Understanding Coma Causes and Nervous System Emergencies in Paramedic Training
960 likes | 1.08k Vues
This comprehensive guide explores the various causes of coma and related emergencies encountered in the nervous system. Key topics include structural and metabolic issues, effects of drugs, cardiac problems like shock and arrhythmias, respiratory challenges, and infectious processes such as meningitis. Additionally, we discuss disorders including ALS, muscular dystrophy, MS, and Parkinson's. Essential assessment techniques and management strategies, including airway support and pharmacological interventions, are covered, providing a thorough understanding for paramedic students at Chemeketa Community College.

Understanding Coma Causes and Nervous System Emergencies in Paramedic Training
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Nervous System Emergencies Chemeketa Community College Paramedic Program
Causes of Coma (We’ll be talking about these…) • Structural • Metabolic • Drugs • Cardiac (Shock, Arrhythmias, Hypertension, Stroke • Respiratory (Toxic Inhalations, COPD) • Infectious Process (Meningitis)
And these….. • Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) • Muscular Dystrophy • Bell’s Palsy • Multiple Sclerosis • Parkinson’s • Peripheral neuropathy • Central pain syndrome
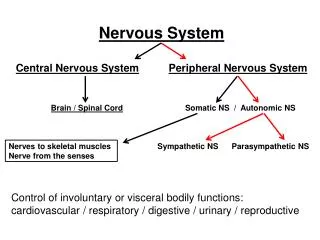
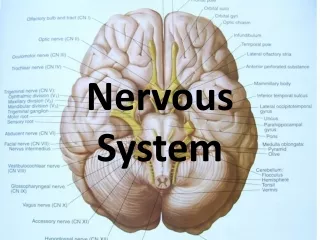
The nervous system • CNS – 43 pairs of nerves • Brain • 12 pairs of cranial nerves • Spinal cord • 31 pairs of spinal nerves • PNS
Neurons • Dendrites, soma, axon, synapse • Neurotransmitters • Acetylcholine, norepi, epi, dopamine • Skull - brain • Spine - spinal cord • Meninges • Dura mater, arachnoid membrane, pia mater • Cerebrospinal fluid
Brain • Cerebrum • Frontal lobe • Temporal lobe • Parietal lobe • Occipital lobe • Cerebellum
Brainstem • Brain stem • Medulla • Pons • Midbrain • Reticular formation • Diencephalon • Hypothalamus • Thalamus • Limbic system
Blood supply to brain • Vertebral arteries • Through foramen magnum • Cerebellum • Basilar artery – pons and cerebellum, cerebrum • Internal carotid arteries • Carotid canals • Anterior cerebral arteries • Frontal lobes, lateral cerebral cortex, posterior cerebral artery • Circle of Willis
Ventricles • Lateral ventricle • Third ventricle • Fourth ventricle
Spinal Cord • 17-18 inches long!! To first lumbar vertebra • Reflexes • Afferent - sensory • Efferent - motor • Interneurons - connecting
Peripheral Nervous System • Cranial nerves • Somatic sensory • Somatic motor • Visceral sensory • Visceral motor • Brachial plexus
I Olfactory smell II Optic vision III Oculomotor Constriction, movement IV Trochlear Downward gaze V Trigeminal Facial sensation, chewing VI Abducens Lateral eye movement VII Facial Taste, frown, smile VIII Acoustic Hearing, balance IX Glossopharyngeal Throat, taste, gag, swallowing X Vagus Larnx, voice, decreased HR XI Spinal Accessory Shoulder shrug XII Hypoglossal Tongue movement Cranial nerves“Some saymarry money, but my brothersays bad boysmarry money."
On Olfactory Old Optic Olympus Oculomotor Towering Trochlear Top, Trigeminal A Abducens Finn Facial And Acoustic German Glossopharyngeal Viewed Vagus Some Spinal Accessory Hops Hypoglossal Learn the cranial nerves OR……
Autonomic Nervous System • Sympathetic • Fight or Flight • Parasympathetic • Feed or Breed
Initial Assessment Be organized and systematic • Mentation • Ensure patent airway • Spinal precautions prn • Monitor for respiratory arrest, vomiting • Oxygenate • If ventilating with BVM, use NORMAL rate • PCO2 • SaO2
Assessment – HistoryBe organized and systematic! • General health • Previous medical conditions • Medications • History with complaint • Bystanders / Family • Length of Coma, Sudden or Gradual Onset, Recent Head Trauma, Past medical hx, alcohol/drug use or abuse, complaints before coma
What led up to 9-1-1? • Time of onset • Seizure activity • Environment • Cold, hot, drug paraphernalia • Medications / Medic Alerts
Assessment - Physical • General appearance • Mentation • Mood • Clarity of thought • Perceptions • Judgment • Memory & attention
Assessment - Physical(cont.) • Speech • Aphasia • Apraxia • Skin • Posture, balance and gait • Abnormal involuntary movements
Assessment - Physical • Vital signs • Hypertension • Hypotension • Heart rate (fast, slow) • Ventilation (rate, quality) • Temperature, fever • Cushing’s Triad
Assessment - Physical(cont.) • Head / neck • Facial expression • Eyes • Acuity, fields, position & alignment, iris, pupils, extraocular muscles
Assessment – Physical (cont.) • Ears • Acuity • Nose • Mouth • Odors • Thorax and lungs • Auscultate
Assessment - Physical(cont.) • Cardiovascular • Heart rate • Rhythm • Bruits • Jugular vein pressure • Auscultation • ECG monitoring
Assessment - Physical(cont.) • Abdomen • Nervous • Cranial nerves • Motor system • Muscle tone, muscle strength, flexion, extension, grip, coordination • Assessment tools • Pulse Oximetry, End tidal CO2, Blood Glucose
Assessment • Ongoing assessment
Management • Airway and ventilatory support • Oxygen • Positioning • Assisted ventilation • Suction • Intubation • Circulatory support • Venous access
Management(cont.) • Non-pharmacological interventions • Positioning • Spinal precautions
Pharmacological interventions • Anti-anxiety agent • Anti-convulsant • Anti-inflammatories • Diuretic • Sedative-hypnotic • Skeletal muscle relaxant • Hyperglycemic • Anti-Emetic
Management (cont.) • Psychological support • Transport considerations • Mode • Facility
Head to Toe • Pupils • Respiratory Status • Spinal Evaluation
Pupils • Cranial nerve III (occulomotor) • Brain herniation = same side dilation • Both dilated = anoxia, brain stem injury • Anisocoria = unequal pupil – normal?
Cardinal Positions of Gaze • Patient should be able to follow your finger • Conjugate gaze - structural lesion • Irritable focus - away • Destructive focus – toward • Dysconjugate gaze – brainstem dysfunction
Respiratory Status • Cheyne-Stokes • Brain Injury • Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation • Cerebral Edema
Respiratory Status (cont.) • Ataxic • CNS Damage = poor thoracic control • Apneustic • Damage to upper Pons
Respiratory Status (cont.) • Diaphragmatic • C-spine • Kussmaul • DKA
Spinal Evaluation • Tingling (pins & needles) • Loss of Sensation or Function • Pain, Tenderness • Priapism • Deformity, tight neck muscles
Spinal Evaluation (cont.) • Motion, Sensation, Position/each extremity • “Gas pedal”, grips • If unconscious, pain response • Incontinence, rectal for S-1
Neurological Exam • Decorticate Posturing • Above Brainstem • Decerebrate Posturing • Brainstem • Flaccid • Babinski’s sign
Neurological Exam • Glascow Coma Scale • Motor, 1 - 6 • Verbal, 1 - 5 • Eye, 1 - 4