Distributed Programming
40 likes | 168 Vues
This resource delves into fundamental distributed programming concepts and notations with a focus on inter-process communication. It covers essential topics such as synchronous and asynchronous messages, the select statement, and remote procedure calls. A practical Ada example illustrates atomic transactions through a task buffer, demonstrating how entries for deposit and fetch operations can be implemented. The provided code showcases a producer-consumer model using a circular buffer, detailing how tasks interact through deposits and fetches efficiently, maintaining synchronization and data integrity.

Distributed Programming
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Distributed Programming Concepts and Notations
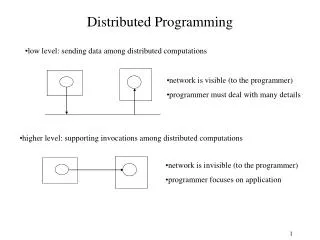
Inter-process Communication • Synchronous Messages • Asynchronous Messages • Select statement • Remote procedure calls • Atomic transactions
Ada example • task buffer; • entry deposit(in value:T); • entry fetch(out value:T); • var • slots:array [0..N-1] of T; • head, tail:0..N-1; • size:0..N; • begin • head, tail, size := 0,0,0; • loop • select • when size < N => accept deposit(in value:T); • slots[tail] := value; • size := size+1; tail:=tail + 1 mod N; • or when size > 0 => accept fetch(out value:T); • value := slots[head]; • size := size-1; head:=head + 1 mod N; • end select; • end loop;
Ada example contd. task produce repeat item := produce(); call buffer.deposit(item); forever; end; task consumer; repeat call buffer.fetch(item); consume(item); forever; end