INSCRIBED ANGLES
210 likes | 363 Vues
INSCRIBED ANGLES. PROBLEM 1a. PROBLEM 1a. CONGRUENT AND INSCRIBED. INSCRIBED TO A SEMICIRCLE. PROBLEM 2. INSCRIBED AND CIRCUMSCRIBED. PROBLEM 3. PROBLEM 4. END SHOW. Standard 21:

INSCRIBED ANGLES
E N D
Presentation Transcript
INSCRIBED ANGLES PROBLEM 1a PROBLEM 1a CONGRUENT AND INSCRIBED INSCRIBED TO A SEMICIRCLE PROBLEM 2 INSCRIBED AND CIRCUMSCRIBED PROBLEM 3 PROBLEM 4 END SHOW
Standard 21: Students prove and solve problems regarding relationships among chords, secants, tangents, inscribed angles, and inscribed and circumscribed polygons of circles. Los estudiantes prueban y resuelven problemas relacionados con cuerdas, secantes, tangentes, ángulos inscritos y polígonos inscritos y circunscritos a círculos.
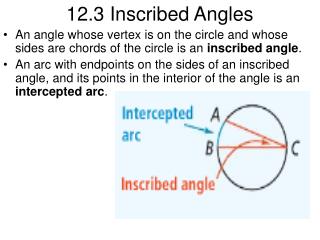
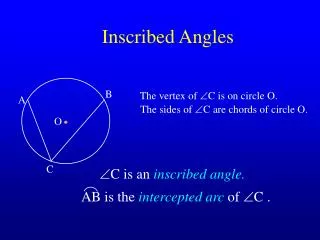
Inscribed angles are angles formed by two chords whose vertex is on the circle. A Ángulos inscritos son ángulos formados por dos cuerdas cuyo vértice esta en el circulo B C ABC KML If an angle is inscribed in a circle then the measure of the angle equals one-half the measure of its intercepted arc. K m KL 1 2 Si un ángulo en un círculo es inscrito entonces la medida de el ángulo es igual a la mitad de su arco intersecado. M L m is an inscribed angle =
= (40°) BAC 3 3 m BC 1 1 2 2 m A (3x+5)° B 40° (3X+5) = C 3X + 5 = 20 -5 -5 3X = 15 X=5
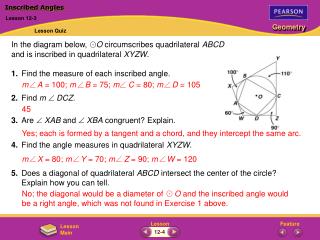
K J (2x+7)° = 54° (54°) L JKL 2 2 m JL 1 1 2 2 m (2X+7) = 2X + 7 = 27 -7 -7 2X = 20 X=10
A AB B P D C ADB ACB ADB ACB and intercept same arc If then If two inscribed angles of a circle or congruent circles intercept congruent arcs, or the same arc, then the angles are congruent. Si dos ángulos inscritos de un círculo o de círculos congruentes intersecan el mismo arco o arcos congruentes entonces los ángulos son congruentes.
AC P A 90° m C B ABC ABC= intercepts semicircle If then If an inscribed angle intercepts a semicircle, then the angle is a right angle. Si un ángulo inscrito interseca a un semicírculo entonces el ángulo es recto.
N = 90° 4X° K L M (6X-10)° 10 10 + (6X-10)° 4X° 10X-10 = 90 +10 +10 10X = 100 X=10
These are concentric circles and all circles are similar. Estos son círculos concéntricos y todos los círculos son semejantes.
K N L M A B P D C E F Q G H
A B P D C E F X Q K G H R N g L M Quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed to circle P. Cuadrilatero ABCD esta inscrito al círculo P. Line g is TANGENT to circle X at point R. Línea g es tangente al círculo X en punto R. Quadrilateral EFGH is circumscribed tocircle Q, having sides to be TANGENT at points K, L, M and N. Cuadrilátero EFGH esta circunscrito al círculo Q, teniendo los lados TANGENTES en los puntos K, L, M y N.
