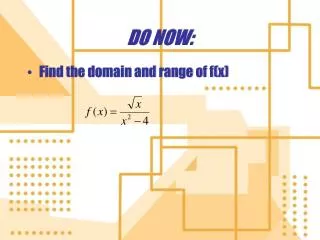
Combining functions algebraically, composite functions, and decomposing functions!
210 likes | 501 Vues
Combining functions algebraically, composite functions, and decomposing functions!. Onward to Section 1.4a…. Definition: Sum, Difference, Product, and Quotient of Functions. Let f and g be two functions with intersecting domains. Then for

Combining functions algebraically, composite functions, and decomposing functions!
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Combining functions algebraically, composite functions, and decomposing functions! Onward to Section 1.4a…
Definition: Sum, Difference, Product, and Quotient of Functions Let f and g be two functions with intersecting domains. Then for all values of x in the intersection, the algebraic combinations of f and g are defined by the following rules: Sum: Difference: Product: provided Quotient: In each case, the domain of the new function consists of all numbers that belong to both the domain of f and the domain of g. As noted, the zeros of the denominator are excluded from the domain of the quotient.
Guided Practice For the given functions, find f + g, f – g, fg, f/g, and gg. Give the domain of each. First, find the domain of the original functions, and determine where these two domains intersect (overlap). Domain of f: Domain of g: Domain intersection: This intersection becomes the domain of all of the algebraic combination functions!!!
Guided Practice For the given functions, find f + g, f – g, fg, f/g, and gg. Give the domain of each. with D: with D: with D:
Guided Practice For the given functions, find f + g, f – g, fg, f/g, and gg. Give the domain of each. with D: with D: Can we simplify this last one???
Guided Practice For the given functions, find formulas for the functions f + g, f – g, and fg. Give the domain of all functions. Domain of all 3 combination functions:
Guided Practice For the given functions, find formulas for f/g and g/f. Give the domain of all functions.
Definition:Composition of Functions Let f and g be two functions such that the domain of f intersects the range of g. The composition of f and g, denoted fg, is defined by the rule The domain of fg consists of all x-values in the domain of g that map to g(x)-values in the domain of f. NOTE: In most cases, fg and gf are different functions!!!
A Few Practice Problems… For the given functions, find (fg)(x) and (gf)(x) and verify (both algebraically and graphically) that the two composite functions are not the same. Now, how do we verify???
A Few Practice Problems… For the given functions, find (fg)(x) and (gf)(x) and give the domain of each composition function. D: D: Let’s check these with the calculator…
A Few Practice Problems… For the given functions, find (fg)(3) and (gf)(–2).
Decomposing Functions…working backwards or undoing a composition… For each function h, find functions f and g such that h(x) = f(g(x)).
Decomposing Functions For each function h, find functions f and g such that h(x) = f(g(x)). Any other ways to solve this one?!?!
Let’s do some modeling… In math-land, not fashion-land… In the medical procedure known as angioplasty, doctors insert a catheter into a heart vein and inflate a small, spherical balloon on the tip of the catheter. Suppose the balloon is inflated at a constant rate of 44 cubic millimeters per second. 1. Find the volume after t seconds. V = 44t
Let’s do some modeling… In math-land, not fashion-land… In the medical procedure known as angioplasty, doctors insert a catheter into a heart vein and inflate a small, spherical balloon on the tip of the catheter. Suppose the balloon is inflated at a constant rate of 44 cubic millimeters per second. 2. When the volume is V, what is the radius r ?
Let’s do some modeling… In math-land, not fashion-land… In the medical procedure known as angioplasty, doctors insert a catheter into a heart vein and inflate a small, spherical balloon on the tip of the catheter. Suppose the balloon is inflated at a constant rate of 44 cubic millimeters per second. 3. Write an equation that gives the radius r as a function of the time. What is the radius after 5 seconds? and At 5 seconds, r = 3.745 mm
Whiteboard Practice For the given functions, find formulas for the functions f + g, f – g, and fg. Give the domain of all functions. Domain of all five functions:
Whiteboard Practice Find f(g(x)) and g(f(x)). State the domain of each.
Whiteboard Practice Find f(x) and g(x) so that the function can be described as y=f(g(x)). one possible solution… Homework: p. 127-128 1-23 odd