Relational Data Model
150 likes | 317 Vues
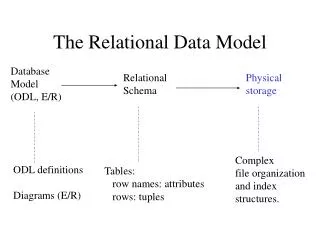
Relational Data Model. Joe Meehean. Relational Data Model. Data stored as a set of relations really just tables Tables related to one another through shared attributes Attributes columns of the tables Domain allowable values for attributes Tuple single row in a relation. Tables.

Relational Data Model
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Relational Data Model Joe Meehean
Relational Data Model • Data stored as a set of relations • really just tables • Tables related to one another through shared attributes • Attributes • columns of the tables • Domain • allowable values for attributes • Tuple • single row in a relation
Tables • Columns and rows • Heading • definition of table (column headings) • Body • content (data rows) • Each column has a data type • characters, numeric, data, boolean, etc…
Relational Data Model • Properties of Relations • distinct name • each cell contains exactly one value • attributes have distinct name • values of attribute all from same domain • no duplicate tuples (rows) • order of attributes unimportant • order of tuples unimportant
Relational Data Model • Relation schema • a named relation • with attributes • domains for attributes • Relational database schema • set of relation schemas • tables that make up database • each with own name
Relational Keys • Superkey • column or combination of columns containing unique values for each row • uniquely identifies a row • Candidate key • minimal superkey • removing any column makes it no longer unique
Relational Keys • Primary key • specially designated candidate key • each table needs one • cannot contain null values • called combined or composite if contains multiple columns • Foreign key • column(s) in which value must match those of candidate key • candidate key usually from a different table • used to create relationships between tables
Connecting Tables • Column values in table match values in another • Allows a connection between tables
Representing Relational Schema • Name(attr1, attr2, …) • College Database • Student (StudentID, LastName, FirstName) • Faculty (FacultyID, LastName, FirstName) • Course (CourseID, DeptID, Number, Name) • Offering (CourseID, Section,Sem., Year) • Enrolled (StudentID, CourseID, Section) • Teaching (FacutlyID, CourseID, Section)
Relational Integrity • Null value • a special value indicating absence of actual value • value may be unknown • or simply not applicable • can cause problems
Integrity Rules • Helps ensure data isn’t corrupted • Entity integrity • ensures each tables valid • each data row must be unique • each table must have at least one candidate key • uniquely identifies row in database • Referential integrity • ensures valid relationships between tables • foreign key must reference a real candidate key • e.g. each Offering.CourseId must match a Course.CourseId
Formal Integrity Rules • Entity Integrity Rule • no two rows of a table can contain the same value for the primary key • primary key cannot be null • Referential Integrity Rule • only two kinds of data can be stored in a foreign key • a value matching a candidate key • a null value
Delete and Update for Referenced Rows • Referenced row • row whose primary key is foreign key in another row • Changing primary key or deleted referenced row • affects the referencing rows • what to do • Possible actions • restrict: do not allow if reference exists • cascade: perform same action for referencing rows • nullify: replace foreign key with null • default: replace foreign key with default