Understanding U.S. Relations Leading to WWII: The Shift from Isolationism to Involvement
200 likes | 310 Vues
This content explores the U.S. diplomatic stance from the 1930s leading up to World War II, highlighting the policy of appeasement adopted by European nations towards Axis powers—Germany, Italy, and Japan. It discusses key legislation such as the Neutrality Act, Roosevelt's initiatives, and the significant events that led to U.S. military engagement, including the attack on Pearl Harbor. The material encourages group research into notable battles of World War II, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the era's complexities.

Understanding U.S. Relations Leading to WWII: The Shift from Isolationism to Involvement
E N D
Presentation Transcript
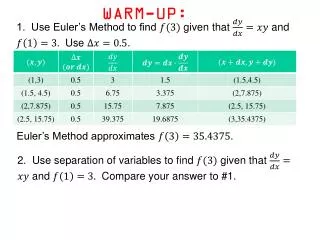
Have your h/w out! Warm up 2. Which term best describes the diplomacy followed by some European nations in their relations with Germany, Italy, and Japan between 1931-1939? Appeasement Non-aggression Isolationism Containment • 1. Which evidence showed that the prosperity of the 1920’s was an illusion? • Prices on consumer goods decreased • Overseas investments declined • Income gap between workers and managers decreased • Many people increased their debt
America Moves Toward War
1939 Neutrality Act • Revised when Germany invaded Poland • Roosevelt convinces Congress to pass “cash and carry” provision (pay in cash, provide own transportation) • Attempt to aid Great Britain and France “A decidedly unneutral act” –Churchill
1 • Axis Powers • Germany, • Italy • Japan • Goal: keep the U.S. out of war • US would face a two-ocean war (Atlantic and Pacific) • President Roosevelt • Increases spending for U.S. Defense • Military draft: 16 million registered– • One million drafted
FDR breaks two term traditionelected 3rd & 4thterms “Great arsenal of democracy.” -Roosevelt
Lend-Lease Act (1941)U.S. would lend or lease arms and supplies to countries vital to the U.S.U.S. spent almost $50 billion under the act
“Lend-Lease” Act (1941) Great Britain.........................$31 billionSoviet Union...........................$11 billionFrance......................................$ 3 billionChina.......................................$1.5 billionOther European.................$500 millionSouth America...................$400 millionThe amount totaled: $48,601,365,000
German Wolf PacksHitler deploys German U-boats to the North AtlanticU-boats sink hundreds of British shipsJune 1941, FDR orders U.S.Navy to protect U.S. shipments
Planning for the WarFDR-Winston Churchill meet off the coast of Newfoundland create the Atlantic Charter.The charter becomes the basis of a “Declaration of the United Nations”Allies: 26 nations including the Soviet Union and China (4/5 of the human race)
The United States is AttackedNovember 1941 Japanese Prime Minister Hideki Tojoorders his navy to prepare to attack the U.S.December 7th, 1941: Japanese attack U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii The attack cripples U.S. Pacific Fleet: 1. 21 ships sunk or badly damaged 2. 350 planes destroyed 3. 2,403 people dead 4. 1,178 people wounded FDR calls this day “a date which will live in infamy”
Pearl Harbor – Dec. 7, 1941 A date which will live in infamy!
December 8th, 1941 - The U.S. Congress declares war on Japan- December 11th, 1941:Germany and Italy declare war on the United States
Group Research Your group will be assigned one of the following battles from World War 2… - Battle of the Atlantic - Battle of Stalingrad - Operation Torch - D-day - Battle of the Bulge - Battle of Midway - Iwo Jima - Battle for Okinawa First- conduct research on your assigned battle, filling out your sheet with COMPLETE details
News Broadcast Your group is to now create a news broadcast. This should cover all the information about your specific battle which you just researched. Within your group- 2 News Reporters 1 Allied Soldier 1 Axis Soldier The soldiers should demonstrate how the consequences/outcomes of the battle had different effects on each side. They should also describe what it was like during the battle for their side. You are required to turn in a written script. Each person should have a minimum of 5 lines. How you will be graded: Chart completion /10 Information presented /15 Creativity /5 Behavior during other groups /5