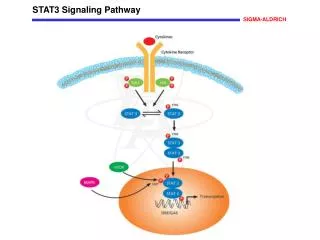
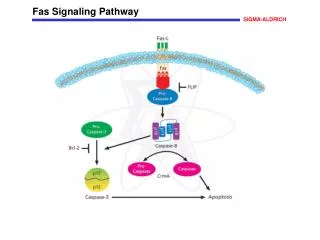
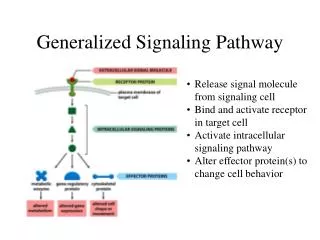
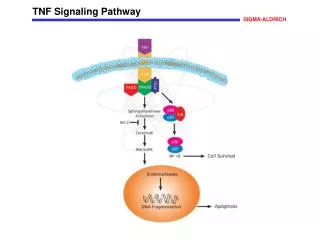
Sirtuin Signaling Pathway
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sirtuin Signaling Pathway Post-translational modifications play an important role in cells, such as DNA recognition, protein-protein interactions, catalytic activity, and protein stability. Protein acetylation/deacetylation is a histone covalent modification that is mainly catalyzed by histone acetylase and histone deacetylase, respectively. There are four types of HDAC, and sirtuin belongs to the third class of HDAC, which is homologous to the yeast transcriptional repressor Sir2. The Sirtuin protein family plays an important role in different cellular processes such as apoptosis, mitochondrial biosynthesis, lipid metabolism, fatty acid oxidation, cellular stress response, insulin secretion, and aging. Sirtuin family The yeast silencing regulator 2 (Sir2) protein and sirtuin in other prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms are a class of proteins that belong to deacetylases and/or ADP ribose that are highly conserved depending on NAD+. As early as 1979, it was discovered that the sir2 gene plays a very important role in maintaining the mating type of yeast, the length of telomeres, and the generation of rDNA-encoded DNA repeats. The reason why researchers are paying more and more attention to the sirtuin protein family is that it has been found that Sir2 plays an important role in life regulation. The sir2 gene can extend the lifespan of the yeast by inhibiting genomic instability. Knocking out the sir2 gene can significantly shorten the lifespan of the yeast, while an additional sir2 gene copy can extend the yeast life by about 40%. It was subsequently found that Sir2.1, a homolog of Sir2 overexpressing in the nematode, prolonged the lifespan of nematodes by 50%, and similar phenomena were found in fruit flies. The Sirtuin protein family also plays an important role in the life extension process caused by caloric restriction, but studies in the online insect and fruit fly in 2011 questioned the relationship between Sir2 and lifespan. Find more at: https://www.creative-diagnostics.com/sirtuin-signaling-pathway.htm