Lim1 expression in E8
130 likes | 430 Vues
14.20 Signals from the paraxial mesoderm induce pronephros formation in the intermediate mesoderm of the chick embryo (Part 1). 14.20 Signals from the paraxial mesoderm induce pronephros formation in the intermediate mesoderm of the chick embryo (Part 2). Lim1 expression in E8.

Lim1 expression in E8
E N D
Presentation Transcript
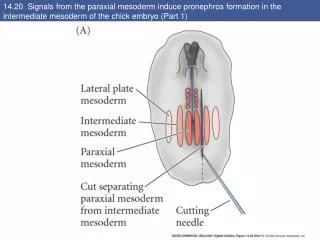
14.20 Signals from the paraxial mesoderm induce pronephros formation in the intermediate mesoderm of the chick embryo (Part 1)
14.20 Signals from the paraxial mesoderm induce pronephros formation in the intermediate mesoderm of the chick embryo (Part 2) Lim1 expression in E8
14.21 General scheme of development in the vertebrate kidney (Part 1)
14.22 Reciprocal induction in the development of the mammalian kidney
The mechanisms of reciprocal induction • The induction of metanephros is a dialogue between the ureteric buds and the metanephrogenic mesenchyme and its devided into 8 major steps. • Only the metanephrogenic mesenchyme has the competence to respond to the ureteric bud and form kidney tubules. • The positional specification of the metanephrogenic mesenchyme is negatively regulated by two trancrisption factors: Foxc1 and Foxc2. • The permanent kidney-forming metanephrogenic mesenchyme is specified by the genes of the Hox11 paralogue group. • The competence to respond to ureteric bud inducers is regulated by a tumor suppressor gene, WT1.
14.24 Ureteric bud growth is dependent on GDNF and its receptors (Part 1) Pax2 and Hox11 GDNF (glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor)
The 3rd signal in kidney development is sent from the ureteric bud to the metanephrogenic mesenchyme. Fgf2 and BMP7: inhibit apoptosis and maintain the synthesis of WT1. The ureteric bud converts metanephrogenic mesenchyme into epithelium. The transition from mesenchymal to epithelial is mediated by several molecules, including Pax2, Wnt6 and Wnt9. Wnt4 is very important for the formation of the nephron.
Once induced, the mesenchyme begins to secrete Wnt4. • Wnt4 acts in a autocrine fashion to complete the transition from mesenchymal mass to epithelium. • One molecule that may be involved in the transition from aggregated mesenchyme to nephrons is Lim1 which are found around the ureteric bud.
14.26 Lim1 expression (dark stain) in a 19-day embryonic mouse kidney