Assessing Spatial and Seasonal Rainfall Variations in the Yangtze River Basin: Impacts on Agriculture and Ecosystems
20 likes | 152 Vues
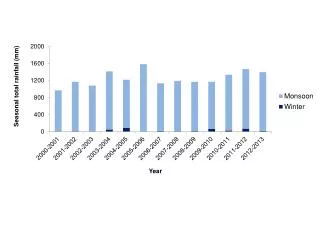
This study examines the spatial and seasonal variations in rainfall across the Yangtze River Basin and their effects on agriculture, flooding, droughts, and overall water quality. With significant factors like pollution, population displacement, and dam construction, the ecological balance faces challenges, including sedimentation issues that disrupt nutrient flow to agricultural lands. The implications of these variations extend to marine life, manufacturing, and transportation. Historical events, such as the 1998 flood, highlight the urgent need for sustainable management practices in the basin.

Assessing Spatial and Seasonal Rainfall Variations in the Yangtze River Basin: Impacts on Agriculture and Ecosystems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
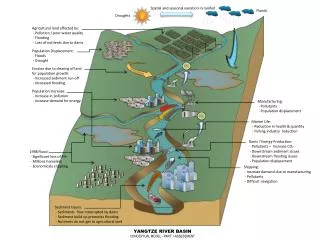
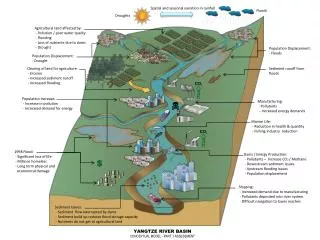
Spatial and seasonal variation in rainfall Floods Droughts Agricultural land affected by: - Pollution / poor water quality - Flooding - Loss of nutrients due to dams Population Displacement: - Floods - Drought Erosion due to clearing of land for population growth: - Increased sediment run-off - Increased flooding Population Increase: - Increase in pollution - Increase demand for energy Manufacturing: - Pollutants - Population displacement Marine Life: - Reduction in health & quantity - Fishing industry reduction Dams / Energy Production: - Pollutants – Increase CO2 - Downstream sediment issues - Downstream flooding issues - Population displacement 1998 Flood: - Significant loss of life - Millions homeless - Economicaly crippling Shipping: - Increase demand due to manufacturing - Pollutants - Difficult navigation Sediment Issues: - Sediments flow interrupted by dams - Sediment build up promotes flooding - Nutrients do not get to agricultural land YANGTZE RIVER BASIN CONCEPTUAL MODEL - PART 1 ASSESSMENT