Linear Acceleration
130 likes | 358 Vues
Linear Acceleration. By Geoff Cuevas and Sahan Luvis Hennedige Fernando. Introduction.

Linear Acceleration
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Linear Acceleration By Geoff Cuevas and Sahan LuvisHennedige Fernando
Introduction • Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity over a period of time. Acceleration is caused by a change in either speed or direction. However unlike with speed, this doesn’t mean a person with 0 acceleration isn’t moving, it means they are moving at a constant rate without speeding up or slowing down. • Acceleration can reflect a change in magnitude of velocity without a change in direction or a change in the direction of velocity. In other words, a change in speed or direction.
Three Phases • There are three phases in acceleration: • The propulsive phase where velocity increases without a change in direction causing acceleration • The breaking phase where velocity decreases during a change in direction or a decrease in speed causing deceleration • The static phase where velocity stays constant and acceleration is 0
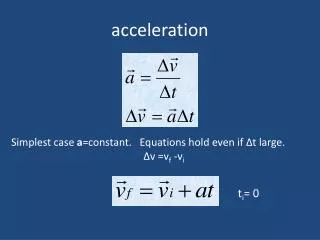
Calculating Acceleration • Acceleration (A) is equal to a change in velocity (v) over time (t). • A(m/) = ∆v/t • ∆v = final velocity – initial velocity • For example, a cyclist rides 15 meters over a period of 2 seconds. • A = 15/2 • = 7.5m/ • Acceleration can also be calculated using force (in Newtons, N) and mass (in kilograms) • A = F/M
Acceleration- Usain Bolt • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y2kOoniBI7c
Quiz time I love quizzes.
Acceleration is the rate of change in______ over ______ Distance over speed Velocity over time Speed over time This isn’t even a question
Acceleration can reflect a change in Magnitude of velocity Direction of velocity A and B Acceleration can’t reflect anything because it’s not a mirror or whatevs
One of the three phases of acceleration includes The Velocity Phase The Static Phase The Displacement Phase The Emo Phase
Quiz Answers • B- Velocity over time • A- Magnitude • B- Static Phase
Bibliography • http://btc.montana.edu/olympics/physbio/glossary/g12.html • https://biomechanics.kookmin.ac.kr/kmu20112/Lecture_05.pdf • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MAS6mBRZZXA • http://www.topendsports.com