Information System Audit Essentials
180 likes | 202 Vues
Explore risk factors, objectives, and controls in information system audits to safeguard assets, maintain integrity, and ensure compliance. Learn about asset safeguarding steps, evidence collection methods, and the importance of audit trails.

Information System Audit Essentials
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 4: Information System Audit Requirements
Risk Factors • The risk factors inherent in business operations include the following: * Access Risk * Business Disruption Risk * Credit Risk * Customer Service Risk * Data Integrity Risk * Misstatement Risk * Physical Harm Risk * Fraud Risk * Legal And Regulatory Risk
Risk analysis and Exposure • A Risk is the likelihood that the organisation would face a vulnerability being exploited or a threat becoming harmful • A Threat is an action, event or condition where there is a compromise in the system, its quality and ability to inflict harm to the organisation. • Attack is a set of actions designed to compromise confidentiality, integrity, availability or any other desired feature of an information system.
Risk and Exposures • Vulnerability is the weakness in the system safeguards that exposes the system to threats. • An Exposure is the extent of loss the organisation has to face when a risk materialises. • Likelihood of the threat occurring is the estimation of the probability that the threat will succeed in achieving an undesirable event.
AVAILABILITY CONFIDENTIALITY INTEGRITY Information System Control Objectives
Information System Control Objectives • Safeguarding information systems assets • Compliance with corporate policies, regulatory and legal requirements • Assuring system reliability • Maintaining data integrity • Assuring system security • Assuring system availability
Information System Control Objectives • Maintaining system controllability • Assuring system maintainability • Assuring system usability ensuring system effectiveness • Maintaining system economy and efficiency • Maintaining system quality
Information System Audit Objectives • Adequacy and effectiveness of internal controls. • Efficient and effective allocation of resources • Provide assurance that computer-related assets are safeguarded. • Ensure that information is accurate, available on request, and reliable. • Provide reasonable assurance that all errors, omissions, and irregularities are prevented, detected, corrected, and reported. • Review the systems to ensure compliance to policies, procedures and standards.
Information System Audit Objectives • Ensure legal requirements are complied with, audit trails are incorporated, documentation is completed and systems data integrity and security is maintained. • To identify and recognize the potential of computer related fraud, embezzlement, misappropriations and thefts. • Ensure that the management takes corrective and preventive actions when required
Information Systems Abuse • Destruction of assets • Theft of assets • Modification of assets • Privacy violations • Disruption of operations • Unauthorised use of assets
Steps to Asset Safeguarding • Compiling functional IT asset list - Mission-critical functions • Detailing the IT systems identified • Asset protection • Assigning of probabilities
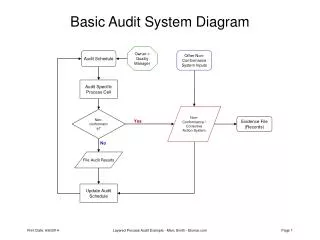
Reviewing the organizational structure, documentation, standards, and practices. Interviewing appropriate personnel Observing processing and operations. Using audit documentation techniques Applying analytical review procedures and sampling techniques. Using software tools to analyse logs and audit trails Evidence Collection during Audit
Physical Examination Confirmation Documentation Observation Inquiry Processing accuracy Screen shots Log Files Testing Software Results Analytical Procedures Audit Trails Evidence Collection during Audit
Audit Trails • Audit trails are records of an activity that can be used to reconstruct the performance of the activity. • Ensure audit trail when: • Access is granted to a sensitive information asset. • Network services are accessed. • Override system controls are used • Unsuccessful attempts are made to access sensitive information or use network services.
Audit Trails • To include in the audit trail as much of the following as is practical: • User identification • Functions, resources and information used or changed • Date and time stamp (including time zone) ; • Work-station address and network connectivity path • Specific transaction or program executed.
Audit Trails • To provide an additional real time alarm for on-line capabilities: • Access attempts that violate the access control rules • Attempts to access functions or information not authorized • Concurrent log-on attempts • Security profile changes
System Logs • Control Total Verification • Transaction logs • Operator logs • System starting and finishing time • System errors and corrective action taken • Confirmation of the correct handling of data files and computer output • Name of the person making the log entry. • Operator’s logs should be compared against operating procedures. • Fault logging