Electronics Value Chain
150 likes | 407 Vues
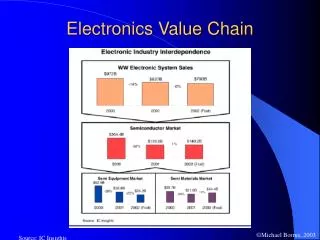
Electronics Value Chain. Source: IC Insights. Chips = Miniature Cities.

Electronics Value Chain
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Electronics Value Chain Source: IC Insights
Chips = Miniature Cities Low-angle scanning electron micrograph of a portion of a partially completed SRAM array containing six-device memory cells. The insulating oxide films have been removed, revealing the lower levels of the interconnection structure of the array. Source: Intel and IBM
Technical Progress I Source: Gordon Moore presentation, SIA 2002
Technical Progress II Source: Gordon Moore presentation, SIA 2002
Worldwide Semiconductor Sales1975-2005 $Billions WW CAGR = 13.3% Source: SIA, WSTS * Forecast
Top 10 Suppliers Selected Years Source: Electronic News, various years
Policy: Military/Space R&D, Procurement; Antitrust, Tax Launch Market: Military, then Computing Demand: High Performance at any Cost Structure: Vertically Fragmented, Start-up Merchants Development Trajectory: Product Innovation Policy: Credit allocation, technology controls, trade and investment protection Launch Market: Consumer Electronics Demand: High Reliability at lowest Cost Structure: Vertically Integrated; Keiretsu Development Trajectory: Manufacturing Innovation Evolution of Chip Competition I1960s-late 1970s U.S. Japan Result: US seizes global market leadership
Evolution of Chip Competition IILate 1970s - late 1980s • Lead Market: Emergence of PCs/desktop systems • Demand: Performance AND Reliability at Lowest Cost • Structure: Merchants vs. Vert. Integr/Keiretsu • Strategic Advantage: Capital spending to add capacity with manufacturing innovation to deliver quality at low cost (i.e., lean production) • Policy: VLSI Project in Japan; US Trade Policy culminating in US-Japan STA Result: Japanese firms become global leaders, dominating memory; US firms retain key position in logic
Sales, Market Shares, Capital Spend1982-1990 Market Shares Capacity Shares Sources: SIA; Leachman and Leachman in Macher, Mowery, Simcoe
Fragmented Open Potential Competitive Dependence Industry Coordination Difficult Assets Accessible Integrated Closed Potential to Marginalize Competitors Strategic Coordination Scale/Price Discrimination Inaccessible Assets Strategic Market Game US Japan Consequences: