CELL MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Part I
100 likes | 307 Vues
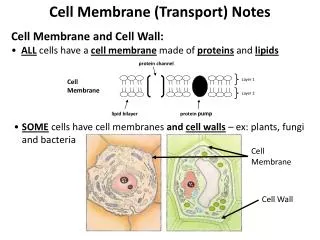
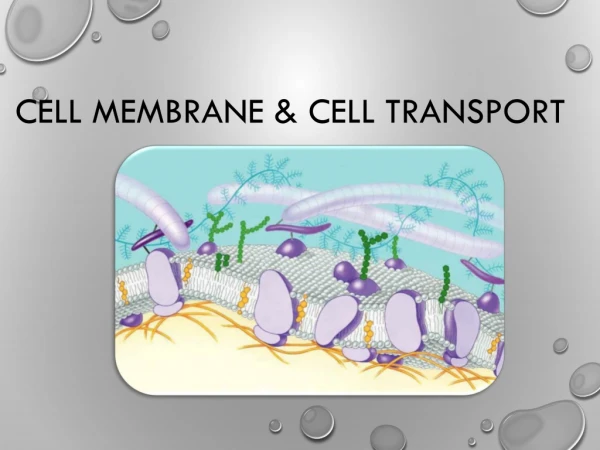
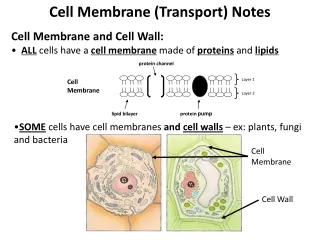
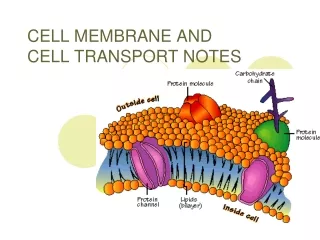
CELL MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Part I. Concentration. The amount of solute or particles within a solution A change in concentration is called a concentration gradient. Which beaker has the highest concentration of solute (particles)? . A B C. A. B. C.

CELL MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Part I
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Concentration • The amount of solute or particles within a solution • A change in concentration is called a concentration gradient
Which beaker has the highest concentration of solute (particles)? • A • B • C A B C
Which beaker has the highest concentration of water? • A • B • C A B C
Both beakers below contain water. Which beaker contains the higher concentration of water? • Beaker one • Beaker two • Both beakers have the same concentration of water Beaker One Beaker Two
Beaker A Beaker B Solute of some type was added to beaker A. Now which beaker has the higher concentration of water • Beaker A • Beaker B • Both contain the same concentration of water.
Diffusion • The movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration
Osmosis • The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane • From high to low concentration
Equilibrium • When the concentration on both sides of the membrane are the same • Particles continue to move but concentration stays the same.
Remember, this is important, Osmosis deals with what? The movement of particles The movement of glucose The movement of water The movement of lipids