Client/Server Architecture
170 likes | 663 Vues
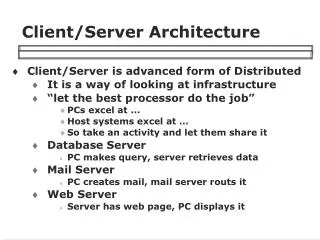
Client/Server Architecture. Advent of Client/Server Technology. In systems centralised around mainframe, a no. of dumb terminals used to be connected to a powerful server, which performed all the processing

Client/Server Architecture
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Advent of Client/Server Technology • In systems centralised around mainframe, a no. of dumb terminals used to be connected to a powerful server, which performed all the processing • It became increasingly difficult to keep up pace with changing scenarios (business rules, technologies etc.) as modifying these systems was a time consuming activity and besides affected all the users
Advent of Client/Server Technology • With the advent of PCs, the processing could be distributed between client and server, which accrued several benefits • A powerful Graphical User Interface (GUI) could be provided to the user instead of Character based interface, which was user-friendly • The processing could be distributed between client and server, thus taking some load off the server
Advent of Client/Server Technology • Improved information access • Increased productivity • Quick reponse to changing market place • Rapid application development
The Tiers • Applications can be logically distributed into several layers, each of which is known as a Tier • Windows DNA refers to these tiers as - • User Services • Business Services • Data Services
Two-Tier Architecture • In a Two-Tier Architecture the applications are mostly divided into a user-services tier and a data-services tier • The application logic resides either in the user interface or on the server, producing two models: • Fat Client (UserInterface + Business Logic on client & database logic on the server) • Fat Server (User Interface logic on client & business+database logic on server)
Client-Server Models • Distributed Presentation • Remote Presentation • Distributed Logic • Remote Data • Distributed Data
Client-Server Models Server D D D D D BL BL BL Network EUD D BL BL BL EUD EUD EUD EUD EUD 1 2 3 4 5 Client
Three-Tier Architecture • In a three tier architecture the business services are assigned a separate tier – called middle tier and is handled by middleware like MTS and IIS