The Kingdom Protista
560 likes | 764 Vues
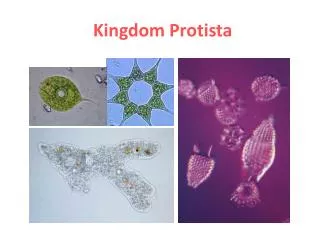
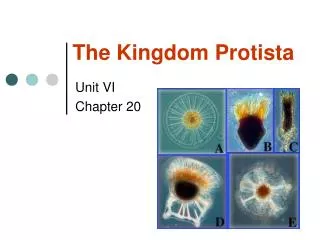
The Kingdom Protista. Protists. are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms. Historically, protists were treated as the kingdom Protista but this group is no longer recognized in modern taxonomy. [.

The Kingdom Protista
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Protists • are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms. Historically, protists were treated as the kingdom Protista but this group is no longer recognized in modern taxonomy.[
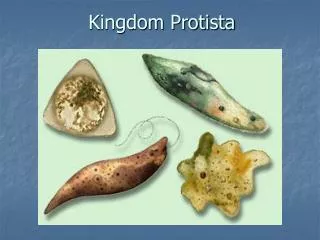
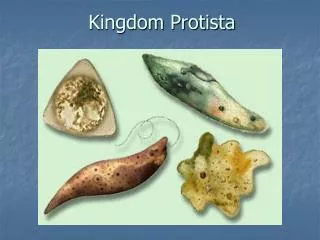
The protists do not have much in common besides a relatively simple organization[3] — either they are unicellular, or they are multicellular without specialized tissues.
This simple cellular organization distinguishes the protists from other eukaryotes, such as fungi, animals and plants.
Protists live in almost any environment that contains liquid water. Many protists, such as the algae, are photosynthetic and are vital primary producers in ecosystems, particularly in the ocean as part of the plankton.
Other protists, such as the Kinetoplastids and Apicomplexa, are responsible for a range of serious human diseases, such as malaria and sleeping sickness.
Most protists are like animal or plants • Except one……………………….
A Euglena is a protist that can both eat food as animals by heterotrophy; and can photosynthesize, like plants, by autotrophy. When acting as a heterotroph, the Euglena surrounds a particle of food and consumes it by phagocytosis. When acting as an autotroph, the Euglena utilizes chloroplasts, (hence green color)
Division Rhizopoda:An example of a member of this Division is genus Amoeba,
Ciliates • Cilia are like tiny paddles….
Plant like Protists • The “algae” • Dinoflagellates • Green algae • Golden Brown algae The Diatoms • Brown Algae • Red Algae
Red Tide • Red tide is a phenomenon caused by algal blooms during which algae become so numerous that they discolor coastal waters (hence the name "red tide")
Green Algae • The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, usually but not always with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid, and filamentous forms
Spirogyra Filaments with spiral shaped chloroplasts
A characteristic feature of diatom cells is that they are encased within a unique cell wall made of silica (hydrated silicon dioxide • That is the same as glass……..
Red Algae • The Red algae (or Rhodophyta, pronounced = plant, thus red plant) are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae,[3] of mostly multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds
Brown Algae • The Phaeophyceae or brown algae, (singular: alga) is a large group of mostly marine multicellular algae, including many seaweeds of colder Northern Hemisphere waters.
Algae in the ecosystem and industry • Coral Reefs