How to Read an EKG
390 likes | 701 Vues
How to Read an EKG. Jason Ryan, MD Intern Report. How to read an EKG. Rate and Rhythm how fast/slow regular/irregular wide/narrow Axis and Intervals PR, QRS, QT Hypertrophy LAE/RAE LVH/RVH ST Changes and Q waves. How to read an EKG. Rate. 100. 60. 40. 300. 75. 150. 50.

How to Read an EKG
E N D
Presentation Transcript
How to Read an EKG Jason Ryan, MD Intern Report
How to read an EKG • Rate and Rhythm • how fast/slow • regular/irregular • wide/narrow • Axis and Intervals • PR, QRS, QT • Hypertrophy • LAE/RAE • LVH/RVH • ST Changes and Q waves
How to read an EKG • Rate 100 60 40 300 75 150 50
Lead aVF (+) (-) Lead I (-) (+) How to read an EKG -90o • Axis QRS LAD -180o 0o RAD Normal Axis 90o
How to read an EKG • Intervals Correct QT 1. QTc=QT/(RR)1/2 (Bazett) 2. QTC=QT + 0.00175(HR-60) (Hodges) QRS 0.7-011 QTc <0.46 PR 0.14-0.21
How to Read and EKG • Atrial Enlargement
How to Read and EKG • Ventricular Enlargement
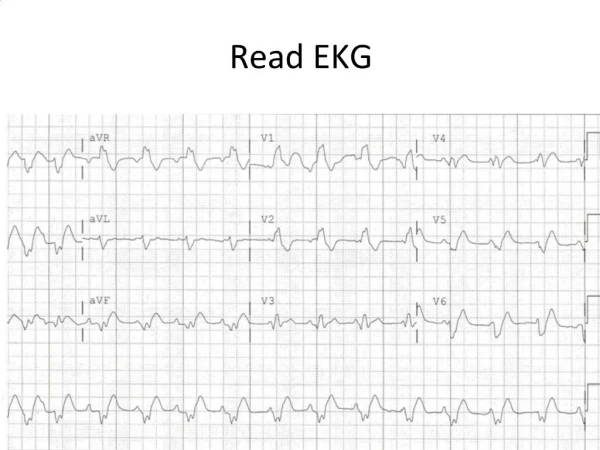
Sinus Rhythm • Rate between 60 to 100 • P wave before every QRS • Smooth contour • Either all positive or all negative except V1 • <0.12s and <0.2mv • Upright P waves in I, II, aVF • Negative P wave in aVR
Limb Lead Reversal • Right and Left arm reversed • P wave positive aVR • P wave negative aVL and I • Limb leads look normal • Right arm and Right leg reversed • P wave positive aVR • P wave negative I, L • Lead II isoelectric (almost no QRS)
Left Bundle Branch Block • Criteria: • QRS > 120ms (3 small boxes) • Broad, notched, or slurred R waves in I, aVL, and V5-V6 • Secondary ST-T changes in I, aVL, and V5-V6 • Absence of Q waves in I, V5-V6 • R-wave peak time >60ms (1.5 small boxes) V5-V6 • Separate criteria for STE AMI
Right Bundle Branch Block • Criteria: • QRS >120ms (3 small boxes) • R’ in the right precordial leads with R’>R • Secondary ST-T changes in R precordial leads • Supporting findings: • Slurred S wave in I, aVL, left precordial leads • Usual criteria for STE AMI apply
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy • SV1orV2+ RV5orV6>35mm • >40 if 30-40yrs old • >60 if 16-30yrs old • RaVL>11mm • RI + SIII >25mm • RaVL + SV3 >28mm(men) or 20mm(wmn)
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy • Associated ST-T wave abnormalities • STD and TWI in V5-V6 • Leads where QRS is mainly positive • Slight STE with upright T in V1-V2 • Leas where QRS is mainly negative
Sinus Tachycardia • All sinus rhythm criteria • P before every QRS • Upright P in I, II, aVF • Inverted P aVR • Rate >100
T Wave Inversions • Indicative of subendocardial or evolving ischemia • Can be a normal variant in several leads or in the presence of BBB • Can be caused by several other conditions • Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy • Intracranial processes (hemorrhage) • Medications or electrolyte abnormalities • Myocarditis/pericarditis or pulmonary embolism
ST depressions • Horizontal ST depressions are strongly suggestive of ischemia in the appropriate clinical setting • Don’t necessarily localize • Stress testing • Reciprocal changes • Several other conditions can provoke ST depressions: • LVH • Medications or electrolytes • Bundle Branch Block • Pulmonary embolism
Localizes best of all ischemic EKG changes Usually indication of acute myocardial injury (occluded artery) Several conditions can also cause ST elevations: Pericarditis Early repolarization LBBB LVH ST Elevations
ST Elevation MI Evolution of EKG changes Normal Acute Hours 1-2 Days 3-7 Days > 7 Days
Anterior Leads go together
Leads go together Lateral
Leads go together Inferior