Analysis of Intrasample and Intersample Divergence in Heteroduplex Mobility Assays
370 likes | 479 Vues
This study presents a comprehensive analysis of the intrasample and intersample divergence in heteroduplex mobility assays (HMA) through density scanning of gel images. We emphasize the importance of the sample control (Ho) in understanding DNA mobility, comparing homoduplex and heteroduplex data. Quantitative analysis of DNA sequences, including mobility measurements and their implication in phylogenetic estimation, is discussed with respect to diversity in 0.7kb fragments. The findings provide insights into genetic variation and its representation in gel mobility profiles.

Analysis of Intrasample and Intersample Divergence in Heteroduplex Mobility Assays
E N D
Presentation Transcript
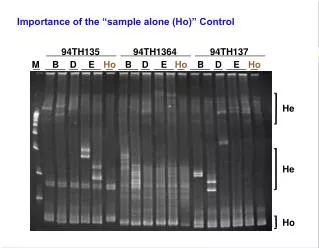
Importance of the “sample alone (Ho)” Control 94TH135 94TH1364 94TH137 M B D E Ho B D E Ho B D E Ho He He Ho
Intrasample Divergence (HMA) Intersample Divergence (HTA) DNA Sequence vs. HMA data
M A2 B1 C2 D1 E2 F2 G2 H2 B2 Rf = Avg. heteroduplex mobility Avg. homoduplex mobility Quantitative analysis of Heteroduplex Mobility 0.7kb FRAGMENTS (ES7/ES8)
0 + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + 0.1 + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + 0.2 + + + + + + + 0.3 + 0.4 + + 0.5 + + 0.6 + + + + + 0.7 + + + 0.8 + + + 0.9 + + + 1.0 1 HMA and Phylogenetic Estimation V1-V5 region Relative Mobility 5 10 15 20 25 30 % DNA Distance
U G 2 7 0 0 . 1 7 6 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 1 3 9 0 . 1 8 4 0 . 1 7 0 0 . 2 1 2 0 . 2 8 2 0 . 2 1 2 0 . 2 1 2 0 . 1 8 4 0 . 2 0 1 0 . 2 5 7 0 . 2 1 2 0 . 1 8 4 0 . 2 1 2 0 . 2 0 1 0 . 2 1 2 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 1 9 2 0 . 2 5 7 0 . 2 5 7 M A L 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 1 7 6 0 . 1 8 4 0 . 1 8 4 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 5 7 0 . 2 2 4 0 . 2 0 1 0 . 1 9 2 0 . 2 0 1 0 . 2 5 7 0 . 2 1 2 0 . 1 8 4 0 . 1 8 4 0 . 1 6 3 0 . 1 9 2 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 1 9 2 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 R W 2 0 0 . 0 9 9 0 . 0 7 6 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 1 4 4 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 0 9 6 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 1 4 0 0 . 1 5 7 0 . 1 4 8 0 . 1 2 7 I C 1 4 4 0 . 1 2 8 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 0 8 5 0 . 1 2 8 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 1 1 1 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 1 6 7 0 . 1 1 7 0 . 1 3 9 U G 2 1 0 . 0 6 3 0 . 2 5 8 0 . 2 3 0 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 2 2 0 . 2 3 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 1 3 5 0 . 1 3 5 U G 3 8 0 . 1 2 3 0 . 1 6 3 U G 4 6 0 . 2 3 0 0 . 1 7 2 0 . 2 8 0 0 . 2 3 0 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 1 5 3 0 . 1 4 4 0 . 2 6 9 0 . 1 6 3 0 . 1 8 4 D J 2 5 8 0 . 1 5 2 0 . 2 5 7 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 1 7 6 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 5 7 0 . 2 2 4 0 . 1 6 3 0 . 1 9 2 0 . 1 3 1 0 . 1 4 3 0 . 1 3 1 0 . 1 7 0 0 . 2 0 1 S F 1 7 0 0 . 2 2 4 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 5 7 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 0 8 5 0 . 1 1 8 0 . 0 9 6 0 . 