Mastering PowerPoint Presentations: Good, Bad, and Ugly Insights for STEM Students
260 likes | 400 Vues
Discover effective techniques for creating impactful PowerPoint presentations in STEM. This guide covers essential principles such as visual layout, presentation skills, and organization. Learn to utilize pre-made templates, maintain readability, and engage your audience through storytelling. Understanding the balance of images and text, the importance of rehearsal, and practical tips for facilitating discussions will enhance your group's performance. Avoid common mistakes and watch your presentations transform into visually compelling experiences.

Mastering PowerPoint Presentations: Good, Bad, and Ugly Insights for STEM Students
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Presenting Effectively With PowerPoint The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
An Effective Group Presentation • A visually interesting, well-organized story on a specific topic • 20 minutes’ time limit • 2 presenters / team • Well-rehearsed IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
PowerPoint: Visual Layout • Start with pre-made templates • Existing spacing • Existing font size & style for best viewing • Existing other pre-set settings: esp. colors • Use readable fonts • Serif vs. Sans Serif • Size (~24 - 60 pts) • Same styles throughout IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
PowerPoint: Visual Layout • Use bulleted lists • Sub-bullets • avoid “sub-sub-bullets”= = too difficult to read • Cognitive theory says our memory is not so good • Limit to 5-7 lines of text • Number One problem in student presentations = too much text IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
PowerPoint: Visual Layout • Vary the slide layouts • Combine text and graphics • Use animation sparingly (if at all) • Leave plenty of “white” space • 1-2 images / slide (max) IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Organization • Footer with basic information • See this slide • Title slide • Image / text to get audience attention • Content slides • Final slide • Image / text to wrap up IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Graphics • Use images that support the content • “Less is more” • Resize from the corners • Web images may pixellate if resized too much • Frame images with line to make them stand out IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Presentation skills: Preparation • Know your material • become The Voice of Confidence! • Practice in front of others • Check timing • Coordinate with partner(s) IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Presentation skills: Voice • Volume • We’ve got to be able to hear you • Pace • Breathe… • Tone • You’re telling a story to friends • Word choice • Proofread your notes and know your content IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Presentation skills: Body Language • Smile • Use gestures carefully • Eye contact • Look around the room, not just at one person (often the Instructor) IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Presentation Skills • Avoid urban slang • Umm, like you guys know, whatever, and so forth, huh? • Dress appropriately • No 4-B’s! IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Presentation skills: Interaction • Be ready to facilitate discussion after presentation • Whole team prepares for questions • Handling questions • The ground rules • During the presentation? • After the presentation? • Who responds? • Don’t know the answer? • Admit find answer bring to next class IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Useful Resources • http://www.cob.sjsu.edu/splane_m/ PresentationTips.htm • http://www.presentation-pointers.com/index.asp • http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/images/ IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
PowerPoint: The Good, the Bad and The Ugly • Good examples • What you see in class • Bad & Ugly examples • Keep going IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
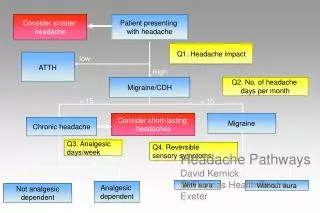
Graphics: The Bad & The Ugly • What’swrongwiththis slide? IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Your Presentation See if you can identify the things to avoid from an actual group presentation… IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Introduction What is Aids? AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome AIDS is caused by a virus called HIV, the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. If you get infected with HIV, your body will try to fight the infection. It will make "antibodies," special molecules to fight HIV. Being HIV-positive, or having HIV disease, is not the same as having AIDS. Many people are HIV-positive but don't get sick for many years. As HIV disease continues, it slowly wears down the immune system. Viruses, parasites, fungi and bacteria that usually don't cause any problems can make you very sick if your immune system is damaged. IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Origins Of aids HIV, the virus that causes AIDS was first noticed in the early 1980s and it has been a puzzle where it actually came from. There is still a lot of debate about this. A recent research article reveals that gorillas living in the wild in Central Africa are infected with an HIV-1 related virus. This result was completely unexpected and has got people thinking afresh about the origins of HIV. Although rarely found in humans, this variant has been the source of cases of AIDS. Some people believe that an ape form of the virus was transferred to humans just before cases of AIDS first started to come to light in the 1980s. During this transfer, the virus may have mutated and become very infectious between human beings, leading to the AIDS epidemic. IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Global Statistics The number of people living with HIV has risen from around 8 million in 1990 to 33 million today, and is still growing. Around 67% of people living with HIV are in sub-Saharan Africa. IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Aids