining one electron