1 4 8 0 . 1 7 6 0 . 1 1 7 0 . 1 1 7 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 1 4 8 0 . 1 5 2 R W / 9 3 / 1 8 0 . 0 6 8 0 . 0 7 9 R W / 9 3 / 1 9 0 . 1 3 6 0 . 0 8 2 R W / 9 3 / 2 0 0 . 1 4 8 0 . 1 1 2 R W / 9 3 / 2 1 0 . 1 6 2 0 . 0 1 5 R W / 9 3 / 2 2 0 . 1 1 8 0 . 0 4 7 C A R / 9 3 / 0 3 C A R / 9 3 / 0 4 FITCH (PHYLIP) C A R / 9 3 / 0 8 R W 8 0 . 1 0 2 0 . 1 3 2 0 . 0 9 3 R W 9 0 . 1 2 5 0 . 0 6 8 0 . 0 7 7 0 . 0 6 8 0 . 1 0 2 0 . 1 1 8 0 . 1 0 2 R W 1 6 0 . 0 7 2 0 . 0 4 7 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 0 7 0 0 . 0 7 2 0 . 0 5 3 0 . 0 8 5 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 0 6 8 R W 2 1 0 . 1 1 1 0 . 1 1 1 R W 2 3 0 . 1 5 7 0 . 0 8 5 0 . 1 0 5 R W 2 4 0 . 1 4 4 0 . 1 8 3 0 . 0 9 0 0 . 1 2 1 0 . 1 5 7 0 . 1 4 0 R W 2 5 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 0 8 5 R W 2 6 0 . 0 8 5 0 . 0 7 2 R W 9 3 - 3 0 . 0 9 0 0 . 1 0 8 0 . 0 8 7 R W 9 3 - 4 0 . 0 8 0 0 . 1 3 2 0 . 0 9 0 R W 9 3 - 5 0 . 1 1 8 0 . 0 8 2 0 . 0 9 9 U G 2 9 0 . 0 9 Matrix for Generation of a Subtype A Tree 37% Of All Comparisons Done (170 / 465) 32% Intra-Subtype Comparisons Done (88 / 276) 6 U G 3 1 U G 3 7
T H 2 3 9 0 . 2 8 2 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 0 3 0 0 . 0 3 8 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 8 2 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 5 7 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 8 2 0 . 2 8 2 0 . 2 2 4 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 5 7 0 . 2 2 4 T H 2 2 0 . 0 7 7 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 6 9 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 8 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 1 5 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 2 2 0 . 2 6 9 0 . 2 8 3 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 0 5 7 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 0 3 2 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 1 5 0 . 2 1 1 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 8 0 0 . 2 4 8 0 . 2 6 9 0 . 2 6 9 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 4 8 0 . 2 0 1 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 3 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 0 7 5 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 0 8 0 . 2 7 3 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 6 9 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 1 6 7 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 4 8 0 . 2 5 8 0 . 2 6 9 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 6 9 0 . 2 4 8 0 . 2 8 0 0 . 0 7 0 0 . 0 9 0 T H 0 6 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 1 6 2 0 . 2 8 9 0 . 2 2 2 0 . 2 4 8 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 4 8 0 . 0 9 0 0 . 2 8 0 0 . 0 9 6 0 . 1 9 5 0 . 2 3 0 0 . 2 2 2 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 8 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 4 8 0 . 2 5 8 0 . 2 0 8 0 . 2 6 9 0 . 2 8 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 2 2 2 0 . 2 6 9 0 . 0 9 9 0 . 2 3 0 0 . 2 0 1 0 . 2 8 5 0 . 2 1 5 0 . 2 9 3 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 3 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 1 5 7 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 5 8 0 . 2 2 2 0 . 2 3 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 9 3 0 . 2 5 8 0 . 