Solving One Step Inequalities by Adding
100 likes | 253 Vues
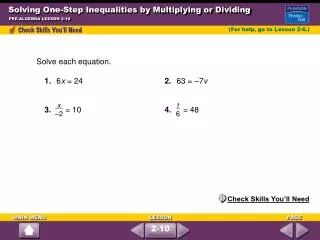
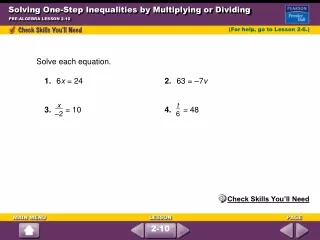
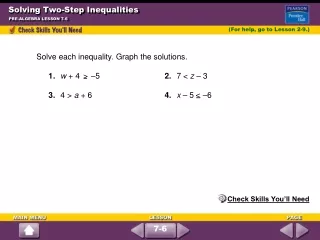
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of solving one-step inequalities through the concept of addition. It highlights the importance of converting subtraction into addition using its inverse and explains the Addition Property of Inequality: if a > b, then a + c > b + c, and if a < b, then a + c < b + c. Several examples are solved and graphed, including m + 3 > 6, 8 + t < 15, and -3 ≤ x + 7. A practical application, such as determining the weight limit for luggage, is also included, reinforcing these concepts with real-world context.

Solving One Step Inequalities by Adding
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Reminder: KFC Turn all subtraction into addition of its inverse
Addition Property of Inequality • If a>b, then a+c>b+c • If a<b, then a+c<b+c Works for –c or +c
An airline lets you check up to 65 lbs of luggage. One suitcase weights 37 lbs. How much can another suitcase weight? X+37≤65
Homework • TB Pg 106 (8-28 even and #31)