The Evolution of Atomic Theory: From Democritus to Quantum Mechanics
180 likes | 317 Vues
This overview outlines the historical development of atomic theory, beginning with Democritus' concept of matter as composed of indivisible atoms in 600 B.C. The description progresses through key contributions from J.J. Thomson, who discovered electrons in 1897, to Rutherford’s identification of the nucleus via the gold foil experiment. It includes important principles established by John Dalton in the early 1800s and concludes with foundational concepts of modern quantum mechanics, electron configurations, and measurement units for mass and elements.

The Evolution of Atomic Theory: From Democritus to Quantum Mechanics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Atomic Theory By Kylee and Caitlin
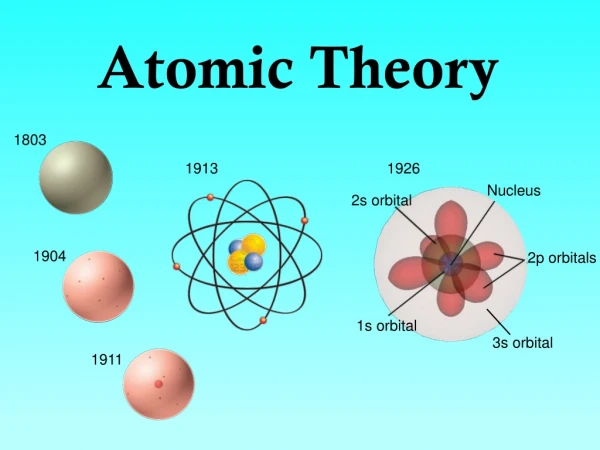
Democrates- 600 B.C. • All matter is made up of atoms
Aerostatale 500 BC. • Matter=Atoms • Learned multiple elements are an atom • Matter made up of 4 elements
Early 1800s- John Dalton • 5 historical principle • 1.All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. • 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.' • 3.Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. • 4.Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. • 5.In chemical reactions atoms are combined separated or rearranged.
1897- J.J. Thompson • Verified the existence of positive particles. • Was the pudding and plum guy • Pudding was positive and plums were spread throughout the pudding • Cathode Ray
1914- Rutherford • Founded Nucleus with radioactive study (Gold foil experiment) • Protons in the nucleus • worked under J.J.
Bohr • Electrons orbit around the nucleus • Planetary model • Protons an neutrons located in the nuecleous
Chadwick • Neutrons in the nucleus :)
Definitions :)Protons- positively charged elementary particle, found in nuclei Neutrons- elementary particle having no chargeElectron- Elementary particle having negative charge
Definitions cont. • Electron configuration- represents the 3 dimensions to space in which a electron could be found. Described as four different quantum numbers • Orbital diagrams S,P,D,F how you write to get to your element • Atomic Mass Unit- Amu, way to measure mass of protons and neutrons
Definitions cont. • Grams- way to measure how much an element weighs • Moles- Unit of measure to measure elements on the periodic table • Molecules- small particles that make up living and nonliving things
Quantum Theory • Short hand way of writing out electron configuration
LEQs • 1) Who discovered different parts of the atom? List all. • 2) How would you write the electron config. for titanium? • 3) Define the different units of measurement.
Sample Problems • Who used the Cathode Ray? • Who came up with the basic idea of an atom? • Draw an orbital diagram of K • Which of the following is a correct set of quantum numbers for an electron in 5 F orbital? • A. N=5, L=3, Ml=+1, • B. N=5, L=2, Ml=+3
Answers • J.J Thomson • Democrates • A.
Helpful Websites • Dictionary.com • www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/periodic_table/atomic_mass.html • Chemistry.about.com/od/electroncicstructuri/a/quantumnumber/htm