2 4 8 0 . 0 6 8 0 . 0 8 0 S F 1 6 2 0 . 1 2 0 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 0 8 5 0 . 0 5 7 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 1 2 5 0 . 1 4 0 0 . 1 1 8 0 . 1 1 8 0 . 1 1 1 0 . 1 0 3 0 . 0 7 5 0 . 0 7 8 0 . 0 7 7 0 . 0 5 5 0 . 0 8 0 0 . 0 7 7 0 . 0 6 3 0 . 1 7 6 0 . 1 6 3 0 . 1 7 6 0 . 1 8 4 0 . 1 8 4 0 . 1 7 0 0 . 1 3 9 0 . 1 3 1 0 . 1 4 3 0 . 1 6 3 0 . 1 5 2 0 . 1 3 5 0 . 0 8 0 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 1 2 8 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 0 9 9 0 . 0 7 7 0 . 2 3 9 0 . 0 7 0 0 . 0 7 0 0 . 0 6 8 0 . 0 9 9 0 . 0 9 0 0 . 0 7 0 0 . 0 9 6 0 . 0 7 7 0 . 0 7 5 0 . 1 4 0 0 . 0 6 3 0 . 0 6 8 0 . 0 7 5 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 7 2 0 . 0 7 0 0 . 0 6 1 0 . 0 7 0 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 6 8 0 . 0 6 1 0 . 0 7 5 0 . 0 6 8 0 . 0 7 0 0 . 0 9 6 0 . 1 4 7 0 . 1 2 5 0 . 0 6 8 0 . 1 3 6 0 . 2 5 8 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 0 6 8 0 . 0 6 3 0 . 0 6 3 0 . 0 7 2 0 . 0 1 3 0 . 0 2 8 T H 1 2 9 0 . 2 5 7 0 . 1 6 3 0 . 0 3 3 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 2 8 2 0 . 0 3 1 0 . 1 7 6 0 . 1 6 3 0 . 1 6 3 0 . 1 7 0 0 . 1 7 0 0 . 1 6 3 0 . 1 3 9 0 . 1 3 5 0 . 1 4 8 0 . 1 9 2 0 . 1 6 3 0 . 1 3 9 B R 2 0 0 . 0 7 2 0 . 1 3 2 0 . 1 6 7 0 . 1 2 8 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 0 7 2 0 . 0 7 5 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 0 7 2 0 . 1 3 2 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 0 7 0 T H 1 4 0 . 1 0 8 0 . 1 5 7 0 . 1 0 8 0 . 2 1 5 0 . 1 0 2 0 . 0 7 7 0 . 0 6 4 0 . 0 9 5 0 . 0 7 5 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 4 7 0 . 1 1 1 0 . 1 0 2 0 . 2 1 5 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 0 5 5 0 . 2 3 0 0 . 0 1 1 0 . 0 1 7 0 . 0 3 7 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 9 0 0 . 0 7 2 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 0 5 0 0 . 0 1 6 0 . 0 3 7 0 . 0 5 9 0 . 0 1 3 0 . 0 1 0 0 . 0 4 9 0 . 0 2 5 0 . 0 1 9 0 . 0 4 3 0 . 0 6 1 0 . 0 3 7 0 . 0 2 0 0 . 0 2 2 0 . 0 4 9 0 . 0 4 5 0 . 0 1 9 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 1 0 2 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 2 5 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 6 3 0 . 0 4 8 0 . 0 6 1 0 . 0 5 3 0 . 0 2 3 0 . 0 1 0 0 . 0 7 7 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 0 7 7 0 . 0 6 3 B R / 9 1 / 1 0 . 1 1 8 0 . 1 1 8 B R / 9 1 / 2 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 1 0 9 B R / 9 1 / 5 0 . 1 1 1 0 . 1 1 0 B R / 9 1 / 6 0 . 1 2 1 0 . 1 3 6 B R / 9 1 / 7 0 . 0 9 9 0 . 1 2 5 B R / 9 1 / 8 0 . 1 1 1 0 . 1 0 8 B R / 9 1 / 9 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 0 9 3 B R / 9 1 / 1 0 0 . 0 9 6 0 . 1 1 4 B R / 9 1 / 1 1 0 . 1 3 2 0 . 1 1 1 B R / 9 1 / 1 2 0 . 0 9 6 0 . 1 5 7 B R / 9 1 / 1 3 0 . 1 0 8 0 . 1 0 5 B R / 9 1 / 1 6 0 . 1 2 6 0 . 1 0 5 B R / 9 1 / 1 7 0 . 1 0 4 0 . 1 0 8 T H 2 6 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 0 8 0 0 . 1 0 2 0 . 1 1 1 0 . 0 8 0 0 . 1 1 1 0 . 1 2 8 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 0 7 7 0 . 0 7 2 0 . 0 8 2 B R 4 0 . 0 9 9 0 . 1 2 1 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 0 7 5 0 . 0 9 6 0 . 0 9 9 0 . 0 8 7 0 . 1 0 2 B R 1 4 0 . 1 2 1 0 . 1 2 1 0 . 0 8 2 0 . 1 3 2 0 . 1 3 2 0 . 1 1 8 B R 1 7 0 . 1 3 2 0 . 