Security Attacks, Mechanisms, and Services
1.26k likes | 3.29k Vues
Security Attacks, Mechanisms, and Services. Attacks, Services and Mechanisms. Security Attack: Any action that compromises the security of information. Security Mechanism: A mechanism that is designed to detect, prevent, or recover from a security attack.

Security Attacks, Mechanisms, and Services
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Attacks, Services and Mechanisms • Security Attack: Any action that compromises the security of information. • Security Mechanism: A mechanism that is designed to detect, prevent, or recover from a security attack. • Security Service: A service that enhances the security of data processing systems and information transfers. A security service makes use of one or more security mechanisms.
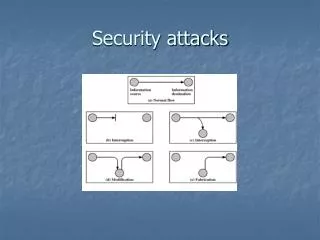
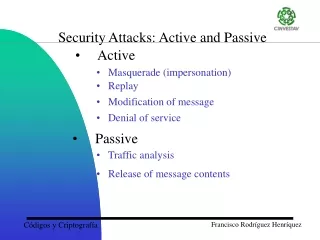
Passive Attacks • These are in the nature of eavesdropping on, or monitoring of, transmission • Attempts to learn or make use of information from system • Does not affect system resources • Difficult to detect because they do not involve any alteration of data • Traffic normally sent and received in a normal fashion • Attempt is made to prevent the success of these attacks, usually by means of encryption • Thus emphasis is on prevention rather than detection
Passive Attacks(cont….) Release of message contents is easily understood • Telephonic conversation, e-mail message, or a transferred file may contain sensitive information • Emphasis is to prevent opponent from learning
Passive Attacks(cont….) Traffic Analysis • Observe patterns of messages • Could determine identity and location of communicating hosts • Could observe the frequency and length of messages being exchanged
Active Attacks • Involves modification of data, or false creation of data • Attempt to alter system resources or affect their operations • Difficult to prevent active attacks • Emphasis is to detect active attacks and recover from the damage
Active Attacks(cont….) Masquarade • One entity pretendes to be a different entity • E.g. Authentication sequences can be captured Replay • Involves passive capture of data unit and its subsequent retransmission to produce unauthorized effect
Active Attacks(cont….) Modification of Message • Means some portion of a legitimate message is altered, or messages are reordered or delayed, to produce unauthorized affect • E.g. ” Allow John Smith to read confidential file accounts” is modified to ” Allow Fred Brown to read confidential file accounts”
Active Attacks(cont….) Denial of Service • Prevents normal use of communication facilities • Disabling or overloading of entire network
Conventional Encryption Principles • An encryption scheme has five ingredients: • Plaintext • Encryption algorithm • Secret Key • Ciphertext • Decryption algorithm • Security depends on the secrecy of the key, not the secrecy of the algorithm
Cryptography • Classified along three independent dimensions: • The type of operations used for transforming plaintext to ciphertext • The number of keys used • symmetric (single key) • asymmetric (two-keys, or public-key encryption) • The way in which the plaintext is processed
Cryptography • can be characterized by: • type of encryption operations used • substitution / transposition / product • number of keys used • single-key or private / two-key or public • way in which plaintext is processed • block / stream