In africa Sub-Saharan Africa is more heavily affected by HIV and AIDS than any other region of the world. An estimated 22 million people were living with HIV at the end of 2007 and approximately 1.9 million additional people were infected with HIV during that year. In just the past year, the AIDS epidemic in Africa has claimed the lives of an estimated 1.5 million people in this region. More than eleven million children have been orphaned by AIDS. Both HIV prevalence rates and the numbers of people dying from AIDS vary greatly between African countries. In Somalia and Senegal the HIV prevalence is under 1% of the adult population, whereas in Namibia, South Africa, Zambia and Zimbabwe around 15-20% of adults are infected with HIV. In three southern African countries, the national adult HIV prevalence rate has risen higher than was thought possible and now exceeds 20%. These countries are Botswana (23.9%), Lesotho (23.2%) and Swaziland (26.1%). West Africa has been less affected by AIDS, but the HIV prevalence rates in some countries are creeping up. HIV prevalence is estimated to exceed 5% in Cameroon (5.1%) and Gabon (5.9%). IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
India is one of the largest and most populated countries in the world, with over one billion inhabitants. Of this number, it's estimated that around 2.4 million Indians are currently living with HIV. HIV emerged later in India than it did in many other countries. Infection rates soared throughout the 1990s, and today the epidemic affects all sectors of Indian society, not just the groups such as sex workers and truck drivers with which it was originally associated. In a country where poverty, illiteracy and poor health are rife, the spread of HIV presents a daunting challenge. In terms of AIDS cases, the most recent estimate comes from August 2006, at which stage the total number of AIDS cases reported to NACO was 124,995. Of this number, 29% were women, and 36% were under the age of 30. These figures are not accurate reflections of the actual situation though, as large numbers of AIDS cases go unreported. IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
AIDS IN CHINA • China’s first AIDS case was reported in Beijing in 1985. In the following five years a small number of further cases were reported among foreigners and Chinese, who were infected overseas or by imported blood products. • During the early stages of the AIDS epidemic the Health Ministry concentrated its prevention efforts on the risk of infection from abroad. In 1986 it announced that it planned to test all foreign students for AIDS who had been in the country for more than a year, and students entering China would require a certificate from their country of origin testifying that they were not infected with HIV. Although a National Programme for AIDS Prevention and Control was set up in 1987, the Public Health Authorities reported that AIDS would not become established as homosexuality and "abnormal" sexuality - thought to be the main causes of the spread of HIV - were a "limited" problem IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
Prevention of Aids • HIV Prevention • Don't have unprotected sex outside marriage or a committed relationship. If you or your partner has ever had unprotected sex -- or if either of you uses injected drugs -- the only way to be sure you don't have HIV is to get tested. Have 2 HIV tests 6 months apart, with no new sex partners or injection drug use between tests. • You can't get HIV if your penis, mouth, vagina, or anus doesn't touch another person's penis, mouth, vagina, or anus. Kissing, erotic massage, and mutual masturbation are safe sex activities. • You can greatly reduce your risk by using a latex or polyurethane condom during sex. Don't use natural-skin condoms -- they prevent pregnancy but don't prevent infections. Learn the right way to use a condom. Put the condom on as soon as a man has an erection, not just when he's ready to ejaculate. Use a lubricant -- but never use an oil-based lubricant with a latex condom. The female condom, called a vaginal pouch, also protects against disease. • Oral sex without a condom or latex dam is not safe, but it's far safer than unprotected intercourse. • Drug Use and HIV Prevention • Using drugs increases your HIV risk. Stop using drugs if you want to prevent HIV/AIDS. If you're not ready to stop taking drugs, you can still reduce your risk of getting HIV. Here's how: • Don't have sex when you're high. It's easy to forget about safe sex when you're on drugs. • If you must use drugs, don't inject them. • If you must inject drugs, don't share the equipment. This includes every piece of it: needles, syringes, cookers, cotton, and rinse water. Some states have needle-exchange programs where you can trade in dirty equipment for new equipment. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gjGoGu4TFZs&feature=related IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
How Do you get aids 1.You don't actually "get" AIDS. You might get infected with HIV, and later you might develop AIDS. You can get infected with HIV from anyone who's infected, even if they don't look sick and even if they haven't tested HIV-positive yet. The blood, vaginal fluid, semen, and breast milk of people infected with HIV has enough of the virus in it to infect other people. 2. Most Common ways of getting the HIV viruses are: having sex with an infected person sharing a needle (shooting drugs) with someone who's infected being born when their mother is infected, or drinking the breast milk of an infected woman Instructor’s note: powerful graphic; text detracts from image that really does not need explanation IDS 1107 - STEM FYE
RESOURCES http://www.avert.org/aafrica.htm http://www.avert.org/aidsindia.htm http://www.indiadaily.org/images/india-aids_26.jpg http://www.csis.org/media/csis/pubs/assessing_aids_initiatives_in_china-gill-web.pdf http://www.sfgate.com/cgi-bin/article.cgi?file=/chronicle/archive/2004/07/04/MNGG87GJJ01.DTL http://www.webmd.com/hiv-aids/understanding-aids-hiv-prevention?src=rss_nafwa IDS 1107 - STEM FYE