Understanding Monopolistic Competition: Short-Run and Long-Run Outcomes
70 likes | 191 Vues
This text analyzes monopolistic competition by exploring the short-run and long-run outcomes depicted in different figures. In the short-run, firms may earn economic profits or losses depending on their positioning relative to marginal cost and marginal revenue. As new firms enter when profits are made, the market adjusts. Conversely, losses prompt existing firms to exit the market. The long-run equilibrium is characterized by normal profits, leading to market stability with no incentive for entry or exit of firms. Interpretations and implications are discussed for various scenarios.

Understanding Monopolistic Competition: Short-Run and Long-Run Outcomes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
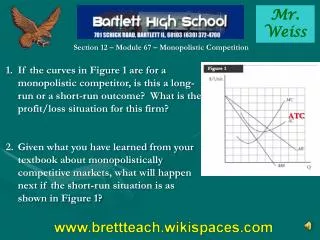
Mr. Weiss Section 12 – Module 67 – Monopolistic Competition • If the curves in Figure 1 are for a monopolistic competitor, is this a long-run or a short-run outcome? What is the profit/loss situation for this firm? • Given what you have learned from your textbook about monopolistically competitive markets, what will happen next if the short-run situation is as shown in Figure 1? ATC
Mr. Weiss Section 12 – Module 67 – Monopolistic Competition • If the curves in Figure 1 are for a monopolistic competitor, is this a long-run or a short-run outcome? What is the profit/loss situation for this firm? Figure 1 necessarily represents a short-run situation for a monopolistic competitor. By operating where MC = MR, the firm will earn economic profits. • Given what you have learned from your textbook about monopolistically competitive markets, what will happen next if the short-run situation is as shown in Figure 1? New firms will enter the market. ATC
Mr. Weiss Section 12 – Module 67 – Monopolistic Competition 3. Suppose that the situation changes to that described in Figure 2. Interpret the new profit/loss situation for this monopolistic competitor. 4. Given what you have learned from your textbook about monopolistically competitive markets, what will happen next if the short-run situation is as shown in Figure 2? ATC
Mr. Weiss Section 12 – Module 67 – Monopolistic Competition 3. Suppose that the situation changes to that described in Figure 2. Interpret the new profit/loss situation for this monopolistic competitor. Even when operating where MR = MC, this firm will experience economic losses. 4. Given what you have learned from your textbook about monopolistically competitive markets, what will happen next if the short-run situation is as shown in Figure 2? Existing firms will exit the market. ATC
Mr. Weiss Section 12 – Module 67 – Monopolistic Competition 5. Suppose that the situation changes to that described in Figure 3. Interpret the new profit/loss situation for this monopolistic competitor. Is this necessarily a short-run situation? 6. What will happen in a monopolistically competitive market in which individual firms are in the situation illustrated in Figure 3? ATC
Mr. Weiss Section 12 – Module 67 – Monopolistic Competition 5. Suppose that the situation changes to that described in Figure 3. Interpret the new profit/loss situation for this monopolistic competitor. Is this necessarily a short-run situation? Figure 3 shows the theorized long-run situation for a monopolistic competitor. By operating where MC – MR, the firm will earn normal profits (that is, zero economic profits). 6. What will happen in a monopolistically competitive market in which individual firms are in the situation illustrated in Figure 3? Since normal profits exist, no new firms are encouraged to enter, and no existing firms have an incentive to leave the market. This situation can persist if all else remains unchanged. ATC
Mr. Weiss Section 12 – Module 67 – Monopolistic Competition