Enhancing Understanding of Two-Phase Transport Dynamics in Complex Natural Gas Networks
10 likes | 120 Vues
This study provides an in-depth analysis of the critical physical factors influencing multiphase transport and flow dynamics in complex natural gas network topologies. It focuses on highly interconnected, closed-loop systems, revealing fundamental relationships and parameters that affect performance. Comprehensive methodologies, including governing equations and thermodynamic principles, were utilized alongside Finite Volume Method (FVM) schemes. Additionally, the research extends into two-phase flow conditions, with preliminary analyses of phase splits at T-junctions, offering valuable insights for gas network optimization.

Enhancing Understanding of Two-Phase Transport Dynamics in Complex Natural Gas Networks
E N D
Presentation Transcript
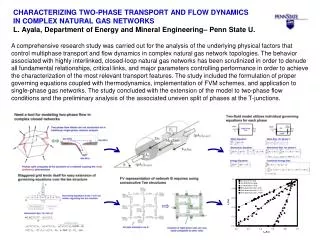
CHARACTERIZING TWO-PHASE TRANSPORT AND FLOW DYNAMICS IN COMPLEX NATURAL GAS NETWORKSL. Ayala, Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering– Penn State U. A comprehensive research study was carried out for the analysis of the underlying physical factors that control multiphase transport and flow dynamics in complex natural gas network topologies. The behavior associated with highly interlinked, closed-loop natural gas networks has been scrutinized in order to denude all fundamental relationships, critical links, and major parameters controlling performance in order to achieve the characterization of the most relevant transport features. The study included the formulation of proper governing equations coupled with thermodynamics, implementation of FVM schemes, and application to single-phase gas networks. The study concluded with the extension of the model to two-phase flow conditions and the preliminary analysis of the associated uneven split of phases at the T-junctions.