1 2 5 0 . 1 1 4 0 . 1 3 6 0 . 0 5 7 0 . 0 9 9 B R 1 8 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 1 3 2 B R 1 9 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 0 8 7 B R 2 1 0 . 1 3 6 0 . 0 9 6 B R 2 3 0 . 1 5 3 0 . 1 6 7 B R 2 4 0 . 1 0 5 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 0 9 0 0 . 1 0 2 B R 2 6 0 . 0 9 6 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 1 0 2 B R 2 8 B R 3 0 B R 9 3 - 8 T H 9 3 / 0 6 7 0 . 0 7 3 0 . 0 4 5 T H 9 4 0 8 6 0 . 0 5 0 0 . 0 6 7 T H 9 4 0 9 1 0 . 1 0 1 0 . 0 9 5 T H 9 4 0 9 5 0 . 0 4 8 0 . 0 6 4 T H 9 4 0 9 8 0 . 3 0 0 T H 9 4 0 9 6 0 . 0 6 6 0 . 0 9 5 T H 9 4 1 0 1 0 . 0 4 7 0 . 0 7 9 T H 9 4 1 0 0 0 . 0 2 4 0 . 0 2 9 T H 9 4 0 8 2 0 . 0 4 8 0 . 0 5 7 T H 9 4 0 9 0 0 . 0 5 0 0 . 0 5 6 T H 9 4 0 9 2 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 5 5 T H 9 4 0 9 3 0 . 0 4 7 0 . 0 7 0 T H 9 4 0 9 4 0 . 0 6 7 0 . 0 8 6 T H 9 4 0 9 9 0 . 0 7 6 0 . 0 9 3 T H 9 4 1 0 2 0 . 0 6 6 0 . 0 7 4 T H 9 4 1 0 3 0 . 0 6 9 0 . 0 8 0 T H 9 4 1 0 4 0 . 0 5 0 0 . 0 5 8 T H 9 4 1 0 5 0 . 0 7 6 0 . 0 4 5 T H 9 4 1 0 8 0 . 0 7 3 0 . 0 6 0 T H 9 4 1 0 9 0 . 0 5 4 0 . 0 5 6 T H 9 4 1 1 0 0 . 0 5 3 0 . 0 5 1 T H 9 4 1 1 2 0 . 0 9 0 0 . 0 5 5 T H 9 4 1 1 3 0 . 0 5 8 0 . 0 5 5 T H 9 4 1 1 4 0 . 0 3 0 0 . 0 7 7 T H 9 4 1 1 6 0 . 0 5 2 0 . 0 6 3 T H 9 4 1 1 7 0 . 0 6 7 0 . 0 5 4 T H 9 4 1 1 8 0 . 0 7 8 0 . 0 7 1 T H 9 4 1 2 0 0 . 0 5 0 0 . 0 6 4 14% Of All Comparisons Done (489 / 3403) T H 9 4 1 2 1 T H 9 4 1 2 2 0 . 0 4 2 0 . 0 6 2 T H 9 4 1 2 3 0 . 0 7 2 0 . 0 6 6 T H 9 4 1 2 4 0 . 0 5 2 0 . 0 6 7 T H 9 4 1 2 7 0 . 0 5 0 0 . 0 5 3 T H 9 4 1 2 8 0 . 0 6 9 0 . 0 6 9 10% Intra-Subtype Comparisons Done (325 / 3160) T H 9 4 1 2 9 0 . 0 9 3 0 . 0 9 6 T H 9 4 1 3 0 0 . 0 4 2 0 . 0 7 6 0 . 0 5 8 0 . 0 5 8 0 . 0 7 6 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 3 7 0 . 0 5 4 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 7 8 0 . 0 5 2 0 . 0 5 4 0 . 0 4 0 0 . 0 5 0 T H 9 4 1 3 1 0 . 0 5 2 T H 9 4 1 3 2 0 . 0 6 3 4 1 3 3 0 . 0 7 8 T H 9 T H 9 4 1 3 4 0 . 0 7 2 T H 9 4 1 3 6 0 . 0 8 5 T H 9 4 1 3 7 0 . 0 6 5 0 . 0 4 8 0 . 0 7 9 0 . 0 6 9 0 . 0 9 5 0 . 0 5 3 0 . 1 5 2 0 . 1 5 7 T H 9 4 1 3 8 T H 9 4 1 3 9 T H 9 4 1 4 0 T H 9 4 1 4 1 T H 9 4 1 4 2 B K 9 1 / 0 0 6 B K 9 1 / 0 0 9 B K 9 1 / 0 1 0 Matrix for Generation of a Subtype B Tree
Phylogenetic analysis: Comparison of HMA to DNA sequence analysis
DNA Sequence Analysis All HIV sequencing projects should consist of five phases: • Data acquisition • Data processing • Quality assurance • Further data analysis • Data submission
Dideoxy DNA sequencing (Sanger) Given a single stranded template, a complementary primer with a 3’ hydroxyl group and all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates,DNA polymerase will catalyze chain extension from the primer, thus synthesizing a stand complementary to the template Thus, chain extension will continue until a dideoxynucleotide is incorporated instead of a deoxynucleotide, resulting in chain termination
HIV Sequence Nomenclature • (1) Character strings that reflect: • Virus type • Year and Place of origin • Subject number and Study source • Bleed number and Clone number • Region sequenced and Lab • Sample and Nucleic acid sourcee.g., HIV198CU001AGMBR or 98n27CU001c. For the first HIV1 strain isolated in the “c” study in Cuba, isolated in November 1998