Inscribed to circle G are quadrilaterals EFBD and EABC, and quadrilaterals EFGD and GABC are rhombi. A F 4X+10 and = m -3X+45 = m Find the following: = ? m 1. ED B E I H G C D EBF EBD
Inscribed to circle G are quadrilaterals EFBD and EABC, and quadrilaterals EFGD and GABC are rhombi. A F 4X+10 and = m -3X+45 = m Find the following: = ? m 1. ED B E I H G C D EBF EBD
Inscribed to circle G are quadrilaterals EFBD and EABC, and quadrilaterals EFGD and GABC are rhombi. A F 4X+10 and = m -3X+45 = m Find the following: = ? m 1. ED B E I H G C D EBF EBD
Inscribed to circle G are quadrilaterals EFBD and EABC, and quadrilaterals EFGD and GABC are rhombi. A F = 4X+10 and = m -3X+45 = m Find the following: 60° = ? m 30° 1. ED B E I H 30° G 60° 90° EFB EDB C and FGDE is a rhombus so all sides D are congruent because the F Reflexive Property EFB EBD EFB EBF EBD EBF EBF EBF EBD EBD EBF EDB EFB E B E B = 30° =-3X+45 m m m m m m =-3( )+45 EAB D EB EB EF ED -7 -7 Since is inscribed to SEMICIRCLE then are right, and then and ; and therefore then: by HL. And by CPCTC. 30° 60° So: Then = -3X+45 = 4X+10 60° 30° -45 -45 5 -3X = 4X – 35 = -15+45 -4X -4X =30° - 7X = - 35 So: Take notes X=5
Inscribed to circle G are quadrilaterals EFBD and EABC, and quadrilaterals EFGD and GABC are rhombi. A F 4X+10 and = m -3X+45 = m 60° Find the following: B E I H G C D (2) (2) 30° = EBD EBD EBF = m ? 2. FE m m m m m ED ED FE ED ED 1 1 1 2 2 2 FE ED m EFED = ? m 30° 1. ED 60° If = 60° 30° 60° then: 30° = = 60° = 60° Since then and
Inscribed to circle G are quadrilaterals EFBD and EABC, and quadrilaterals EFGD and GABC are rhombi. A F = = = 4X+10 and = m -3X+45 = m Find the following: B E I 60° H G C D (2) (2) 30° = EBD EBF BGD BED EBD BED = m ? 2. FE m m m m m FE ED ED ED ED 1 1 1 4. 3. ? ? 60° 2 2 2 FE ED m m m m EFED 60° = ? m 30° 1. ED 60° If = 60° 30° 60° then: 30° = = 60° = 60° Since then and From figure
Inscribed to circle G are quadrilaterals EFBD and EABC, and quadrilaterals EFGD and GABC are rhombi. A F = = = = = = 4X+10 and = m -3X+45 = m Find the following: B E I 60° H G C D (2) (2) 30° = DEG BGD EGD BGD BGD BED EBD BED EBF EBD BGD = m ? 2. FE m m m m m ED ED ED FE ED 1 1 1 3. 4. ? ? 60° 2 2 2 FE ED m m m m m m = m DGE because EFGD is a rhombus m 180° + m m EFED 180° 60° + 120° 60° = ? m 30° 1. ED 60° If = 60° 30° 60° then: 30° = = 60° = 60° Since then and From figure and then Take notes -60° -60°
Inscribed to circle G are quadrilaterals EFBD and EABC, and quadrilaterals EFGD and GABC are rhombi. A F 4X+10 and = m -3X+45 = m Find the following: B E I H G m 5. DB = 120° C D EBD EBF 60° 120° 60° 120°
Inscribed to circle G are quadrilaterals EFBD and EABC, and quadrilaterals EFGD and GABC are rhombi. A F 120° 4X+10 and = m -3X+45 = m Find the following: B E I H G m 5. DB = C D 90° 7. = AIB EBD EBF m = 6. m DEB 60° 120° 60° 60°+60°+120° 120° = 240°
Reasons Statements = a. a. Alternate interior are b. b. have the same measure c. c. S d. d. = e. e. = f. f. An inscribed is half its intercepted arc ABD CDB CDB ABD ABD CDB DC DC AB AB = g. h. g. h. = m m BC AD m m m m AD BC AD BC 1 1 1 1 Arcs with the same measure are 2 2 2 2 AD BC AD BC m m An inscribed is half its intercepted arc S m m B C Given A D Given: Prove: Transitive Property. Division Property of Equality