XPOLA — An Extensible Capability-based Authorization Infrastructure for Grids
150 likes | 364 Vues
XPOLA — An Extensible Capability-based Authorization Infrastructure for Grids. Liang Fang, Dennis Gannon Indiana University Frank Siebenlist Argonne National Laboratory . Outline. The Grid security The problems to be solved XPOLA Macroscopic view Microscopic view User ’ s view

XPOLA — An Extensible Capability-based Authorization Infrastructure for Grids
E N D
Presentation Transcript
XPOLA—An Extensible Capability-based Authorization Infrastructure for Grids Liang Fang, Dennis Gannon Indiana University Frank Siebenlist Argonne National Laboratory
Outline • The Grid security • The problems to be solved • XPOLA • Macroscopic view • Microscopic view • User’s view • Challenges and future work • Conclusion PKI R&D 05
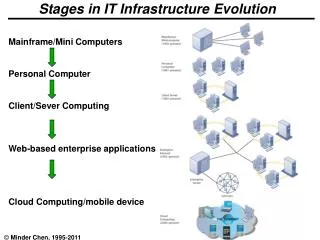
The Grid OGSA 2004 2002 1997 Pre-Web services era (SOAP-based) Web services era Grid service = Web service + OGSA PKI R&D 05
Grid Security Infrastructure (GSI) • GSI adopts public key cryptography as the basis to provide the Grid three main functionalities: • Secure communication: SSL, WS Security • Mutual authentication: PKI • Delegation: proxy certificate • Authorization (& Authentication): • A gatekeeper daemon maps a Grid identity to a local account at run time according to a gridmap file. • The Grid identity is allowed to do all the account’s rights. PKI R&D 05
A Grid User’s Odyssey • Alice wants to access a Grid service. Unfortunately, she has to … Account Application Certificate Application Grid-map Registration ~3days ~1wk ~0.5 day (Learn how to) Manage her X.509 cert Finally, Time to use the Grid service. (Learn how to) Configure Her Service Environment (Learn how to) Get her Grid proxy cert ready ~1day ~0.5 hr ~0.5 day PKI R&D 05
The Authorization Problems in Real Grid Applications • Inscalable in administration and maintenance • Host accounts • X.509 certificates • Coarse-grained authorization • An authorized user can do much more than accessing a service • For example, in Linked Environments for Atmospheric Discovery (LEAD) project • How to provide the authorization to meteorological Grid services running on TeraGrid to THOUSANDS of scientists and grade school students? • Only a few privileged UNIX accounts available. • Grid services could be dynamically generated (by workflow engines as well as individual scientists). • Of course, no security breach is acceptable . PKI R&D 05
1 2 Client Resource Authority 1 2 Authority Client Resource Existing Grid Security Solutions to Fine-grained Authorization • ACL Model • Akenti, Shibboleth, PERMIS • Capability Model • CAS, VOMS, PRIMA • Why we need XPOLA • The above (was) not addressing general Web/Grid services in compliant with Web services security specs. • With central admins, most of them do not address dynamic services well. The Access Control Matrix The ACL Model PKI R&D 05 The Capability Model
XPOLA: The Characteristics • Principle of Least Authority/Privilege (POLA)-compliant: Strictly fine-grained authorization. • Scalable in administration and maintenance: It is never assumed that the service user has an account on the machines. The infrastructure is built on a Peer-to-peer chain-of-trust model. No central administrator involved. • WS-Security Compliant: Conforms to WS-Security for both persistent and transient Web/Grid services. • Extensible: PKI and SAML-based, but allows other alternatives. • Dynamic and Reusable: Grid resources (Web services and Grid services) are made available to users through manually or automatically generated capabilities, which can be used for multiple requests in their valid lifetimes. PKI R&D 05
XPOLA: The Big Picture Service Provider Persistent Storage Request Processing create Registry (EPRservice A, …) Capability Manager (Capman) Community Informative Authority update Capability Request destroy Host Token Agent Processing Stack SVC A capability token Service Requester PKI R&D 05
A capability includes: Policy Document Bindings of the provider’s distinguished name (DN), as well as the users’ DNs. Identifier of the Grid resource. Optional: operations of a Web service instance Life time (notbefore, notafter) The provider’s signature generated with his private key. Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML): Each capability is a set of SAML assertions AuthorizationDecisionStatement However the policy document and protection mechanism can be extensible: XACML, symmetric keys, … XPOLA: Capabilities PKI R&D 05
Web services security A series of emerging XML-based security standards from W3C and OASIS for SOAP-based Web services, to provide authentication, integrity, confidentiality and so on. XSOAP conforms to Web services security. SOAP Binding XPOLA: Web Services Security SOAP Message Header Capability Token Policies (SAML Assertions) Provider’s Signature WS Security Section (User’s Signature, …) Body PKI R&D 05
An arriving SOAP Msg A dispatched SOAP Msg Authentication Processing Node SOAP Sig Verification SOAP Sig Generation N Valid? Fault Generation Y Token Verification Token Insertion Token Sig Valid? Authorization Processing Node Owner/User Match? N Fault Generation Policy Decision? Expired? Other Processing Nodes Application Service XPOLA: Enforcement PKI R&D 05
XPOLA: User’s View in Grid Portals Provider User capability token Capability Manager Portlet Proxy Manager Portlet Weather Service Portlet Weather Service capability token proxy certificate proxy certificate capability token capability token capability token Grid Portal User Context PKI R&D 05
Challenges and Future Work • Revocation • Performance and Scalability • Message level session-based communication • Load balancing • Denial of Service (DoS) Mitigation PKI R&D 05
Conclusion • XPOLA provides fine-grained authorization infrastructure to general Web and Grid services. • More than that • It scales • Extensible • WS-Security compliant • Adaptable for dynamic services • Reusable • User (as well as provider) friendly PKI R&D 05