HIV Sequence Nomenclature • (2) Biological character strings: • Health status • Time from seroconversion • Presumed transmission route • Virus phenotype • Genetic subtype and method
Quality Assurance -1 • Considerations for the use of PCR in sequence generation • Error rate during amplification • ~0.7% after n-PCR (70 cycles) • When attempting to measure level of diversity, the number of amplifiable templates needs to be quantitated • Cloning: easier, errors detected • Endpoint dilution: more expensive but errors not detected (maximum number of PCR-mutant signal is 25% of total)
Quality Assurance -2 • Search for homologies between new sequences and sequences in local and public databases • Generate multiple sequence alignments and a distance matrix to identify unexpected similarities • Optimize alignment visually • Generate phylogenetic trees to identify potential contaminants
The Estimation of DNA Distances Requires A Model of Evolution (not all models are equal)
A C Jukes-Cantor (JC) G T Assumes equal nucleotide frequencies, and that all substitutions are equally likely
A C Kimura 2 parameter (K2) G T Assumes equal base frequencies but differences in transitionand transversion rates
A C Hasegawa, Kishino & Yano (HKY-85) G T Allows differences in base frequencies and between transitionsand transversions
A C General Time-Reversible (GTR) G T • Allows differences between all substitutions (with symmetry preserved, i.e., A>G = G>A) and differences in base composition. Also allows rates to vary from site to site
Modeltest Tries to pick the best substitution model for your dataset Posada, D., and Crandall, K. A. (1998). MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14, 817-818
Phylogenetic Reconstruction-1 • The goal is to find the “best” tree. There are 2 basic methods of approach: • Using “Optimality Criteria”Examines all possible phylogenetic trees for the given set of sequences and chooses the best fit to the criteria, e.g., minimize total branch lengths • Maximum parsimony (MP) • Character based method. The tree that requires the fewest number of substitutions to account for the evolution is chosen as the best (most parsimonious)
Phylogenetic Reconstruction-2 • Maximum Likelihood (ML) • Also character based. Used when a probalistic model of evolution is available, you can calculate the probability that a given mutation will occur • You can then calculate the probability that a given tree would result in the observed data • This probability is called the likelihood • The tree picked is the one that maximizes the probability of obtaining the observed data • Incredibly computationally intensive • Distance-Based Optimality Criteria • Seek to minimize the difference between the observed pairwise difference distances, and the pairwise distances obtained from a phylogenetic tree
Simulate phylogenies with ease and high speed • Unweighted paired group method of averages (UPGMA) • Assumes all taxa are equally distant from the root • Not used often since distances rarely conform to requirements • Neighbor joining (NJ) • Requires a matrix of distances • Stepwise clustering method, adds sequences to a growing tree of miminized relationships • Sensitive to order of addition • “Algorithmic methods”
