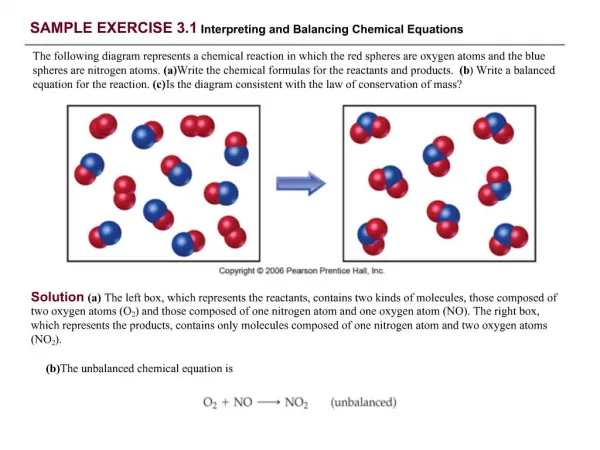
Sample of Stocktaking Exercise Replies
110 likes | 256 Vues
Sample of Stocktaking Exercise Replies. Changes in African Agriculture Resulting from Implementation of CAADP Approaches Josue Dione, AUC/DREA. Background. Purpose : To assess progress country is making and challenges country is facing in implementation of CAADP NAIP

Sample of Stocktaking Exercise Replies
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sample of Stocktaking Exercise Replies Changes in African Agriculture Resulting from Implementation of CAADP Approaches Josue Dione, AUC/DREA
Background • Purpose: To assess progress country is making and challenges country is facing in implementation of CAADP NAIP • Questions based on elements from the 2013-23 Results Framework used to monitor changes in African Agriculture because of CAADP approaches • N = 11 countries so far • Still receiving replies so not all response tabulated
1. Increasing Agriculture Production & Productivity • Progress: • Programs / Policies established • Investments being financed through bilateral projects by different donors • Gaps: • NAIP is not fully implemented • Little current data on progress available • Slow mobilization of allocated resources
2. Improving Functioning of Ag Markets, Increased Market Access and Trade • Progress • Programs / Policies in place • Some legislation passed, esp. for commodity exchanges • Gaps • Smallholder issues: high transaction costs, low participation in contract/structured marketing, average level of production very low • Markets for most commodities not well structured
3. Increasing Private Sector Involvement along Ag Value Chains • Progress • Governments are promoting enabling environment for agriculture and agribusiness development • Legislation is improving – PPP bill passed • Gaps • Private investors not yet part of strategy, little or no civil society participation in planning • Bureaucratic barriers (e.g. customs clearances for duty free imports) • Private sector is not homogeneous in size, characteristics and needs • Donor issues: not all bilateral players are on board
4. Increasing Availability & Access to Food and Productive Safety Nets • Progress • Multi-stakeholder involvement in assessing food security issues and establishing EWS • Important budget expenditures being made on food reserves • New programs and policies are being developed that include performance indicators • Gaps • Nutrition level still poor (but gradually improving) • Confusion around M&E systems & roles – responsibilities of different players
5. Improving Management of Natural Resources for Sustainable Ag Growth • Progress • Programs in fisheries, agro-ecological zoning, sustainable development policies, development of Pastoral Code • Gaps • Limited capacity of local government staff to initiate interventions • Inadequate technical competency of extension workers and farmers
6. Women Smallholder Farmers • Progress • New programs underway to improve women’s access to ag inputs, equipment, information, training and technology • Establishment of National Directorate of Women in Livestock and Ministry of Women and Youth Affairs • New policies that allow property rights to women • Gaps • Integration of gender issues in planning process • Development of gender related indicators • Limited availability of targeted capacity building programs • Still difficult for smallholder farmers to access land titles and credit
7. Implementation of Agreed Investment Plan • Progress: • Coordinated efforts exist among many different stakeholders (Govts-partners; NEPAD-Govts; efforts to align commitments from all donors; etc.) • Gaps • Institutional reform needed to facilitate programs being put in place • Securing funding is formidable task • Developing capacity at ministry level to increase implementation capacity and develop more efficient implementation mechanisms
Conclusions • More examples available in handout • Purpose is not to be comprehensive – want to start dialogue to: • Identify and share experiences • Outline next steps on what might be done to address gaps / challenges