Eon
410 likes | 1.16k Vues
Eon. Era. Period. Epoch. Phanerozoic Eon. Paleozoic Era. Mesozoic Era. Cenozoic Era. Hadean Eon Archean Eon Proterozoic Eon. Precambrian Time. Phanerozoic Eon. Eon. Paleozoic Era Cambrian Ordovician Silurian Devonian Carboniferous Permian.

Eon
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Eon Era Period Epoch
Phanerozoic Eon Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era
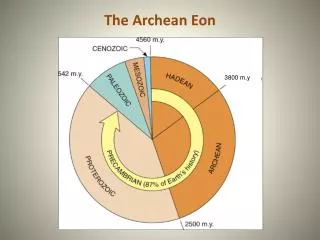
Hadean Eon Archean Eon Proterozoic Eon Precambrian Time Phanerozoic Eon Eon Paleozoic Era Cambrian Ordovician Silurian Devonian Carboniferous Permian Mesozoic Era Triassic Jurassic Cretaceous Cenozoic Era Tertiary Quaternary Era Period Eon Era Period Epoch Epoch
Geologic Time Scale Coach p. 237 Textbook p. A64 Dictionary p. 148 Era
Most recent “Ice Age” QUARTERNARY “Humans” arrive TERTIARY Major Mass Extinction Age of Dinosaurs Major Mass Extinction Age of Coal Formation Geologic Time Scale Age of Fishes First multi-celled organisms Origin of the Earth 4.6 Billion years
A Brief view of the History of Life on Earth Early earth 4.6 BYA
Early earth 4.0 BYA
Stromatolites- cyanobacteria 3.8 BYA – 630 MY Shark Bay, Australia
Ediacaran 630 – 570 MYA - More complex organisms (soft tissue)
Cambrian (Burgess shale) -1st hard shelled fossils -trilobites dominant 570 - 505 MYA
Ordovician -appearance of coral reefs -nautiloids dominant -limestone formation -Predators 505 - 438 MYA
Silurian -appearance of fish 438 - 408 MYA
Silurian Fish 438 - 408 MYA
Devonian -land plants become common -1st land animals 408 - 360 MYA
Devonian -1st amphibians 408 - 360 MYA
Carboniferous -Pennsylvanian (290-320mya) -Mississippian (320-360mya) -extensive marine life (coral reefs); flora (crinoids) -brachiopods; giant insects -extensive tropical forests 360 - 286 MYA
Dimetrodon Permian -Primitive reptiles -shallow marine life (sponges/clams) -reptile-like creatures become large -at end largest mass extinction ever (>90%); large volcanic eruptions 286 - 245 MYA
Triassic -Age of Dinosaurs 245 - 208 MYA
Jurassic “Age of Reptiles” -large dinosaurs dominant 208 – 144 MYA
Jurassic -fish, marine reptiles dominant 208 – 144 MYA Plesiosaur
Cretaceous mammals, birds appeared 144 - 65 MYA
Cretaceous 144 - 65 MYA Cretaceous extinction 65 MYA
Paleocene -marsupials -after KT extinction of dinosaurs 65 - 58 MYA
Eocene -modern mammals 58 – 37 MYA Earliest Bat Pygmy Horse
Miocene 24 – 5 MYA
Pliocene 5 MYA Australopithecus spp.
Pleistocene 2 MYA - 100,000 YA Cave Bear
Pleistocene 2 MYA – 100,000 YA Homo habilis
Homo erectus Homo sapiens var. Neanderthal
Hot Dog Style Phanerozoic Eon Down 2 cm Cut through 1 layer