Chapter 7 - Photosynthesis
110 likes | 237 Vues
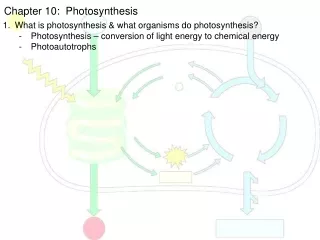
Photosynthesis is a vital process that allows nearly all plants, certain bacteria, and protists to produce their own organic matter through light reactions and the Calvin cycle. It occurs within chloroplasts, where chlorophyll absorbs light energy, initiating a series of reactions that split water molecules, releasing oxygen, and converting carbon dioxide into glucose. The light reactions occur in the thylakoid membrane, while the Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma. This remarkable process not only fuels plant life but also plays a crucial role in regulating atmospheric CO2 and O2 levels.

Chapter 7 - Photosynthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
(c) Euglena (d) Cyanobacteria (b) Kelp (a) Mosses, ferns, and flowering plants Chapter 7 - Photosynthesis • Almost all plants are photosynthetic autotrophs, as are some bacteria and protists • They generate their own organic matter through photosynthesis..
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts, which: • Are found in the cells of the mesophyll • Contain stroma, a thick fluid • Contain thylakoids, membranous sacs in stacks called grana.. Vein Chloroplast Meso- phyll Inner membrane Outer membrane Stomata Leaf cross section Mesophyll cell Grana Stroma Thylakoid Thylakoid space
Light energy Photo-synthesis Oxygen gas Glucose Carbon dioxide Water The Overall Equation for Photosynthesis • The reactants and products of the reaction..
Photosynthesis is a two-step process: • Light reactions – require sunlight energy to split water molecules into 2H and O2 • Calvin Cycle (dark reactions) – hydrogen generated from the light reactions is used to reduce CO2 to generate sugar – does not require sunlight • Leaves absorb CO2 through stomata..
Light Chloroplast NADP ADP + P Calvin cycle Light reactions
Excited state e 1 2 Heat Light (b) fluorescence of isolated chlorophyll in solution Light (fluorescence) Photon Ground state Chlorophyll molecule (a) Absorption of a photon (c) Fluorescence of a glow stick • Chlorophyll molecules absorb photons • Electrons in the pigment gain energy • The energy is released and used..
The light reactions in the thylakoid membrane 2NADP+ 2NADPH2 • 2H2O O2 ..
To Calvin Cycle Light Light ADP + P NADP Stroma Electron transport chain Thylakoid membrane ATP synthase Inside thylakoid 1/2 Light Reactions
The Calvin Cycle: Making Sugar From Carbon Dioxide • The Calvin cycle • Functions like a sugar factory within a chloroplast • Regenerates the starting material with each turn 6NADPH2 6NADP + 12H 6CO2 C6H12O6
Input 3 CO2 3 RuBP 6 3-PGA 6 3 ADP 6 ADP + 6 Calvin cycle 6 3 6 NADP 6 G3P 5 G3P 1 G3P Glucose and other compounds Output
Photosynthesis has an enormous impact on the atmosphere • It swaps CO2 in the atmosphere for O2 Why do we need the O2?..