The Binomial Theorem
130 likes | 488 Vues
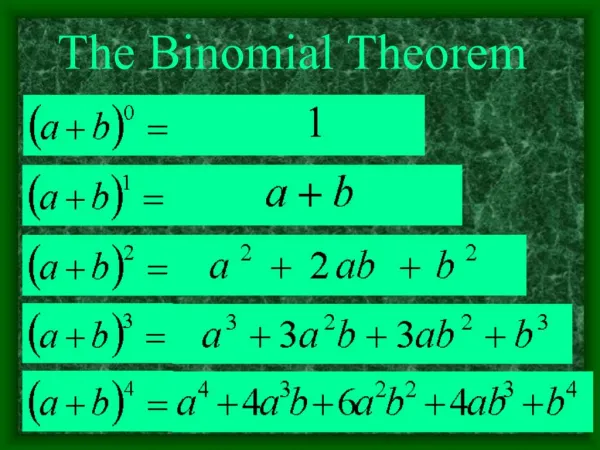
The Binomial Theorem. Connecting binomial expansion to combinations. Used in science, probability theory, game theory, statistics and combinatorics. Expand (3x – 2) 10. (3x – 2)(3x – 2)(3x – 2)(3x – 2)(3x – 2)(3x –2)(3x – 2) (3x – 2)(3x – 2)(3x – 2) = Have fun!!!

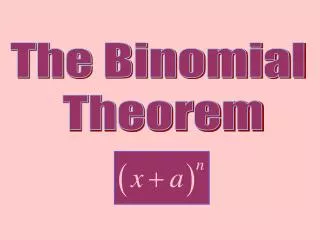
The Binomial Theorem
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Binomial Theorem Connecting binomial expansion to combinations. Used in science, probability theory, game theory, statistics and combinatorics
Expand (3x – 2)10 (3x – 2)(3x – 2)(3x – 2)(3x – 2)(3x – 2)(3x –2)(3x – 2) (3x – 2)(3x – 2)(3x – 2) = Have fun!!! The binomial theorem is a method used to expand binomials raised to large powers.
The Binomial Theorem: notation is just another way of writing a combination such as n C k .
So to find (x + 2)5 or Notice that the exponents on each term always add up to n. Find the combination values and simplify.
Back to (3x – 2)10 = Take your time and write the expansion steps out to avoid mistakes. (3x – 2)10 = 10C0 (3x)10–0(–2)0 + 10C1 (3x)10–1(–2)1 + 10C2 (3x)10–2(–2)2 + 10C3 (3x)10–3(–2)3 + 10C4 (3x)10–4(–2)4 + 10C5 (3x)10–5(–2)5 + 10C6 (3x)10–6(–2)6 + 10C7 (3x)10–7(–2)7 + 10C8 (3x)10–8(–2)8 + 10C9 (3x)10–9(–2)9 + 10C10 (3x)10–10(–2)10 =
(1)(59049)x10(1) + (10)(19683)x9(–2) + (45)(6561)x8(4) + (120)(2187)x7(–8) + (210)(729)x6(16) + (252)(243)x5(–32) + (210)(81)x4(64) + (120)(27)x3(–128) + (45)(9)x2(256) + (10)(3)x(–512) + (1)(1)(1)(1024) = 59049x10 – 393660x9 + 1180980x8 – 2099520x7 + 2449440x6 – 1959552x5 + 1088640x4 – 414720x3 + 103680x2 – 15360x + 1024
Practice Expand • (x2 + 3)6 x12 + 18x10 + 135x8 + 540x6 + 1215x4 + 1458x2 + 729 • (2x – 5y)7 128x7 – 2240x6y + 16800x5y2 – 70000x4y3 + 175000x3y4 – 262500x2y5 + 218750xy6 – 78125y7
Finding a specific term. • Notice that every expansion has one more term than the original exponent on the binomial. • If you are asked to find the 5th term of (x – 3)9 the k value will be 5 – 1= 4 so: the 5th term would be 9C4x9-4(-3)4 =126x5(81) = 10206x5
Find: • the tenth term in the expansion of (x + 3)12 4330260x3 • Find the 5th term of (3x – 4)12 831,409,920x8