The Cold War 1945-1991
460 likes | 951 Vues
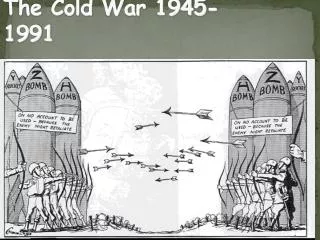
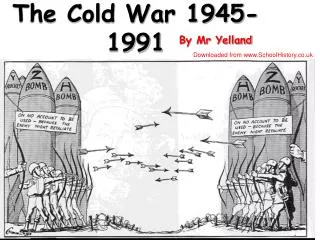
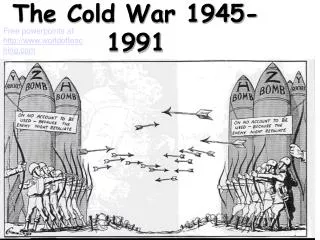
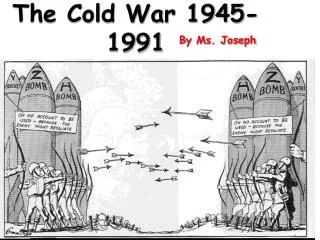
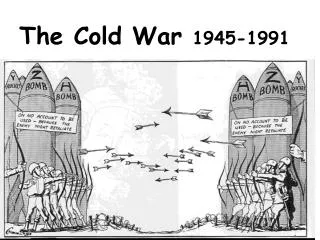
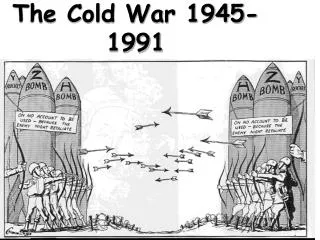
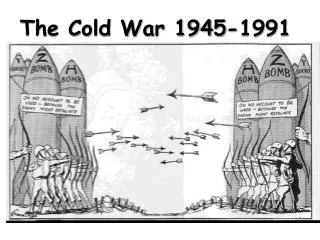
The Cold War 1945-1991. Cold War. The Cold War was a time after WW2 when the USA and the Soviet Union were rivals for world influence. Two sides of Cold War. NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organization USA, France, Great Britain, Canada, West Germany CAPITALISM.

The Cold War 1945-1991
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cold War • The Cold War was a time after WW2 when the USA and the Soviet Union were rivals for world influence.
Two sides of Cold War • NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organization • USA, France, Great Britain, Canada, West Germany • CAPITALISM • Warsaw Pact – pro Soviet countries – USSR, East Germany, and all countries controlled by the USSR. • COMMUNISM
The Ideological Struggle Soviet & Eastern Bloc Nations[“Iron Curtain”] US & the Western Democracies GOAL “Containment” of Communism & the eventual collapse of the Communist world. GOAL spread world-wide Communism
METHODOLOGIES: • Espionage [KGB vs. CIA] • Arms Race [nuclear escalation] • Ideological Competition for the minds and hearts of Third World peoples [Communist govt. & command economy vs. democratic govt. & capitalist economy] “proxy wars” • Bi-Polarization of Europe [NATO vs. Warsaw Pact]
The “Iron Curtain” From Stettin in the Balkans, to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lies the ancient capitals of Central and Eastern Europe.-- Sir Winston Churchill, 1946
The Road to the Iron Curtain • Soviets reached Berlin first (Hitler found dead in bunker—a suicide) • Victory in Europe(V-E Day) proclaimed May 8, 1945 • War in Europe finally over after nearly six years, both Europe and Asia in ruins • Tens of millions dead; heaviest losses in Eastern Europe • Germany, Japan, and China had also suffered greatly • Physical devastation; cities, villages, and farms destroyed • National economies near collapse • Millions uprooted • former prisoners of war, survivors of concentration camps, refugees of fighting and of national border changes
Atlantic Charter (1941) • Joint declaration of Churchill and Roosevelt • Outlined purpose of war (to provide freedom from fear) • Sought no territorial gains • All nations could choose their own government • Work for mutual prosperity
Tehran Conference • December 1943 • Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin • Agreed on schedule for D-Day invasion • Would work together in peace after the war (United Nations was tentatively agreed on)
Yalta (in the USSR) Feb. 1945 Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin
Yalta Conference • Held in Soviet territory in early 1945; Allies on brink of military victory • Roosevelt, Stalin, and Churchill agreed on plans for Germany • Primary goal to reach agreement on postwar Europe • Stalin got his way with Eastern Europe because the Soviet Union had suffered terribly (20 million died) • Confirmed decision to organize the United Nations
Potsdam (in Germany July 1945 Churchill/Atlee, Truman, and Stalin
Potsdam Conference • Churchill/Atlee, Stalin, and Truman • Four power control over Germany. • Disagreements over “spheres of influence”. • Stalin has less bargaining power. • Cold War begins.
