Digital Music and Audio
350 likes | 518 Vues
Digital Music and Audio. Sound. Sound is a disturbance of mechanical energy that propagates through matter (like air) as a longitudinal wave and impacts the ear drum. Sound Waves. loud. soft. A sound wave is measured in amplitude (loudness in decibels dB) and frequency (pitch in Hz).

Digital Music and Audio
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sound • Sound is a disturbance of mechanical energy that propagates through matter (like air) as a longitudinal wave and impacts the ear drum.
Sound Waves loud soft • A sound wave is measured in amplitude (loudness in decibels dB) and frequency (pitch in Hz). amplitude low high time • Humans can generally hear sounds with frequencies between 20 Hz and 20 kHz (the audio range) • Most human speech communication takes place between 200 and 8,000 Hz • Prolonged exposure to a sound pressure level exceeding 85 dB can permanently damage the ear • Sound levels in excess of 130 dB are more than the human ear can safely withstand and can result in serious pain and permanent damage. oscilloscope demo
Sound Wave seconds
Zoomed Sound Wave milliseconds
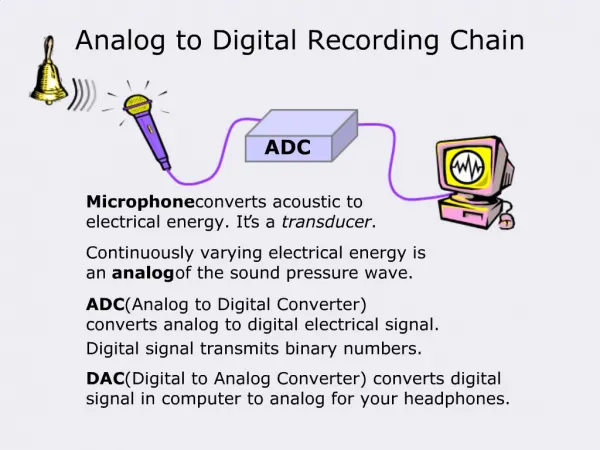
Digitizing Sound • The sound wave is measured or “sampled” at regular time intervals to transform it into a list of numbers. .28 .27 .08 .08 0 -.1 -.45 -.5 millseconds
Sampling Rates • The amount of times per second that a sound wave is measured (sampled), measured in Hz. • 8,000 Hz - telephone • 22,050 Hz - FM quality • 44,100 Hz - CD quality • 192,000 Hz –HD-DVD
Bit Rate • The combination of the sampling rate, amount of bits used with each sample, and mono vs. stereo determines the total number of bits processed per second, or the bit rate. The higher the bit rate the higher the quality of sound. • 4 kbit/s — minimum necessary for recognizable speech • 8 kbit/s — telephone quality • 32 kbit/s —AM radio quality • 96 kbit/s — FM radio quality • 128 - 160 kbit/s - Decent quality • 192 kbit/s — Good quality • 224 - 320 kbit/s — High quality, nearly lossless quality • 500 kbit/s–1 Mbit/s — lossless audio • 1411 kbit/s — PCM sound format of Compact Disc Digital Audio
Calculating CD Quality Bit Rate • 16 bits are used for each sample value • x 44,100 samples per second (CD) • x 2 for stereo • = 1,411,200 bits per second a three minute CD song uses 1,411,200 x 180 (seconds) = 254,016,000 bits/8 = 31,752,000 bytes or about 31 MB. The main uncompressed audio format is PCM. It is used on CDs and stored as a .wav on Windows or as .aiff on Mac OS
Digital audio compression: MP3 • MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3, more commonly referred to as MP3, is a popular digital audio encoding and lossy* compression format and algorithm, designed to greatly reduce the amount of data required to represent audio, yet still sound like a faithful reproduction of the original uncompressed audio to most listeners. • MP3 uses psychoacoustic models to discard components less audible to human hearing, and recording the remaining information in an efficient manner - typically 1/10th the size of the original uncompressed audio file. • LAME produces the highest-quality MP3 files for bitrates greater or equal to 128 kbit/s. *Lossless compression allows the original sound recording to be rebuilt from the compressed file, lossy loses some of the original sound characteristics. Lossy compressed files can never be returned to the original recording quality.