Efficiency of Methods • ML, MP and NJ perform well • In general: • ML > Weighted MP > NJ • ClustalW - creates NJ trees • PHYLIP - uses DNADIST and NEIGHBOR to create the distance matrix and NJ trees • Each has problems with long branches
Number of distinct bifurcating trees as a function of the number of taxa (i.e., sequences) (ML Tree) Number Number of taxa of trees 10 2x106 22 2x1023 50 *2x1074 100 2x10182 1,000 2x102,860 10,000 2x1038,658 100,000 2x10486,663 1,000,000 2x105,866,723 * greater than the number of atoms in the universe
Identify phylogenetically informative sites* CU1 ACTGGAATTCCGATGGATCGGATA CU2 AGTGTATTTCTGATGGATGGGAGA CU3 AGTATAATTCCGATCAATTGAACG CU4 ACTGGATTTCCGATTGATCAAATA REMOVE INVARIANT SITES CU1CGGACGGCGGTA CU2GGTTTGGGGGGA CU3GATACCATGACG CU4CGGTCTGCAATA & OTHER NONINFORMATIVE (UNIQUE) SITES CU1CGAG CU2GTTG CU3GTAA CU4CGTA *An informative site is one at which at least two sets of sequences (of 2 or more seqs) have a character in common
1 AG TA 4 CU1CGAG CU4CGTA CU2GTTG CU3GTAA CG GT TG AA 2 3 CU1CGAG CU3GTAA CU2GTTG CU4CGTA CU1CGAG CU2GTTG CU3GTAA CU4CGTA 1 3 1 2 CGG CGA CGA CGT G A A T 2 4 3 4 GTG GTA GTT GTA Creating a maximum parsimony (MP) tree
NonparametricBOOTSTRAP ANALYSIS 1234 CU1CGAG CU2GTTG CU3GTAA CU4CGTA 4 COLUMNS PICKED AT RANDOM WITH RESAMPLING 1234 1134 4212 CU1CGAG CCAG GGCG CU2GTTG or GGTG or GTGT CU3GTAA GGAA ATGT CU4CGTA CCTA AGCG GENERATE 3 (USUALLY 100 OR 1,000) TREES FIND THE MOST FREQUENT TREE, REPORT CLUSTERINGFREQUENCY AT EACH NODE
JACKNIFE ANALYSIS 1234 CU1CGAG CU2GTTG CU3GTAA CU4CGTA COLUMNS PICKED AT RANDOM WITHOUT RESAMPLING 12 34 42 CU1CG AG GG CU2GT or TG or GT CU3GT AA AT CU4CGTA AG
Software tools on the World Wide Web:http://hiv-web.lanl.gov/HTML/tools.html • Software produced by the HIV Database and Analysis Group: • RIP: Intersubtype Recombination Analysis. A user-friendly interface to RIP, a program for detecting evidence of inter-subtype recombination • VESPA: Signature Pattern Analysis. For identifying sites shared by one group of sequences, and are rare in another group • SNAP: Synonymous-Nonsynonymous Analysis Program. This code calculates syn and nonsyn values for an alignment • ODprep/ODfit. These programs calculate antibody titers based on concentration and optical density data
More software tools on the Web:http://hiv-web.lanl.gov/HTML/tools.html • Web interfaces to other programs: • Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCOORD) - A technique for identifying patterns of correlated positions in the sequences • HMA gel analysis - An interface to HDent and HDdist, programs for analysing data from HMA and HTA experiments. • Sequence quality control - Tools for detecting possible contamination in your dataset.
Even more software tools on the Web:http://hiv-web.lanl.gov/HTML/tools.html • Links to other software resources: • Phylogenetic Analysis - A comprehensive list of programs for creating phylogenetic trees, maintained by Joe Felsenstein at the University of Washington • HIV Subtyping using BLAST - This website allows subtyping of a new sequence by comparing it to a set of reference sequences using the BLAST local similarity search algorithm • Multiple Sequence Alignment - Programs for aligning nucleic acid or amino acid sequences, including pre-calculated Hidden Markov Models for lentiviral sequences • Sequence Submission to Databases - SEQUIN and BANKIT were developed by NCBI for automating and error-checking database submissions