Iron Curtain – A term used by Winston Churchill to describe the separating of Those communist lands of East Europe from the West. Divided Germany
Improve your knowledge Divided Berlin • The Russians took very high casualties to capture Berlin in May 1945. They spent the early occupation trying to take over all zones of the city but were stopped by German democrats such as Willy Brandt and Konrad Adenauer. Reluctantly the Russians had to admit the Americans, French and British to their respective zones.
The “iron curtain” • Potsdam conference ended with little agreement over key issues. • Stalin continued to influence Eastern European nations and by 1946 Poland, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Albania all had Communist governments. • Churchill described it as an iron-curtain, the name stuck.
Capitalism vs. Communism • Today’s task is to ensure our understanding of the two competing ideologies during the Cold War: • Capitalism • Communism • Your next small assignment is a small poster that will demonstrate your understanding of communism or capitalism. Use the information in the next slides to help you.
Sort the following keywords into two groups. Communism & Capitalism • Freedom • Collective • Equality • Individual • Community • Totalitarian • Democratic • Free competition • State-owned • private
What is Capitalism & Communism? • Both are ideologies (a set of beliefs) • Both talk about the economy and how the economy should run • Capitalism: • Little government involvement in the economy • Let people decide what to do with their money • INDIVIDUAL FREEDOM IS THE FOCUS • Communism: • Lots of government involvement in the economy • Government decides what is best for everybody • EQUALITY IS THE FOCUS
Cold War Propaganda • As we look at some examples of American and Soviet propaganda, take note of the characteristics. • EQUALITY VS. FREEDOM
How to Read a Historical Image • SIGHT • Scan for important details • What is being shown? What is the focus of the image? • Identify the conflict or tension (if one) • Guess the creator’s message or intent • What point of view is being displayed? • Hear the voices • If they could speak, what would they say? • Whose voices are absent or ignored? Why? • Talk about your observations
http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918
http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918
http://www.designer-daily.com/10-amazing-cold-war-propaganda-posters-2901http://www.designer-daily.com/10-amazing-cold-war-propaganda-posters-2901
http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918
http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918
http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918
http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918http://www.designer-daily.com/examples-of-american-cold-war-propaganda-2918
Emerging Super Powers • What happened to Britain & France? • Why was their tension between the USA and the USSR? Weren’t they friends and allies before?
Greece as a beginning… • Complete your handout.
Truman Doctrine • The USA was prepared to send money, equipment and advice to any country which was, in the American view, threatened by a Communist take-over. • Essentially it helped countries resisting communism.
Marshall Plan USA’s plan to send food, blankets, fuel to Europe to help them AND to keep them from turning communist.
Marshall Plan – helped countries economically so they won’t go red.
Is this generous or self-interest? • Discuss with your partner for a few minutes.
Embargoes • Refusing to trade or aid countries in order to punish them
Cuba embargo • Still today, the USA has an economic embargo on communist Cuba. • Their only cars are from before the embargo!
Why all the talk about the Berlin Wall? • By 1946, Britain, France, & the USA combined their zones in Germany to form West Germany. Their goal was to help Germany recover (not too quickly!). • In response Stalin blockaded Berlin. He did not like what the Western countries were doing and he wanted to force them out of Berlin. • What would you do?
June 1948 • Allies air-lift supplies into West Berlin. • No shots were fired, but planes flew for ten months supplying West Berlin. • Eventually the USSR gave up.
Berlin Wall • Berlin is Germany’s capital city. • The Soviets built the wall to keep people from escaping to the American sector. • 1961 • Started as a barbed wire barricade and evolved into the concrete structure we know today.