Chap. 2
310 likes | 519 Vues
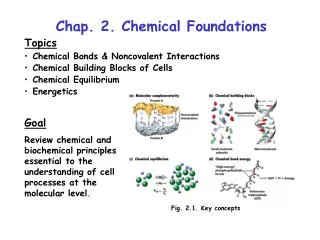
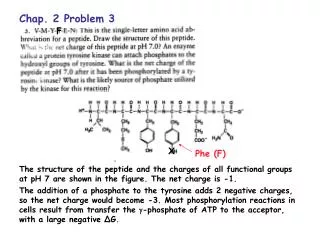
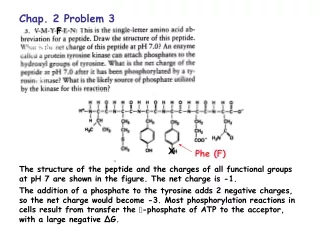
Chap. 2. Embedded Linux Concept. Outline. 2.1 Linux Overview Unix/Linux History Linux Concept Linux Command 2.2 Embedded Linux Overview ARM Linux uClinux Embedded Linux Concept. Unix/Linux History. 1985: The “GNU manifesto” is published in the March

Chap. 2
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chap. 2 Embedded Linux Concept
Outline 2.1 Linux Overview • Unix/Linux History • Linux Concept • Linux Command 2.2 Embedded Linux Overview • ARM Linux • uClinux • Embedded Linux Concept
Unix/Linux History • 1985: The “GNU manifesto” is published in the March 1985 issue of Dr. Dobb's Journal. • 1989: SCO ships SCO UNIX System V/386, the first volume commercial product licensed by AT&T to use the UNIX System trademark • 1991 : Linus Torvalds develops Linux as an open source Unix clone • 1994 : Linux 1.0 is released. • 1995: SCO acquires UNIX Systems source technology business from Novell Corporation (which had acquired it from AT&T's UNIX System Laboratories). SCO also acquires UnixWare 2 operating system from Novell
Unix/Linux History • 1996: Real-time Linux designated the RTLinux project released in 1996 by Michael Barabanov under Victor Yodaiken's supervision • 1997: Caldera ships OpenLinux Standard 1.1 May 5, 1997, the second offering in Caldera's OpenLinux product line • 2003: Linux Kernel Archive http://www.kernel.org/. The current full-featured version is 2.6 (released December 2003) and development continues • 2005: The latest stable version of the Linux kernel is 2.6.12.4 (released 2005-08)
Outline 2.1 Linux Overview • Unix/Linux History • Linux Concept • Linux Command 2.2 Embedded Linux Overview • ARM Linux • uClinux • Embedded Linux Concept
Linux Architecture • Linux Kernel • Provide basic OS mechanisms, file systems, device drivers...etc. • Libraries • C libraries, run-time libraries...etc. • Shell (Command line interface) • A user program that provides an environment for user interaction. • GUI • Graphic User Interface • System Services • Disk manager, Web server...etc. • System Utilities & User Applications • vim, ftp, ifconfig, firefox...etc. System Services System Utilities User Applications Shell (Bash, Csh…) GUI (Gnome, KDE…) Libraries (glibc) Linux Kernel Hardware (PC)
Important Concept of Linux • You can simply regard a complete Linux system as two major parts: • Kernel • Root Filesystem • A roughly boot sequence of Linux: Now we can see the directory structure and files in hard disk Boot code Kernel Initiate hardware Mount Root FS Mounted as root (/) Execute /sbin/init Initiate Kernel functions Root Filesystem (Stored in hard disk) Execute /sbin/login
Linux Root File System Ref. [1]
Typical Directories • / : Root of the tree. • bin, sbin, usr/bin: software for the shell and most common Linux commands. • dev: device files, Linux regards devices as files, for example: HD0 /dev/hd0, printer1 /dev/lpt1. • home: contains individual user home directory (/export/home on sun computers). • tmp: holds temporary files. • var: contains files that vary in size. (Mail directories, printer spool files,logs, etc.) • etc: administrative files such as lists of user names and passwords. • usr: contains application programs
The Linux Kernel • Task management • System calls • Memory management • Scheduler • IPC • File system • Device driver • Network stack
Linux Kernel architecture • Architecture of a generic Linux system Ref. [3]
Outline 2.1 Linux Overview • Unix/Linux History • Linux Concept • Linux Command 2.2 Embedded Linux Overview • ARM Linux • uClinux • Embedded Linux Concept
Linux command -Basics man command: display online help, type q is exit • ls : display Information about files and directories -l display detail information -a display information for every file including hidden file in a directory • cd : move to directory • cd ~ : move to home directory • cd .. : move one directory up • cd dirname : change to directory dirname • cp : copy file (cp from-filename to-filename) • rm : delete file (rm filename ) • mv : move file (mv filename ./directory) • mkdir : create new directories • rmdir : delete empty directories
Linux command - Basics • df : reports the amount of free disk space on any currently mounted filesystem • ln : creates a symbolic link to a files (ln -s originalfile linkfile) • more : display file contents in full screen and page by page (more filename) • shutdown : shutdown the system -h halt the system when the shutdown is complete -r reboot the system when the shutdown is complete • halt : shutdown the system now • reboot : restart computer • pwd : report current directory • who : show who is logged on • passwd : change password • login, logout : log in or log out system • startx : start X window
Linux command - File Management • chown : change the ower user and group of file or directory (chown user:groupfile or directory) • chmod : change the permissions user and group of file or directory [ex] chmod ug+rx dirname, chmod 755 dirname • mount : attach the device to the filesystem [ex] mkdir /c (first make directory) mount /dev/hdc /c • umount : detach the device from the filesystem [ex] umount /c • uname : display system information <ex> uname -a • mkbootdisk : [ex] mkbootdisk --device /dev/fd0 2.4.20-8 build floppy boot disk ,kernel Ver. 2.4.20-8 • cat : concatenates files [ex] cat a.txt >> b.txt • fdisk : partition tool • mke2fs : format tool [ex] mke2fs /dev/fd0
