McEliece Public Key system
120 likes | 321 Vues
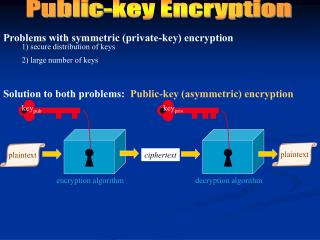
McEliece Public Key system. A.J. Han Vinck. Content. - The system ( 1978, progress report JPL ) Encryption Decryption Some attacks guessing exhaustive search guessing k independent coordinates. The system. Public key: k x n binary matrix G‘ property: G‘ corrects t errors

McEliece Public Key system
E N D
Presentation Transcript
McEliece Public Key system A.J. Han Vinck
Content - The system ( 1978, progress report JPL ) • Encryption • Decryption • Some attacks • guessing • exhaustive search • guessing k independent coordinates Han Vinck February 2003
The system Public key: k x n binary matrix G‘ property: G‘ corrects t errors property: decoder for G‘ has exponential complexity Encrypt: C‘ = mG‘ r property: r is vector of length n of weight t r is used to avoid retrieval of m by direct Gaussian elimination, O(k3) Han Vinck February 2003
Decrypt Let: G‘ = SGP property: - S = k x k nonsingular matrix (scrambler) - P = n x n permutation matrix property: decoder for G has polynomial complexity Decrypt: form C = [mG‘ r] P-1 = mSG r P-1 decode: mS and calculate mSS-1 = m Suggestion: k=512/n=1024 = ½ and t > 50 Han Vinck February 2003
Attacks: guessing S and P Knowledge of S and P gives G Guessing S: O( 2k2) P: O( n! ) Han Vinck February 2003
Attacks: exhaustive search Look for closest of 2k codewords generated by G‘ C‘ = mG‘ m Han Vinck February 2003
Attacks: guess k correct positions - k independent error free positions give m with Gaussian elimination Prob( error free in k positions) ~ ( 1 – t/n)k Example: n = 1024, k = 512, t = 50 ( 1 - 0.05 )512 10-8 every guess takes about (5123) steps This is considered to be insufficient! Han Vinck February 2003
Weak point encryption of the same message: C‘ = mG‘ r C‘‘ = mG‘ r‘ C‘ C‘‘ = r‘ r Positions where r‘ and r are different can be detected thus easier to find k independent positions Han Vinck February 2003
Conclusion Up to now difficult to find a general solution Performance depends on: code parameters decoding complexity Han Vinck February 2003