Newer Compressed Audio Formats: AAC & MWA • Apple’s Advanced Audio Coding (AAC, or .m4a) format achieves better quality sound than MP3 for the same compression level or smaller file sizes for the same quality audio. • Microsoft’s Windows Media Audio (WMA or .wma) format reduces file size but does not necessarily improve sound quality. • WMA 10 Pro (Media Player 11) is much better than plain WMA
Review • How is music digitized? • What is sampling rate? • As the sampling rate increases what happens to the sound quality? • What is the sampling rate for CD quality sound? • What is bit rate? • How is bit rate calculated for CD quality sound?
Review • How do MP3 files compare in quality and size to CD audio? • What is Psychoacoustic and how does it relate to MP3? • What are lossless and lossy in regards to audio compression? • What is Microsoft’s preferred audio file format? • What is Apple’s preferred audio file format?
Digital Rights Management (DRM) • DRM provides a way to control if and how many times a digital music file can be copied. • Fairplay: Apple’s DRM technology used in m4p files. • Janus: Microsoft’s DRM technology used in wma files (wma-drm 9.0). • Zune wma-drm 9.1: Microsofts new DRM for Zune not compatible with Janus. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_rights_management
Wma drm 9.0 Online Stores AOL Music Now Yahoo! Music Unlimited Musicmatch Napster Rhapsody To Go Ruckus Sony Music Store URGE Virgin Digital Tesco Downloads M4P Stores iTunes Online Music Distribution • Wma drm 9.1Stores • Zune • No DRM Stores • www.eMusic.com The public’s reaction to DRM…
Audio File Formats & Players http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Audio_file_format
Ripping CD’s & Encoding • Ripping: Transferring Music from CD to hard drive • Encoding: Changing the format of a music file • Demo
Restrictions: Fairplay & iTunes • FairPlay will allow a protected track to be used in the following ways: • The protected track may be copied to any number of iPod portable music players. • The protected track may be played on up to five authorized computers simultaneously. • The protected track may be copied to a standard Audio CD any number of times. • The resulting CD has no DRM and may be ripped, encoded and played back like any other CD. • A particular playlist within iTunes containing a protected track can be copied to a CD only up to seven times before the playlist must be changed. Demo iTunes
Restrictions: Janus & Napster • Monthly Subscription: • $10 per month to download and stream an unlimited amount of music while subscribed to the service. • $5 per month to use the music on “PlaysForSure” portable device. • $.99 song purchases • Unlimited burns of individual tracks. • Unlimited transfers to Napster compatible portable devices. • Copy your music to three computers. Demo Napster
Restrictions: WMA DRM 9.1, Zune • Zune Marketplace Subscription$14.99/month • Access millions of songs from 3 PC • Transfer to Zune player • No burning to disk • Purchase songs with Microsoft Points, 400 for $5 = 79 points per song = $0.99 • Wirelessly share music with other Zunes. Shared songs last three days or three plays. Demo: Zune
Review • What is the purpose of DRM? • What are the three popular forms of DRM in use today? • Which DRM is supported by the most online music services? • What portable player would you buy if you wanted to use Napster? • How about iTunes or Zune? • Would you consider the online music industry to be well organized?
Online Music • Pay Per Track • www.itunes.com • Monthly Subscription • www.napster.com • Internet Radio • www.live365.com • www.wmnf.org • Free Services • www.pandora.com
Portable MP3 Players • www.cnet.com > MP3 • Portable players selection based on • compatibility • capacity (flash or microdrive) • ease of use • Selecting headphones (www.cnet.com)
Podcasts RSS (Really Simple Syndication) is a family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated digital content, such as blogs, news feeds or podcasts. • www.podcast.net • http://www.ipodder.org • iTunes • Podcast Software • http://juicereceiver.sourceforge.net/ • Making Podcasts • GarageBand (demo) • http://www.podcastingnews.com/topics/Podcasting_Software.html
Home/Auto MP3 Players • www.cnet.com > Home Audio > Network Audio Player • iPod Complimentary Speaker Systems • iPod Compatible Auto Sound Systems • CD/MP3 Players
Cell Phone Music Service • http://getitnow.vzwshop.com • www.cingular.com/learn/music-video/music-center.jsp
Satellite Radio • Sirius vs. XM: Choice based on • Price ($12.95/month) • Quality of Service • Quality of Receivers • Programming
Digital Radio • www.hdradio.com