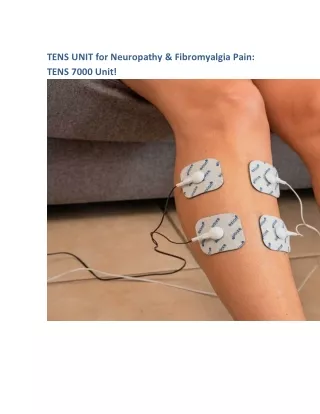
TENS
120 likes | 660 Vues
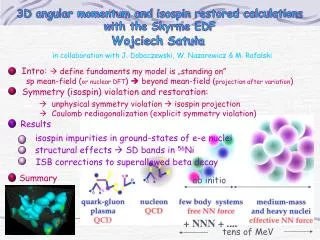
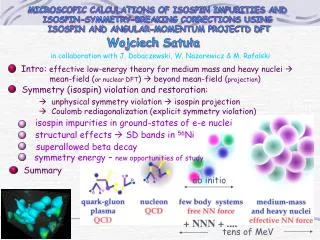
TENS. TENS - What Is It?. “T” Through the skin “E” Use of electrical current “N” Nerve involvement “S” Stimulation to cause depolarization of sensory, motor or pain nerves. Electrotherapeutic Pain Control. 2 types of approach Gate Control Mechanism

TENS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
TENS - What Is It? • “T” Through the skin • “E” Use of electrical current • “N” Nerve involvement • “S” Stimulation to cause depolarization of sensory, motor or pain nerves
Electrotherapeutic Pain Control • 2 types of approach • Gate Control Mechanism • Centrally through the release of endogenous opiates
Electrical Parameters Parameter Range Intensity 0 – 100 mA Pulse Frequency 1 – 150 pps Pulse Duration 10 – 500 μsec
Biophysical Effects • Decrease perception of pain by decreasing the conductivity and transmission of noxious impulses from the small fibers to the CNS • Affecting large motor fibers, may interfere with muscle guarding (spasms) • Stimulate visceral organs to release endogenous opiates
Parameter High TENS Low TENS Intensity Sensory Motor Pulse Frequency 60-100 pps 2-4 pps Pulse Duration 60-100 μsec 150-250 μsec Mode Modulated rate Mod. Burst Treatment Duration As Needed 30 min. Onset of Relief < 10 min. 20-40 min. Duration of Relief min. – hours hours
High TENS • Pain modulating gate at the spinal cord level • Pain impulses travel along slow-transmitting, un-myelinated, small diameter nerves (A-beta and C fibers) • Non-painful impulses travel along large diameter neurons • TENS stimulates large A-delta fibers blocking transmission of pain impulse (COWS & GOATS)
So What Happens? • High-frequency, low intensity stimulation to somatic receptive fields decreases the activity of spontaneously firing nerves, decreases the activity in noxiously evoked dorsal neurons, and decreases activity compared with the low-frequency TENS, high-intensity protocol.
Low TENS • The activation of small-diameter nociceptors and motor pain relief is obtained through the release of β-endorphins – results in narcoticlike pain reduction.
A Better Explanation Stimulation of pituitary gland to release of chemicals (ACTH) to trigger production of β-endorphins. These β-endorphins bind to receptor sites of A-beta and C fibers, blocking the transmission of pain.
Electrode Placement • Parallel A B A B • Crossing A B B A Try to place electrode over nerve root in injured area – Thumb = radial nerve