ROCK Signaling Pathway
10 likes | 30 Vues
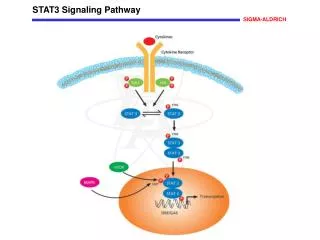
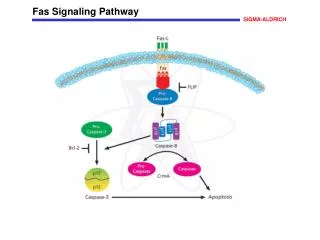
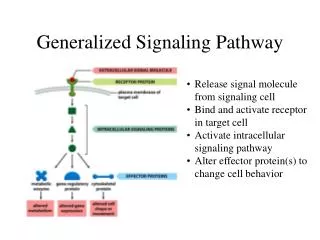
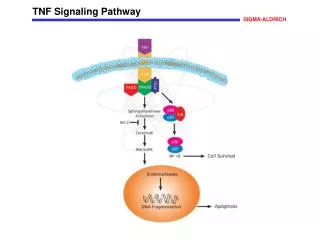
The Rho subfamily belongs to a member of the small molecule G protein in the Ras superfamily and has GTPase activity. It converts between an activated state (bound to GTP) and an inactive state (bound to GDP), acting as a molecular switch, and is a Rho protein that exerts various biological effects by binding to its downstream target effector molecule.

ROCK Signaling Pathway
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ROCK Signaling Pathway The Rho subfamily belongs to a member of the small molecule G protein in the Ras superfamily and has GTPase activity. It converts between an activated state (bound to GTP) and an inactive state (bound to GDP), acting as a molecular switch, and is a Rho protein that exerts various biological effects by binding to its downstream target effector molecule. Among them, Rho kinase (ROCK) is one of the most important effector molecules downstream of Rho. ROCK is a serine/threonine protein Kinase with a relative molecular mass of approximately 160000. There are two homologous isomers in the cell: ROCK1 (ROCK-I, ROKβ or p160 ROCK) and ROCK2 (ROCK-II, ROK α or Rho kinase). Rho/ROCK signaling pathway regulates cell morphology, polarity, and cytoskeletal remodeling by regulating actin and cell migration. Studies on the function of ROCK proteins have focused on the cardiovascular system and the central nervous system. Studies have found that abnormal expression of ROCK protein plays an important role in the development of tumors. ROCK family The ROCK1 and ROCK2 genes contain 33 exons, each located in the 18q11 and 2p24 chromosome regions. In addition to the full-length transcript, ROCK2 also has a splicing mutant (mROCK2). mROCK2 has an additional exon 27, and the 5th exon deleted ROCK1 pseudogene, called the small ROCK, appears to be a product of partial gene duplication and is expressed only in chromosome 18p11 of vascular smooth. The ROCK molecular structure consists of three parts, and the first part is the N-terminal kinase region, consisting of approximately 300 amino acid residues. The composition consists of a serine/threonine protein kinase-associated conserved sequence that catalyzes the phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of a series of downstream substrates; the second is a coiled-coil region located in the middle that interacts with other α-helix proteins. The Rho-binding domain (RBD) consisting of approximately 80 amino acid residues is included, which can accept the activation signal of Rho transduction, such an activating the phosphotransferase activity of ROCK; The third part is located at C-terminal.