Linux command - Network • ping : send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST packets to network hosts[ex] ping 140.118.123.173 • telnet : connects the local host with a remote host[ex] telnet 140.118.123.173 • ifconfig : configure a network interface[ex] ifconfig eth0 140.118.123.173 • netstat : display network state • route : show/manipulate the IP routing table • ftp : file transfer tool [ex] ftp 140.118.123.173 • bin : switch to binary transfer mode • ascii : switch to ascii transfer mode • get filename : download file • put filename : upload file • bye : quit ftp • ls : list file and directory
Linux command - Compress & Decompress For file • compress : • bzip2 : [ex] bzip2 filename form filename.bz2 • zip : [ex] zip filename1 filename form filename1.zip • gzip : [ex] gzip filename form filename.gz • decompress : • bzip2 : [ex] bzip2 -d filename.bz2 • unzip : [ex] unzip filename1.zip • gzip : [ex] gzip -d filename.gz
Linux command - Compress & Decompress For directory • tar : The GNU version of the tar archiving utility -z: gzip/ ungzip type -c: create a new archive -x: extract files from archive -v: verbosely list files processed -f: use archive file or device F (default "-", meaning stdin/stdout) • compress : [ex] tar -zcvf directory.tar.gz directory • usegzip to compress directory and generate directory.tar.gz. • decompress : [ex] tar -zxvf directory.tar.gz • use gzip to decompress and extract directory.tar.gz.
Linux command - Search • find : find [pathnames] [conditions] • An extremely useful command for finding particular groups of files. • grep : grep [options] pattern [files] • Search one or more files for lines that match a regular expression pattern.
Linux command - Process • ps : ps [options] -a : list all processes on a terminal -u : display processes for the specified users -x : display processes without an associated terminal
Linux command - Process • Kill : kill [options] [PIDs] • Send a signal to terminate one or more processes.
Outline 2.1 Linux Overview • Unix/Linux History • Linux Concept • Linux Command 2.2 Embedded Linux Overview • ARM Linux • uClinux • Embedded Linux Concept
ARM Linux • ARM Linux [7] is a port of the successful Linux Kernel to ARM processor based machines. • ARM Linux is under almost constant development by various people and organizations around the world. • It reserves mostly generic Linux Kernel features, such as multi-tasking, memory management, and so on.
ARM Linux • Important features for developers: • Multi-tasking • Support fork() system call • Memory Management Unit (MMU) • Support virtual memory • Support brk() system call • Executable File Format • Support standard ELF executable file format
Outline 2.1 Linux overview • Unix/Linux History • Linux Concept • Linux Command 2.2 Embedded Linux Overview • ARM Linux • uClinux • Embedded Linux Concept
uClinux • The name ‘uClinux’ [2] comes from ‘Micro(μ)-Controller Linux’. • The original uClinux was a derivative of Linux 2.0 kernel intended for micro-controllers without MMUs. • uClinux first ported to the Motorola MC68328: DragonBall Integrated Microprocessor.
uClinux • Important features for developers: • Multi-tasking • fork() system call is not implemented • vfork() is used instead of fork() • No Memory Management Unit • Does not have autogrow stack and no brk() • Need to use mmap() to allocate memory • Need to set stack size of a program at compile time • No memory protection • Any program can crash another program or the kernel • Executable File Format • Only support FLAT executable file format
Outline 2.1 Linux overview • Unix/Linux History • Linux Concept • Linux Command 2.2 Embedded Linux Overview • ARM Linux • uClinux • Embedded Linux Concept
Embedded Linux Architecture • Basically, the embedded Linux architecture is the same as the generic Linux architecture. • The software such as glibc, bash, Gnome and KDE ... etc, are too large to be used in embedded system. • The common substitution for software in embedded system is listed below: • Glibc uClibc • Bash busybox, Sash • Gnome, KDE Microwindow, Qt Embedded, MiniGUI • Login Tinylogin • Standalone Utilities busybox NOTE: Busybox is a program that integrates a lot of frequently used utilities into it.
Embedded Linux Build Procedure • Make a Kernel image for your board • The make procedure of distribution of embedded Linux that you are using is different from the others but they are similar. • The common make procedure of Linux Kernel: • make xconfig (or menuconfig) • Configure your Kernel • make dep (not necessary in 2.6 Kernel) • Check dependency • make • Compile your Kernel and produce the Kernel image • Build a Root Filesystem • You can build it manually or automatically build via some tools or scripts. • Put all files you want in the Root Filesystem image. • Commonly used file systems: ext2 and romfs. • Copy Kernel and Root FS to Flash memory
Reference [1] 鳥哥的linux私房菜 鳥哥著 上奇 [2] http://www.uclinux.org [3] http://www.xml.com/ldd/chapter/book/ bookindexpdf.html [4] http://linux.about.com [5] http://linux.vbird.org/ [6] http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~reid/csc209/02f/ [7] http://www.arm.linux.org.uk/