Contraceptive methods
400 likes | 2.19k Vues
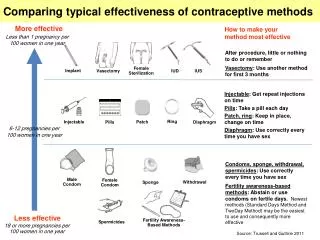
Contraceptive methods . Abstinence. Choosing not to have vaginal, anal or oral sex No side effects No STI’s No pregnancy 100% effectiveness . The pill. 97-99% Effective. A pill taken daily Contains oestrogen and progesterone to prevent pregnancy by stopping ovulation.

Contraceptive methods
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Abstinence • Choosing not to have vaginal, anal or oral sex • No side effects • No STI’s • No pregnancy • 100% effectiveness
The pill 97-99% Effective • A pill taken daily • Contains oestrogen and progesterone to prevent pregnancy by stopping ovulation. • Can come in a 21 or 28 day pack. • Advantages • Simple and easy to use • Regulates menstration • Disadvantages/Side effects • Must be consistently taken • Does not protect against STI’s • May cause irregular bleeding • Headaches • Breast tenderness • Mood swings • Nausea • A decrease in some vitamin levels (eating a well balanced diet is needed)
Depo-Prevera • 4 injections yearly of the hormone progesterone • Prevents pregnancy by stopping release of an egg • Also thickens the mucus in cervix to stop sperm from reaching the egg. • Advantages • Nothing daily • Does not contain estrogen • Disadvantages • Irregular bleeding • Decrease in bone mineral density • Possible weight gain • Does not prevent STI’s 99% effective if taken every 12 weeks
Female Condom 80-95% effective • Barrier at time of intercourse • Placed in the vagina • Prevents direct contact • Prevents fluid exchange • Advantages • No prescription • No routine • Protects against some STI’s
Disadvantages • Requires proper insertion • May cause uncomfortable • More expensive than male condoms • Approximately $3.50-$5.00 each
12-18% of women will become pregnant within the first year Diaphram • Rubber cup • Used with spermicide • Fits over the cervix opening • Prevents sperm from meeting the egg • Advantages • Does not effect fertility • Nothing daily • Can be inserted up to 6 hours before intercourse • Disadvantages • Limited protection against STI’s • Irritation • May move during intercourse • Fit by doctor • Bladder infections
The patch EVRA, the contraceptive patch • 1 ¾ inch square patch worn on your skin • slowly releases the hormones estrogen and progestin through the skin and into the bloodstream. • Prevents pregnancy by stopping an egg from being released each month (ovulation) and by changing the cervical mucous to make it difficult for sperm to enter the uterus. • The patch is only available by a prescription from a doctor. • Each patch = 1 week • Replace on the same day of each week to increase effectiveness • Once a week for 3 weeks, fourth week is a ‘patch free week’. You will have your period this week. • Continue with a new patch for another 4 week cycle
Can cause some side effects when you first start using the patch, like bleeding, breast tenderness, skin irritation, headaches or nausea. • Does not effect STI’s • May cause skin irritation • May not be effective if you are over 190 pounds • Does not work if you are a smoker • Higher chance of developing blood clots • Decreased effectiveness 99% effective
The Sponge • Small round sponge made of polyurethane foam. It is latex and hormone free. • Contains spermicide to disable sperm • Sponge fits in the vagina over the cervix, traps & absorbs sperm, effective for 12 hours • One time use only • Advantages • Does not contain hormones • Available without prescription 90% effective 98% effective with a condom
Disadvantages • Can be used by women who smoke • Does not protect against STI’s • Requires proper insertion • Vaginal irritation • Must be left in for 6-8 hours after intercourse • Approximately $9.00 per box
Male condom 86.2%-97.4% effectiveness • Thin sheath of latex, lamb skin • Acts as a barrier • Collects sperm • Advantages • Not hormonal • Easily Accessible • Helps prevent STI’s • Low cost • Disadvantages • Could break • Skin irritation • Possibly Allergic • Important Notes: • Check expiry date • Oil based lubricants can break down the condom
IUDIntrauterine Device • An IUD is a small plastic or copper device that fits inside the uterus. • It is shaped like a ‘T’ • An IUD prevents pregnancy by slowing the sperm as they move toward the egg and by altering the lining of the uterus so that a fertilized egg is not able to attach to the uterine wall.
Should be checked once a month to ensure the IUD is still in the correct place • Should be replaced 1-5 years by a doctor • Advantages • 94-97% effective to preventing pregnancy • Nothing daily • Disadvantages • Does not protect against STI’s • Can cause Cramping and discomfort • Could cause longer/heavier periods • Spotting between periods • If you get an STI while on the IUD there is an increased risk of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (which may cause infertility)
The Ring • The vaginal contraceptive ring is a flexible ring that slowly releases low doses of hormones (estrogen and progesterone). • 1 ring is inserted for 21 days, and then taken out for 7 days. During these 7 days, you will get your period. • Works similar to the pill. The hormones stop the egg from being released each month (ovulation) and by changing the cervical mucous to make it more difficult for sperm to enter the uterus. • prescription from a doctor is required
92 % effective Disadvantages • Does not prevent STI’s • prescription from a doctor is required • Side Effects • Upset stomach or nausea. • Weight gain/loss. • Headaches. • Sore breasts. • Less interest in sex. • Mood swings. • Increased vaginal discharge. • Break through bleeding. • You should NOT smoke while using the ring
Implanon • This contraceptive implant is a thin flexible plastic rod, 40 mm in length and 2 mm in diameter (about the size of a cardboard matchstick). • Inserted under the skin on the inner side of your upper arm. • Provides about 3 years of pregnancy protection. • Insertion requires a local anesthetic and only takes a few minutes. The implant can also be removed anytime before the 3 years are up. • Continually releases a low dose of estrogen • After the third year, Implanon will still release some hormone, but it will not be enough to prevent pregnancy. • Works by stopping ovulation, changing the cervical mucus making it harder for sperm to swim through, and thinning the uterine lining, so it is less receptive to implantation.
Advantages • After removal, a woman’s ability to become pregnant returns quickly • Nothing daily • Disadvantage • Does not protect against STI’s • Irregular bleeding • mood swings • weight gain • breast tenderness • headache • acne • Low levels of depression • Dizziness • Stomach pain • Painful periods • Nervousness • Back pain • Nausea • Viral infections (colds, sore throats, sinus infections, or flu-like symptoms)
74-94% effective Contraceptive Foam • A chemical foam (spermicide) is placed in the vagina before intercourse. • The Spermicide helps to kill the any sperm that enters into the body. • Advantages • Easily available at a pharmacy or sexual health clinic • Relatively inexpensive • If paired with a condom it can be 98% effective Disadvantages • May cause burning or irritation • May have allergic reaction • May be messy • Does not protect against STI’s
Plan B: Emergency Birth Control PillMorning After Pill • Pill containing the hormone progestin • Must be started 72 hours after unprotected sex • When to use the Plan B pill • A condom broke or slipped • You missed some birth control pills and didn’t use a condom • You were late getting your depo injection • Your diaphragm slipped • You were sexually assaulted If you are already pregnant Plan B will NOT cause an abortion
How to use Plan B • You will receive 2 pills in a package • Eat something and take the first pill as soon as possible • 12 hours later, eat again and take the second pill. • Most Common side effect is nausea. Mild abdominal pain, fatigue, headache and spotting or bleeding can occur. • Plan B will not affect your ability to get pregnant in the future.
Read through the STI articles and answer the following questions.... • What is it? (description) • Signs and symptoms • How do you get it? • How do you prevent it? • Can it be cured?